
MyBox User Guide – Data Tools v6.5.9

MyBox: Easy Tools Set
User Guide – Data Tools
Author: Mara
Version: 6.5.9
Date: 2022-8-31
Contents
1 Introduction 6
1.1 Main Interface 6
1.2 Resources Addresses 7
1.3 Documents 8
1.4 Menu of Tools 8
2 Two-dimensional Data 9
2.1 Edit Data 9
2.1.1 Data Objects 9
2.1.2 Functions Menu 10
2.1.3 Define Columns 11
2.1.4 Define Attributes 12
2.1.5 "Table" Edit Mode 13
2.1.6 "Text" Edit Mode 13
2.1.7 View Html 14
2.1.8 View Text 14
2.1.9 Load Contents in System Clipboard 15
2.1.10 Import Examples 16
2.1.10.1 Statistic Data of China 16
2.1.10.2 Data of Regression 16
2.2 Row Expression 17
2.3 Row Filter 19
2.4 Modify 20
2.4.1 Set Values 20
2.4.2 Delete 21
2.4.3 Set styles / Mark Abnormal Values 22
2.4.4 Paste Content in System Clipboard 23
2.4.5 Paste Content in MyBox Clipboard 23
2.5 Trim 24
2.5.1 Copy/Filter/Query 24
2.5.2 Sort 25
2.5.3 Transpose 26
2.5.4 Normalization 27
2.6 Calculation 28
2.6.1 Row Expression 28
2.6.2 Descriptive Statistic 29
2.6.3 Group b Equal Values 30
2.6.4 Simple Linear Regression 33
2.6.4.1 Regression 33
2.6.4.2 Model 34
2.6.4.3 Fitted Chart 35
2.6.4.4 Residual Chart 36
2.6.5 Simple Linear Regression - Combination 37
2.6.6 Multiple Linear Regression 38
2.6.6.1 Regression 38
2.6.6.2 Model 39
2.6.7 Frequency Distributions 40
2.6.8 Values Percentage 41
2.7 Chart 42
2.7.1 XY Chart 42
2.7.1.1 Data 42
2.7.1.2 Bar Chart 43
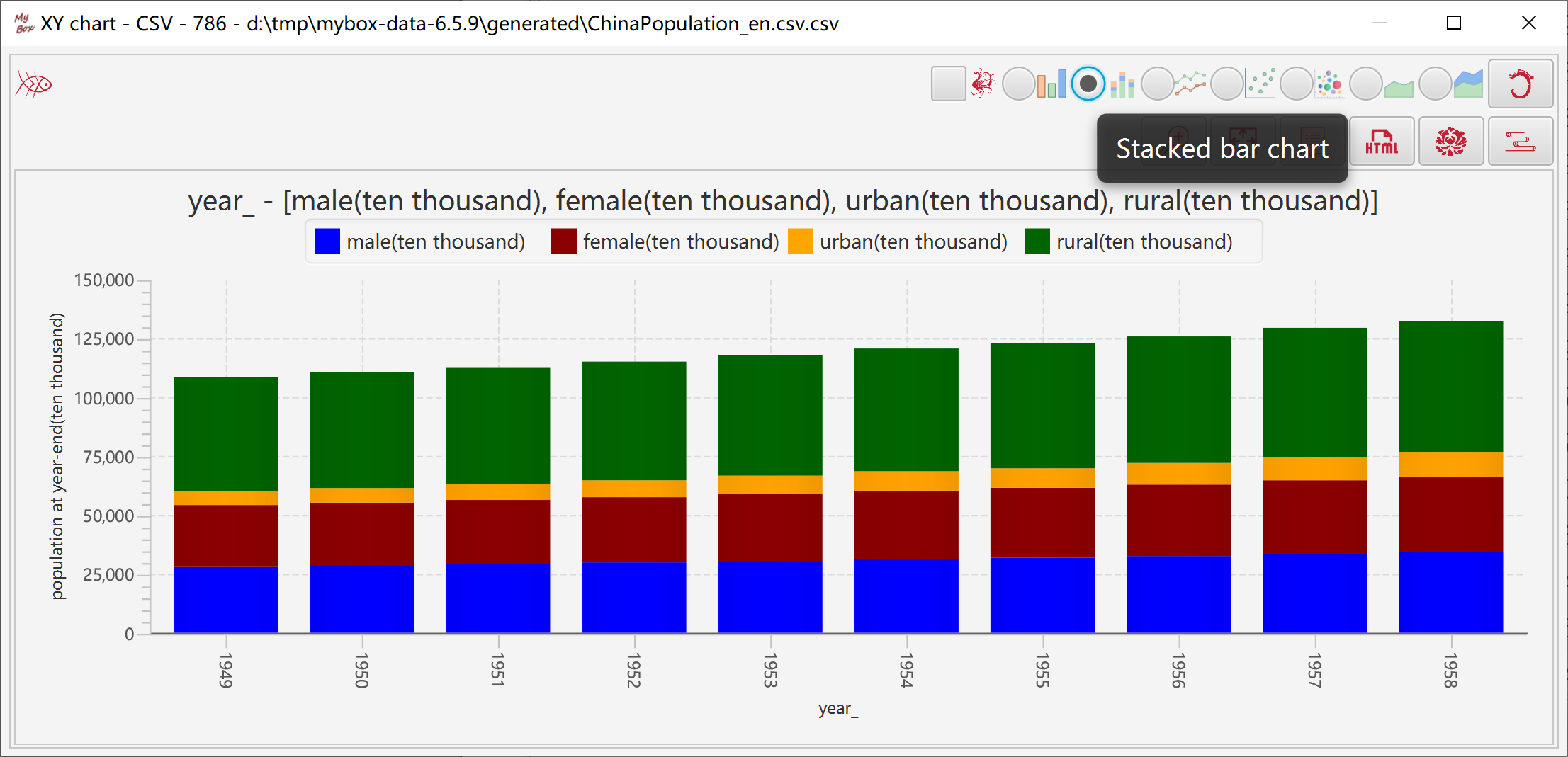
2.7.1.3 Stacked Bar Chart 43
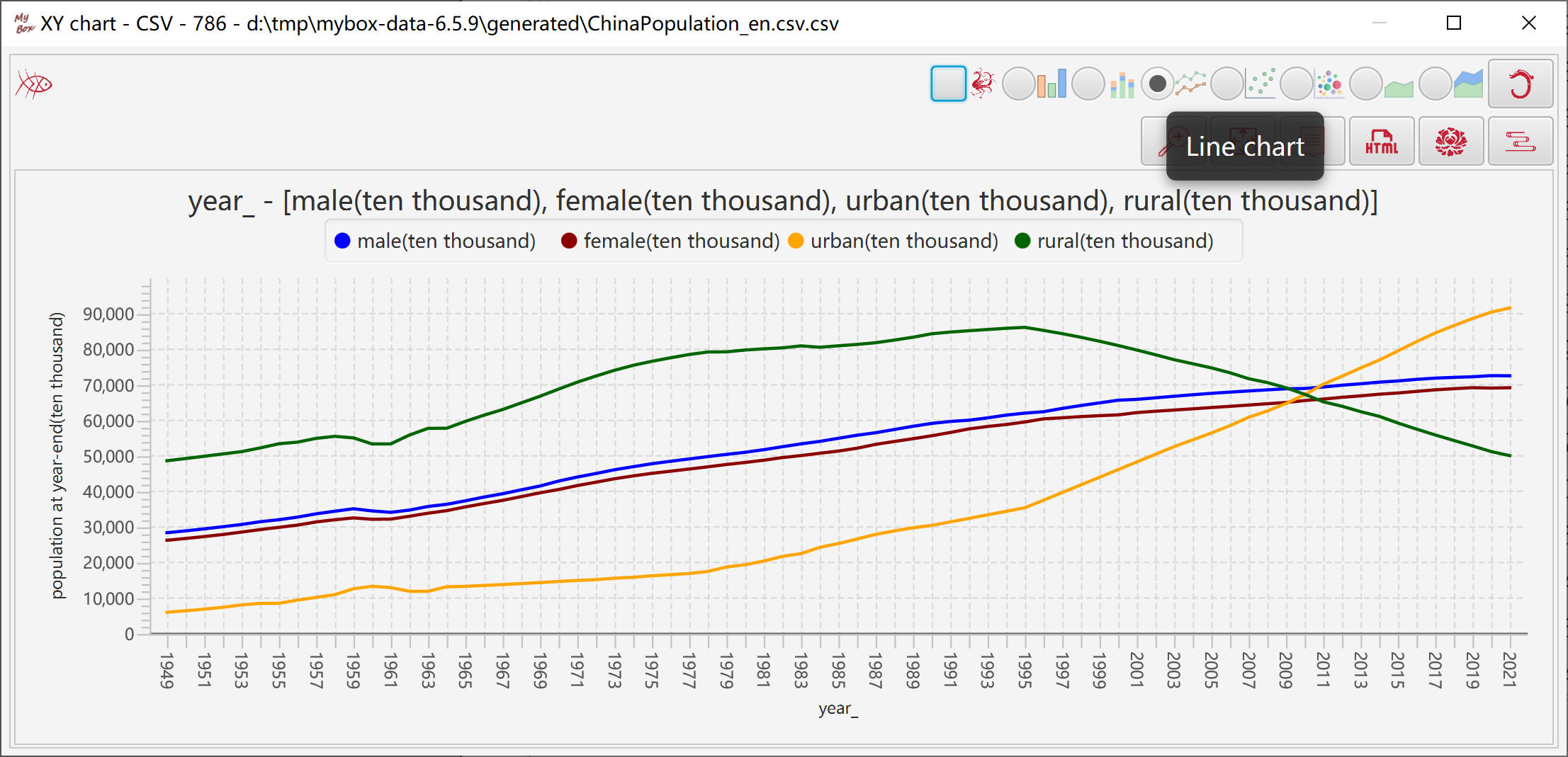
2.7.1.4 Line Chart 44
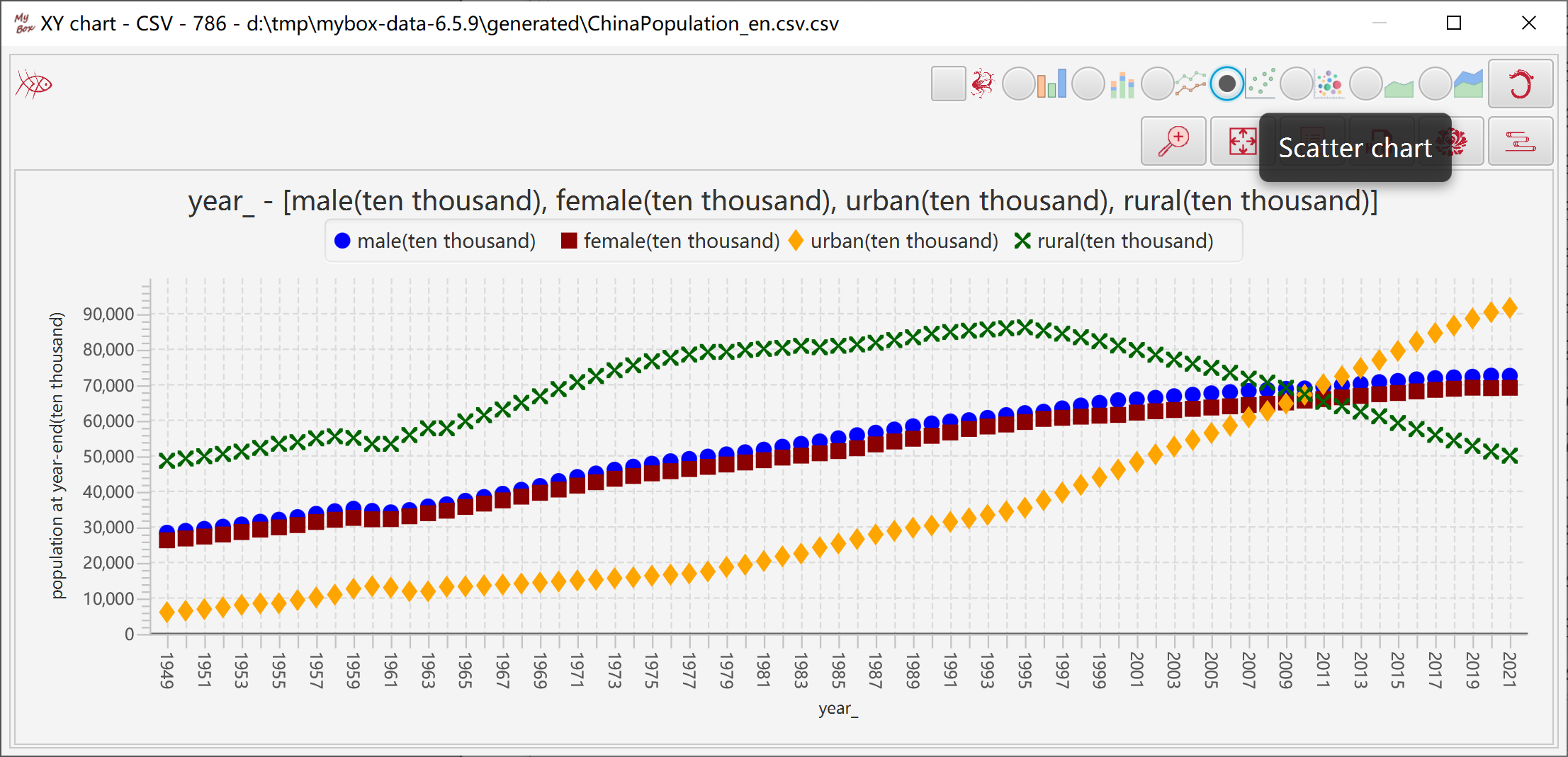
2.7.1.5 Scatter Chart 44
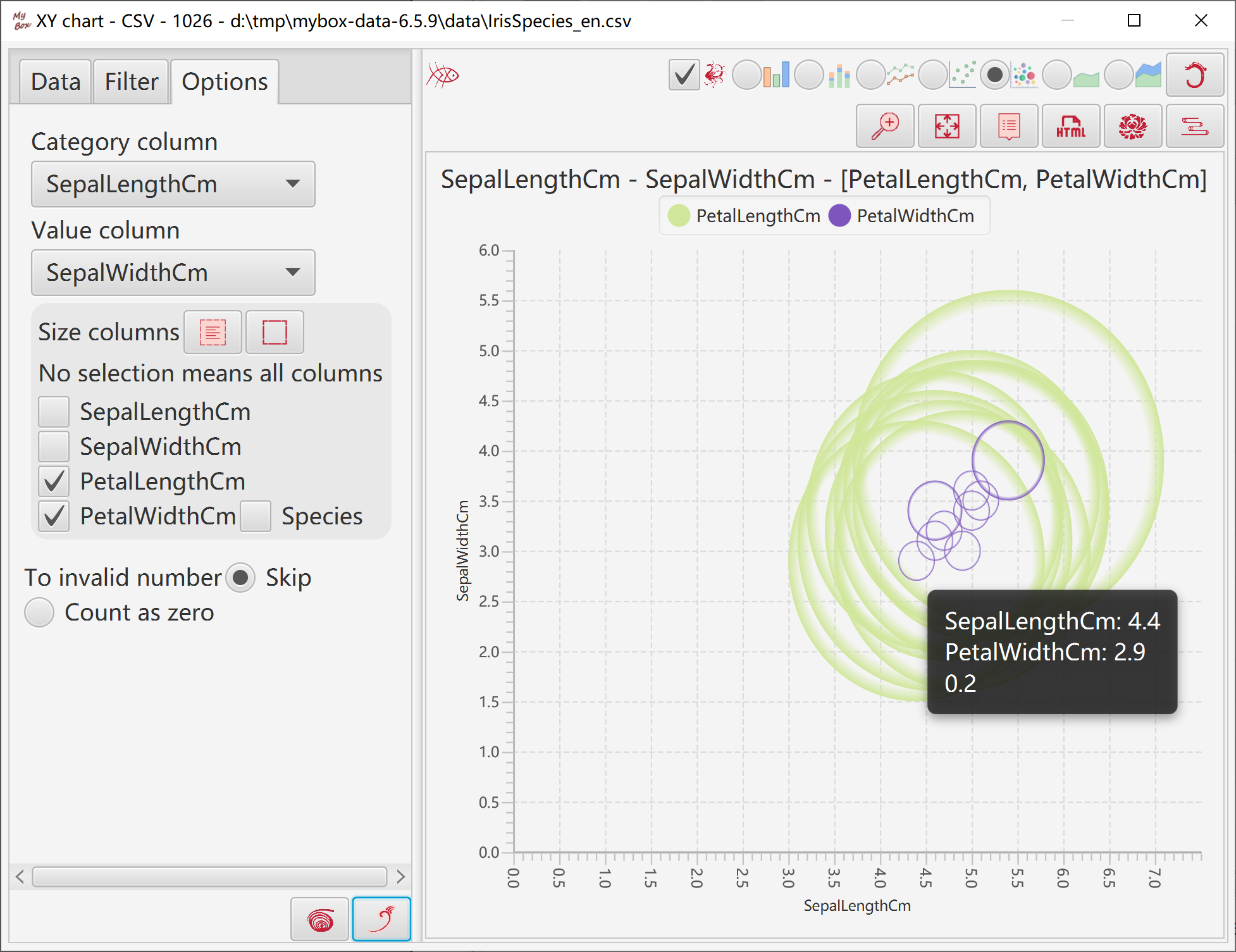
2.7.1.6 Bubble Chart 45
2.7.1.7 Area Chart 46
2.7.1.8 Stacked Area Chart 46
2.7.1.9 Parameters of Data in Chart 47
2.7.1.10 Layout 48
2.7.1.11 Category Axis 49
2.7.1.12 Number Axis 50
2.7.2 Pie Chart 51
2.7.3 Box-and-whisker Chart 52
2.7.4 Self Comparison Bars Chart 54
2.7.5 Comparison Bars Chart 56
2.8 Manage Data 58
2.9 Splice Data 59
2.10 Data File 60
2.10.1 CSV File 60
2.10.2 Text File 61
2.10.3 Excel File 62
2.10.4 Convert/Split Data Files in Batch 63
2.10.5 Merge Data Files 64
2.11 Data in System Clipboard 65
2.12 Data in MyBox Clipboard 66
2.13 Matrix 67
2.13.1 Edit and Manage Matrices 67
2.13.2 Unary Matrix Calculation 68
2.13.3 Binary Matrices Calculation 69
2.14 Database Tables 70
2.14.1 Manage Database Tables 70
2.14.2 Limitations of SQL Identifier 71
2.14.3 Database SQL 72
2.14.4 SQL Query 73
2.15 Export 74
2.16 Convert to Database Table 75
3 Calculation Tools 76
3.1 JShell(Java interactive coding tool) 76
3.2 JEXL(Java Expression Language) 78
3.3 Javascript 80
4 Data of Location 81
4.1 Data Constraints 81
4.1.1 Invalid Value 81
4.1.2 Coordinate System: 81
4.1.3 Coordinate Values 81
4.1.4 Time 81
4.1.4.1 Date Formats 81
4.1.4.2 Era 81
4.1.4.3 Examples 82
4.2 Data Operations 82
4.3 Map Data 83
4.4 Geography Code 85
4.4.1 Data Definition 85
4.4.2 Data Constraints 85
4.4.3 Edit Data 85
4.4.4 Define Condition 85
4.4.5 Import Data 85
4.4.5.1 Predefined Data 85
4.4.5.2 CSV Format 86
4.4.5.3 Data from geoname.org: 86
4.4.6 Settings 86
4.5 Location in Map 88
4.6 Location Data 89
4.6.1 Data Definition 89
4.6.2 Data constraints 89
4.6.3 Define Conditions 89
4.6.4 Map Data 89
4.6.5 Snapshots 90
4.6.6 Import Data 90
4.6.6.1 CSV Format 90
4.6.6.2 Data from movebank.org 90
4.6.6.3 Examples 90
4.7 Location Tools 92
4.8 Epidemic Reports 93
4.8.1 Data Definition 93
4.8.2 Data Constraints 93
4.8.3 Edit Data 93
4.8.4 Import Data 94
4.8.4.1 Predefined Data 94
4.8.4.2 CSV format: 94
4.8.4.3 COVID-19 historical data from Johns Hopkins University(Global) : 94
4.8.4.4 COVID-19 daily data from Johns Hopkins University(Global) : 94
4.8.4.5 Handle Data of Imported 94
4.8.5 Statistics Data 95
4.8.6 Define Conditions 95
4.8.7 Display Charts 95
4.8.8 Settings 96
5 Others 97
5.1 Create Barcodes 97
5.2 Decode Barcodes 97
5.3 Message Digest 97
5.4 Encode/Decode Base64 97
5.5 Extract ttf files from ttc file 97
This is desktop application based on JavaFx to provide simple and easy functions. It's free and open sources.

|
Contents |
Link |
|---|---|
|
Project Main Page |
|
|
Source Codes and Compiled Packages |
|
|
Submit Software Requirements and Problem Reports |
|
|
Data |
|
|
Documents |
|
|
Mirror Site |
|
|
Cloud Storage |
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1fWMRzym_jh075OCX0D8y8A#list/path=%2F |
|
Name |
Version |
Time |
English |
Chinese |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Development Logs |
6.5.9 |
2022-8-31 |
||
|
Shortcuts |
6.5.6 |
2022-6-11 |
||
|
Packing Steps |
6.3.3 |
2020-9-27 |
||
|
Development Guide |
2.1 |
2020-8-27 |
||
|
User Guide - Overview |
6.5.9 |
2022-8-31 |
||
|
User Guide – Document Tools |
6.5.9 |
2022-8-31 |
||
|
User Guide - Image Tools |
6.5.9 |
2022-8-31 |
||
|
User Guide - File Tools |
6.5.9 |
2022-8-31 |
||
|
User Guide - Network Tools |
6.5.9 |
2022-8-31 |
||
|
User Guide - Data Tools |
6.5.9 |
2022-8-31 |
||
|
User Guide - Media Tools |
6.5.9 |
2022-8-31 |
||
|
User Guide - Development Tools |
6.5.9 |
2022-8-31 |
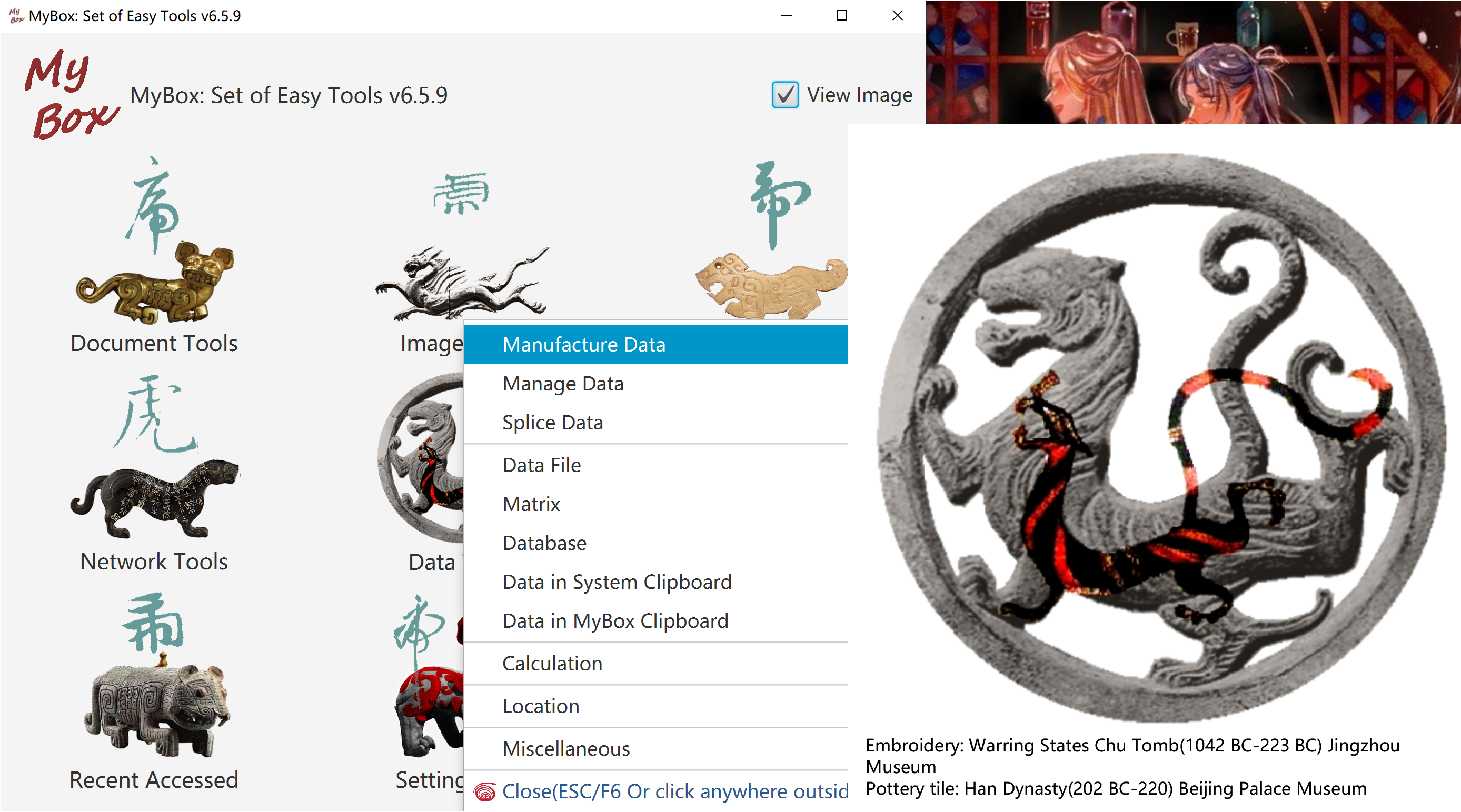
Following objects can be edited in consistent way:
Data files, including CSV File, Excel file, texts file.
Data of MyBox Clipboard
Matrices
Database tables.
Data should be in same width. That is all rows have equal number of columns.
Data are paginated. When pages number is larger than 1, changes should be saved before run some functions.
When changed, * is displayed in tab header. And ** is displayed when modifications have not applied.
Click button "Save" to write modifications to file and database:
Changes of rows in "Table", including modify/add/delete/sort, affect rows of current page in file.
Changes in "Columns" tab, including modify/add/delete/sort, affect all rows in file.
Changes of attributes and columns are saved in database.
Click button "Recover" to discard all modifications and load data from file and database.
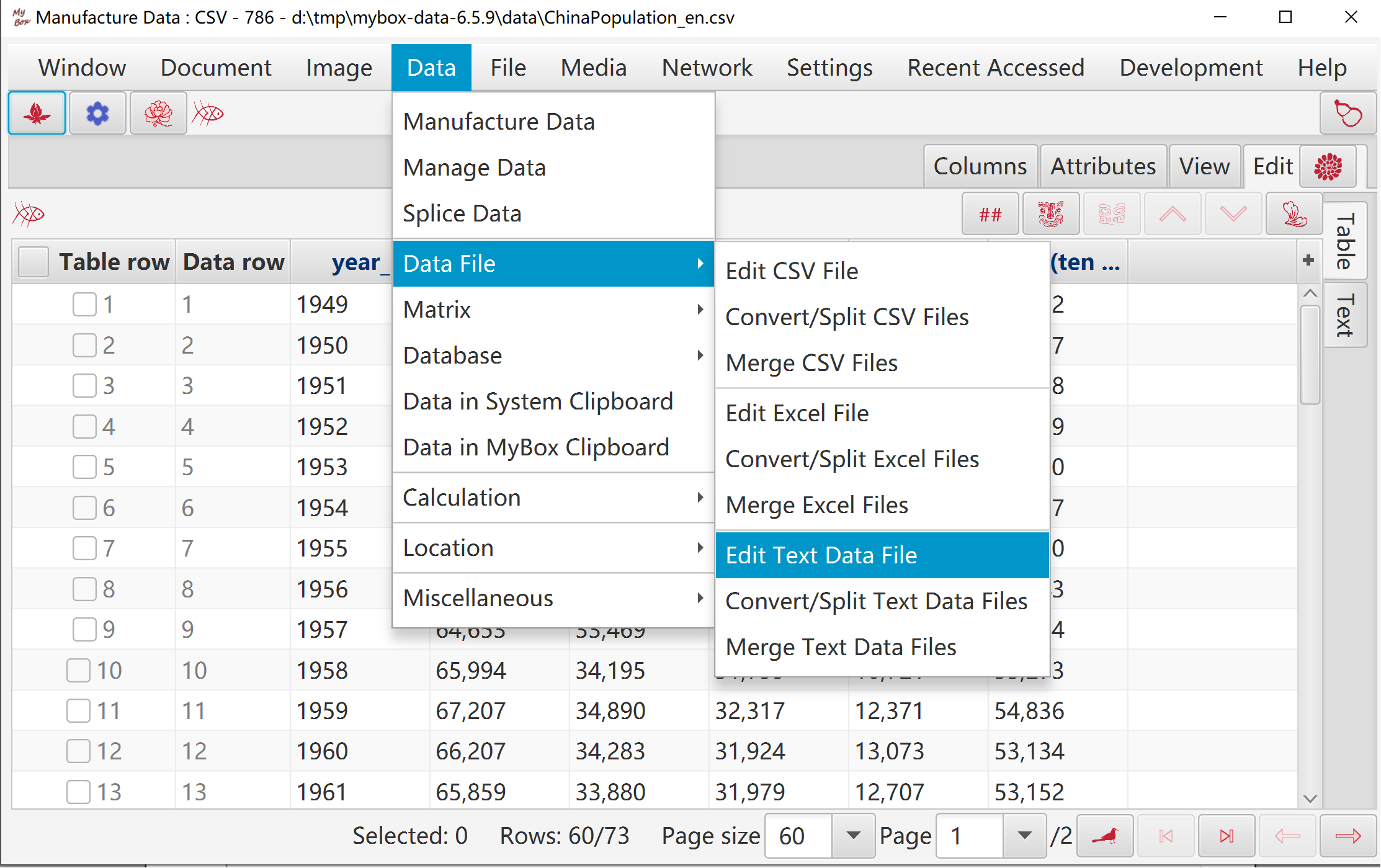
Hover or click button “Functions” top pop Functions Menu.
Column names should not be null nor duplicated.
Data types are used to validate data values:
Invalid value is rejected when edit data.
Type is ignored when read or calculate data.
Data type affects sorting results.
Click button "OK" to apply it modifications to "Table".
Click button "Cancel" to discard its modifications and pick data from "Table".
Can rename all columns with sequence numbers.
Can set random colors.
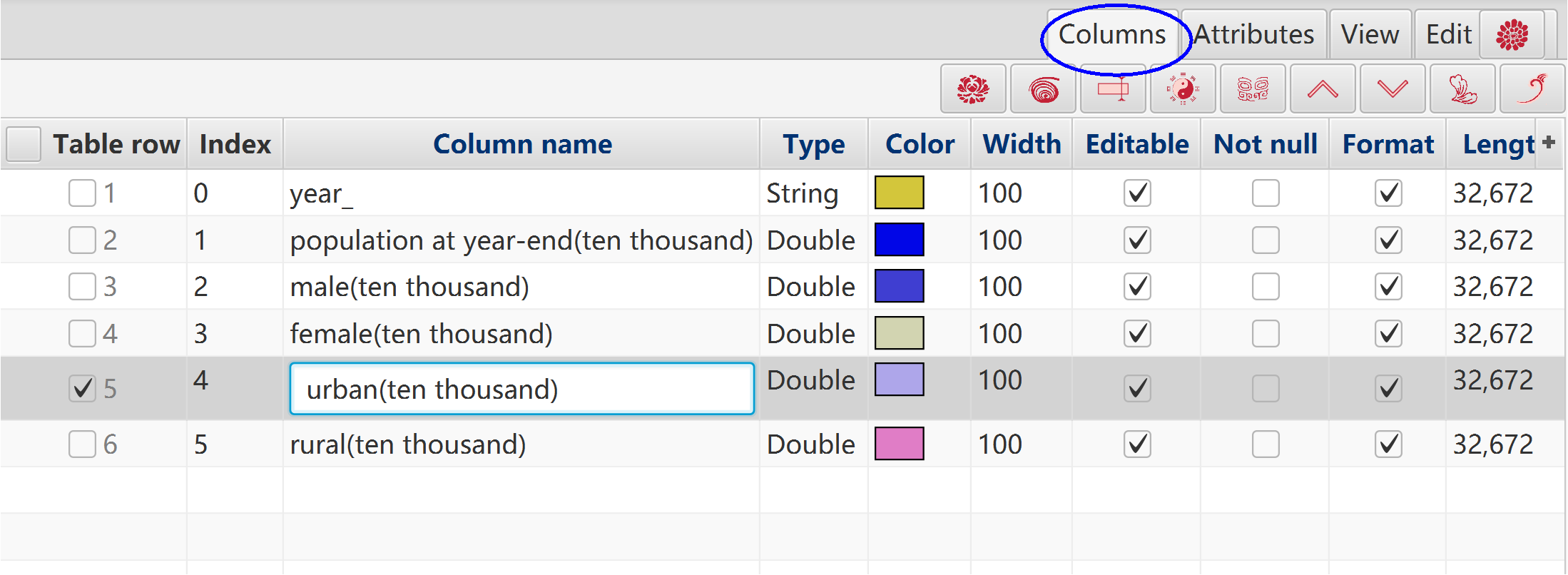
Data name, decimal scale, and maximum value of random.
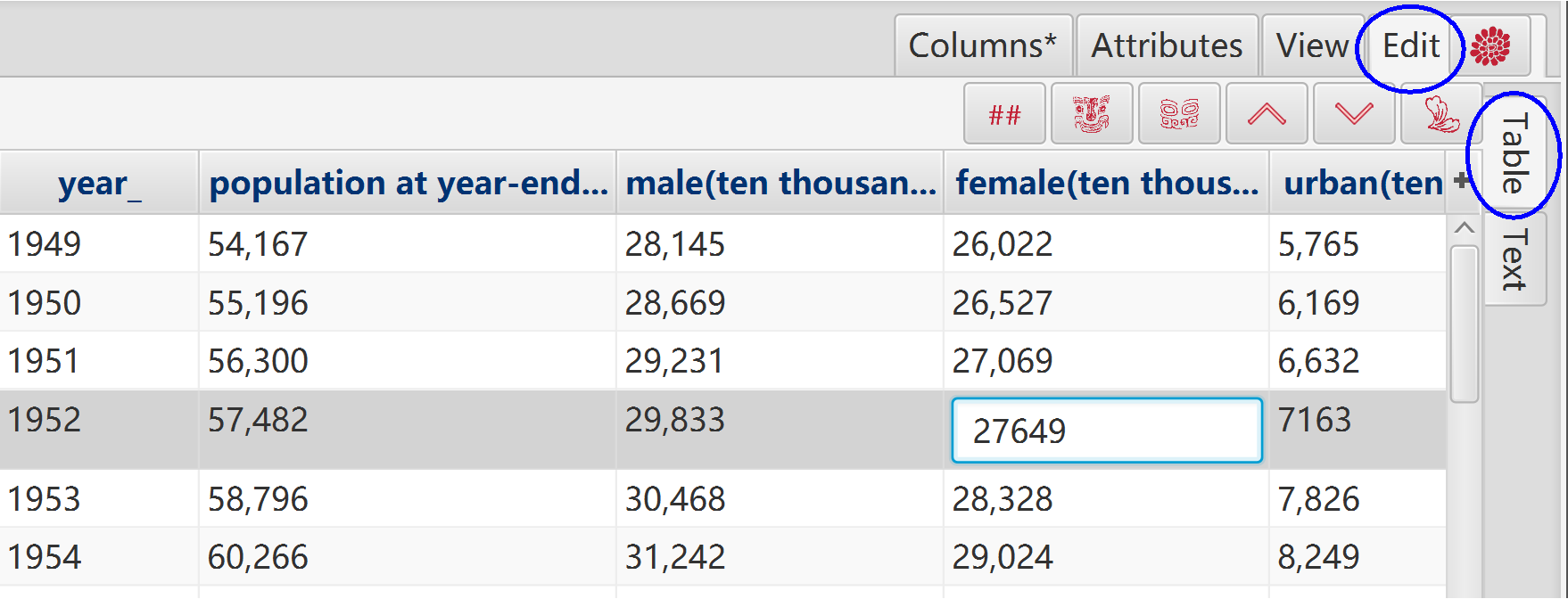
"Table" is the master edit mode:
Its modifications are applied to other panes automatically.
It is the final data to save.
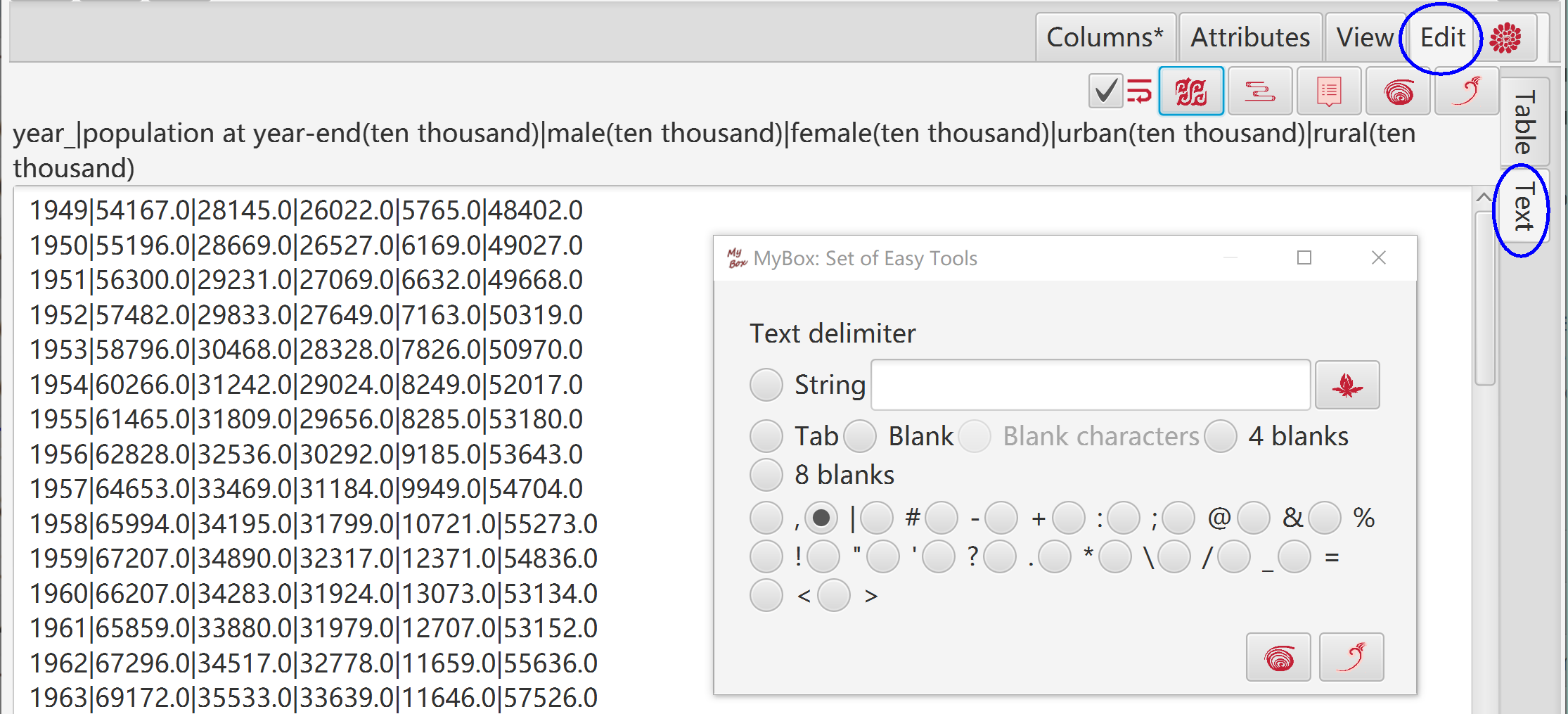
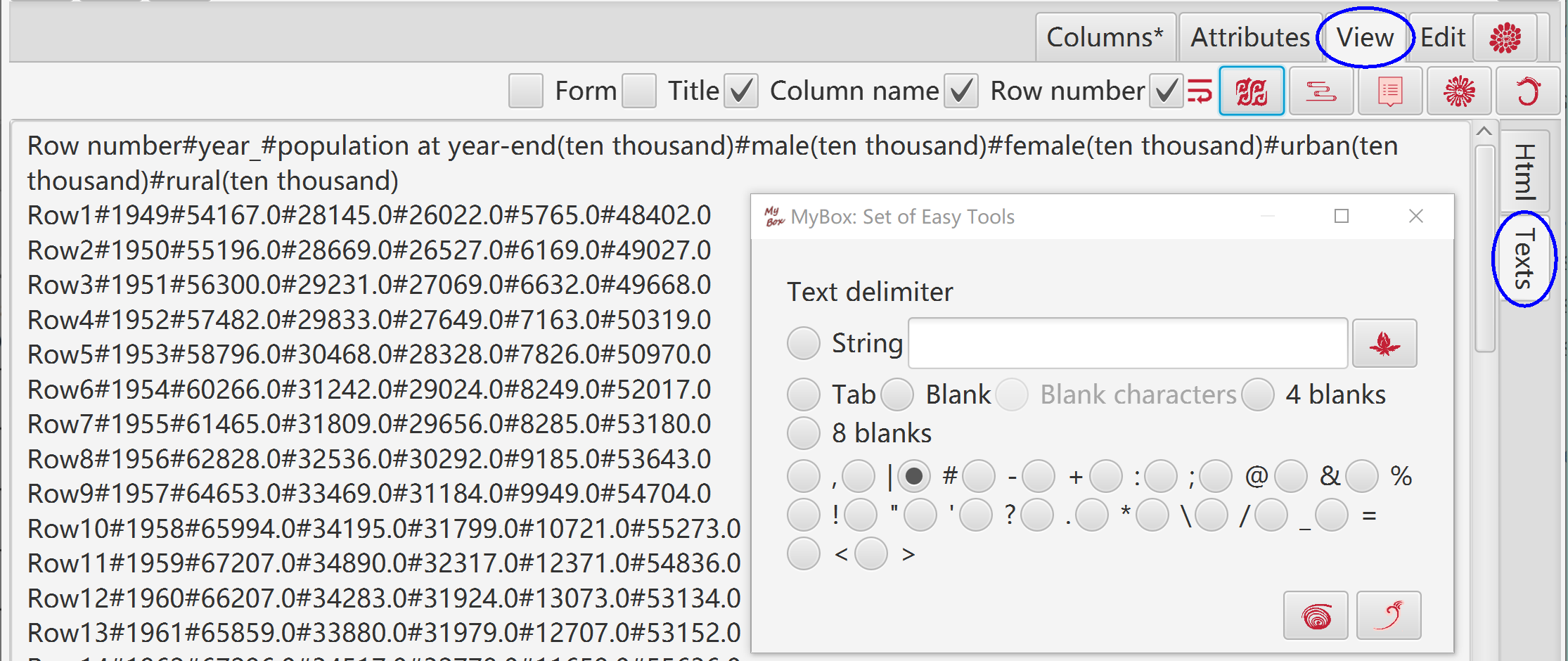
"Text" is the assist edit mode.
Click button "OK" to apply its modifications to "Table".
Click button "Cancel" to discard its modifications and pick data from "Table".
Click button "Delimiter" to pick data from "Table" and apply new delimiter while its modifications are discarded.
View data of current data.
Options: Form, Title, Column Names, Row Numbers.
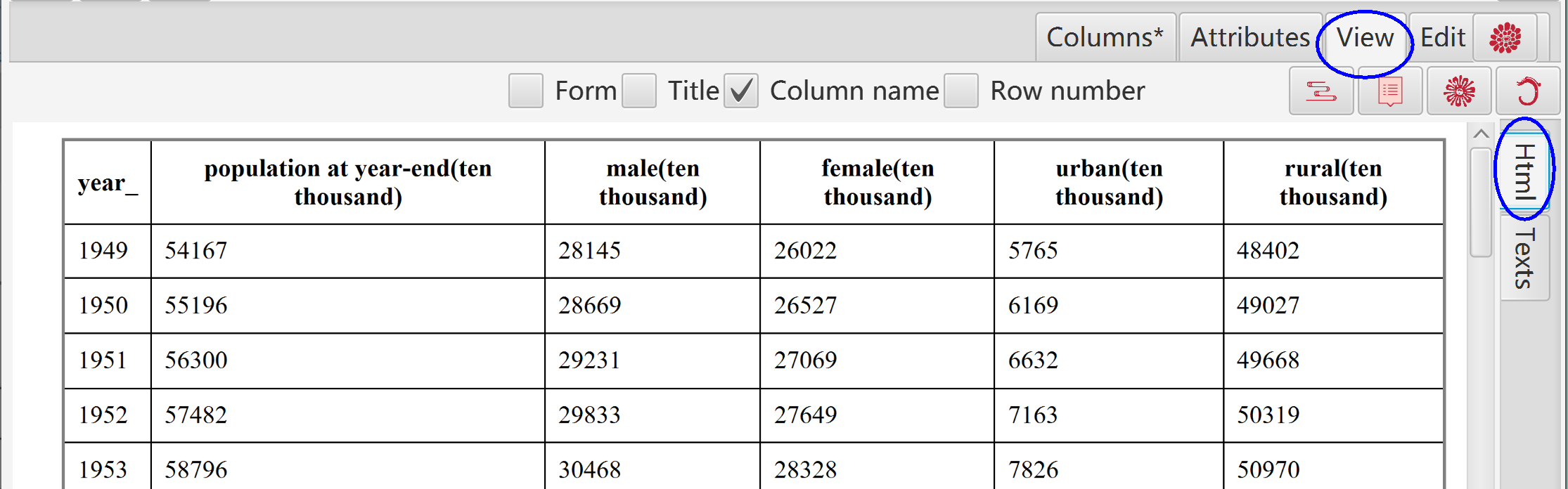
View data of current data.
Options: Form, Title, Column Names, Row Numbers.
Set delimiter.
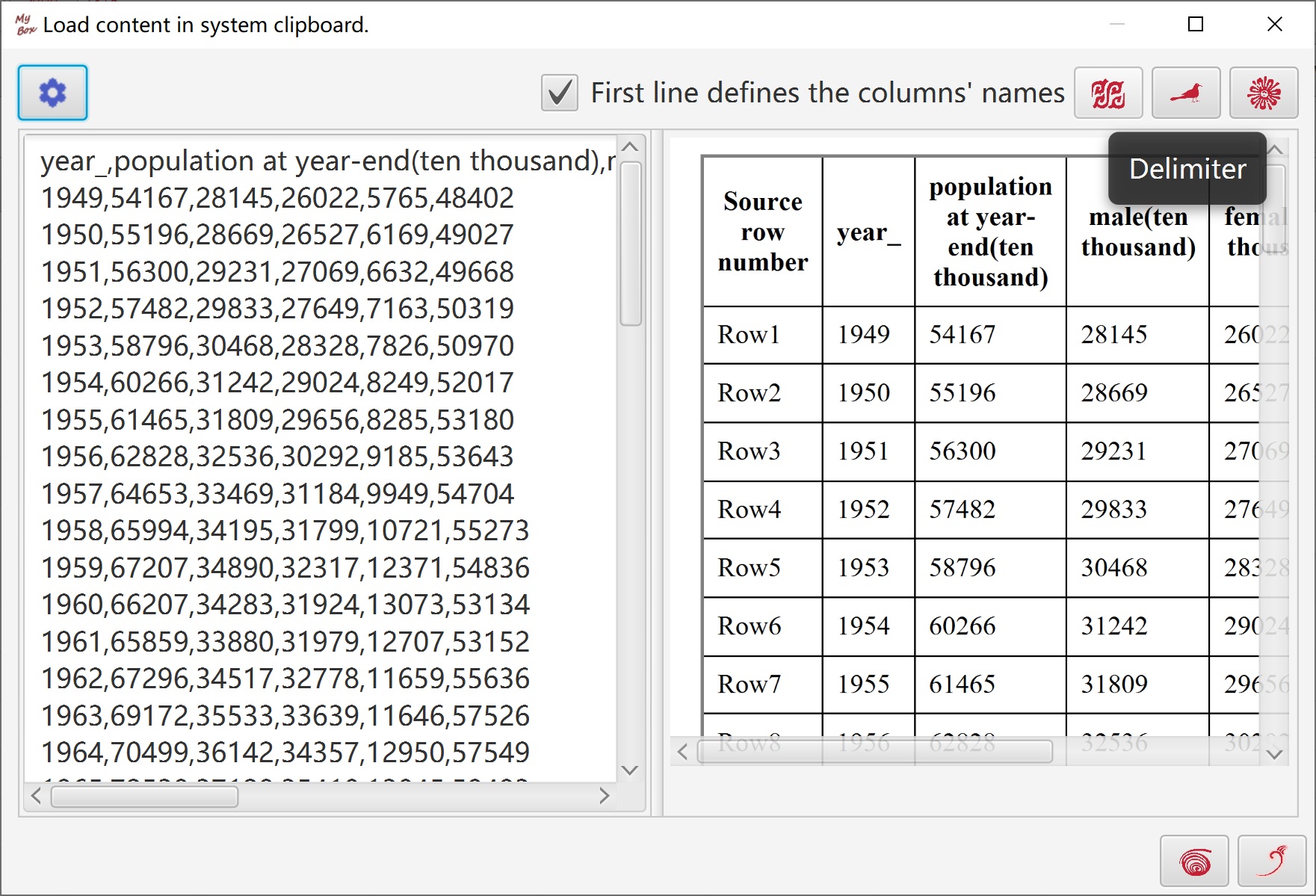
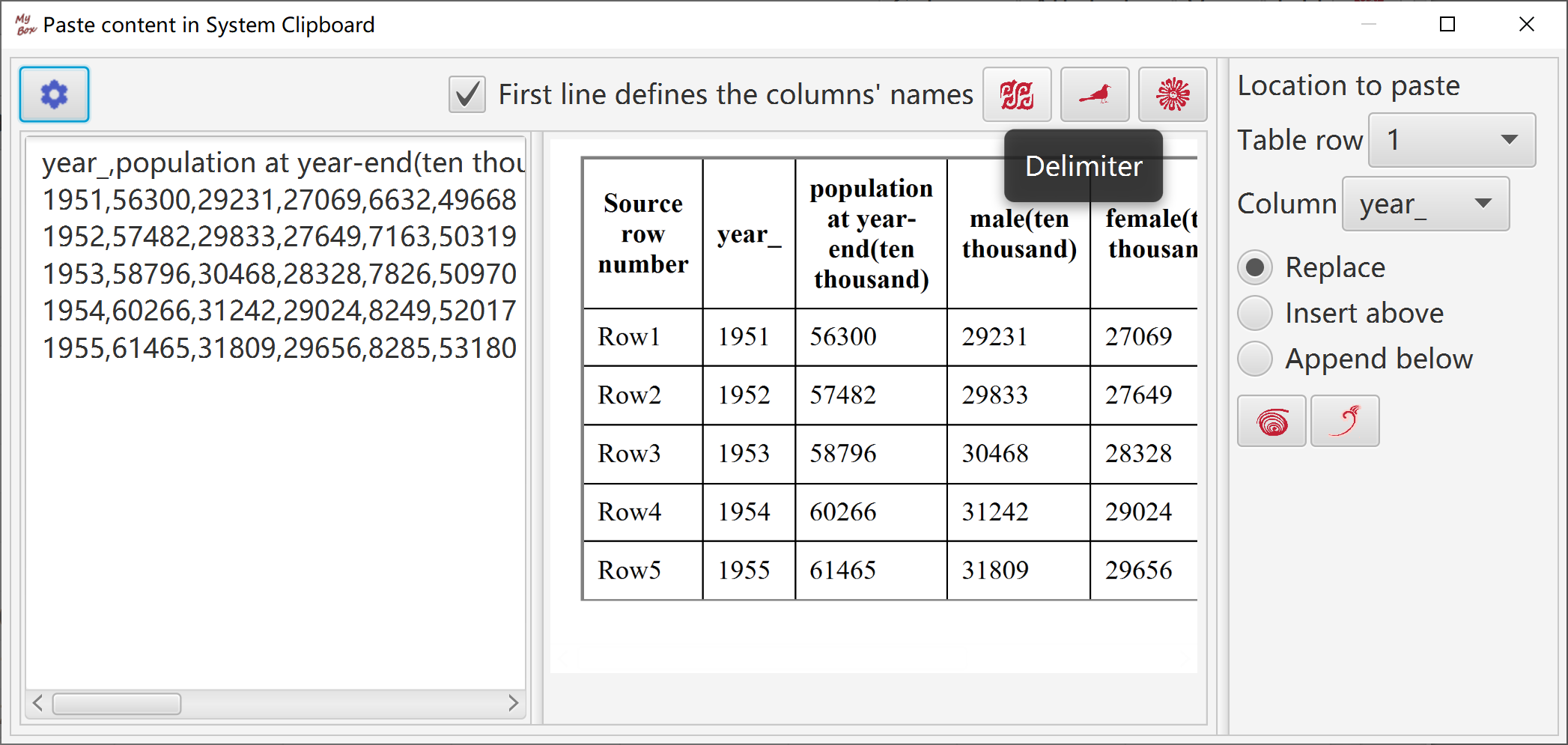
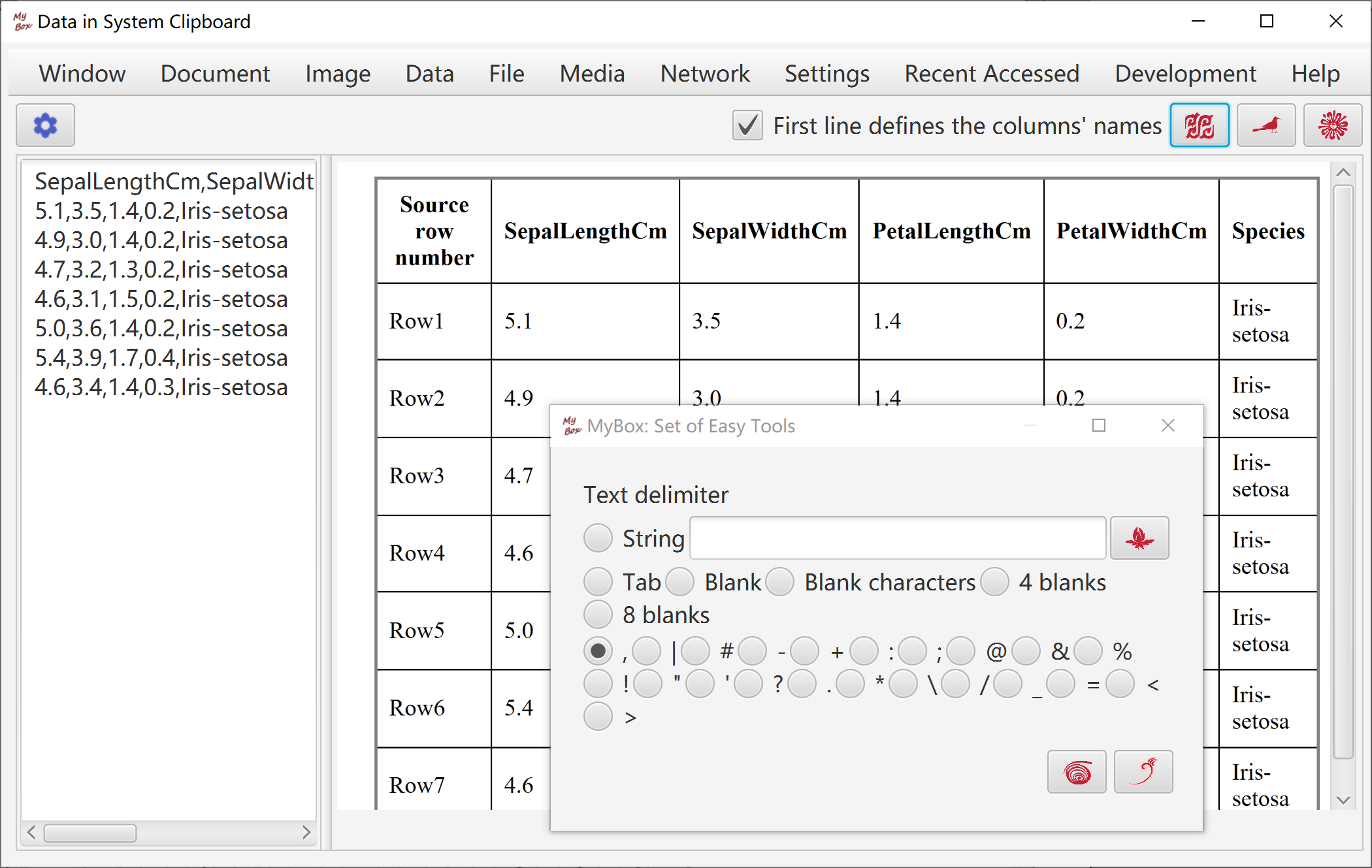
Read and parse contents in system clipboard.
Guess delimiter automatically.
Delimiter can be chosen from special characters or inputted regular expression.
First row can be set as column names.
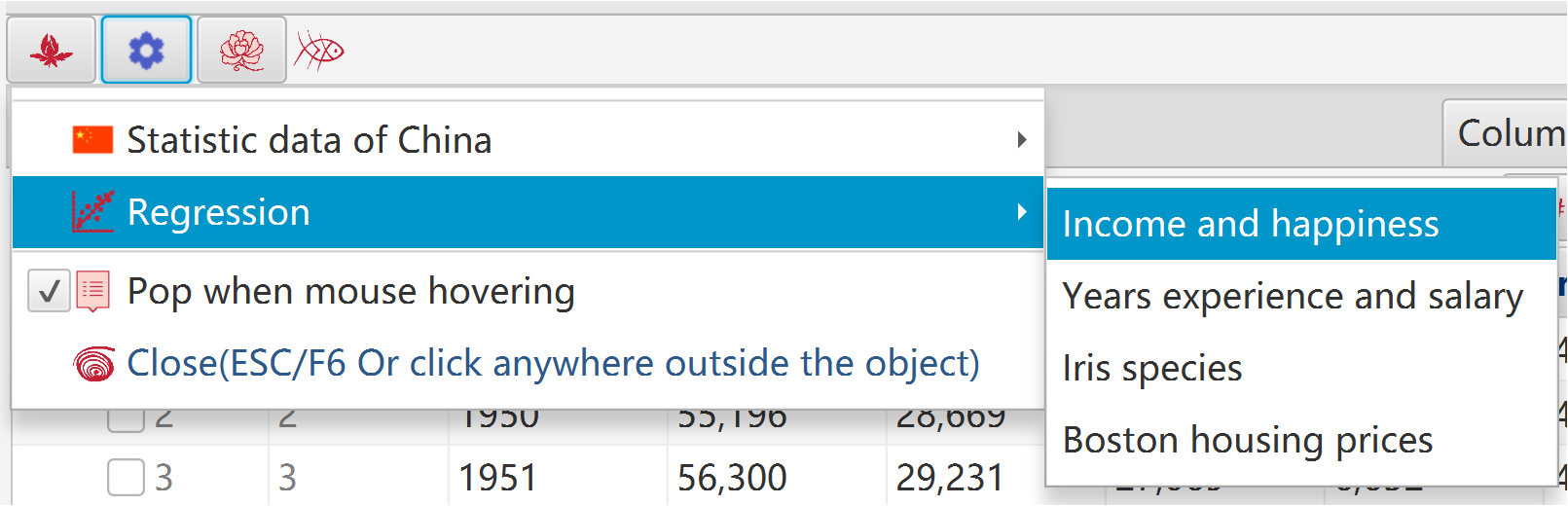
JavaScript expression can be data values when manufacture/trim/calculate data or generate chart:
If the script is blank, then return empty string.
Edit the script:
It can include any valid JavaScript elements.
It should return a value finally.
It can include following placeholders:
#{TableRowNumber}
#{DataRowNumber}
#{<column_name>}
#{<column_name>- }
When MyBox evaluates the expression:
Placeholders are replaced with actual values of each data row .
'#{xxx}' is handled as string while #{xxx} is handled as number.
When handles all pages, script fails when it includes “#{TableRowNumber}” .
Hover or click button “Examples” to paste example codes.
Hover or click button “Histories” to paste codes in histories.
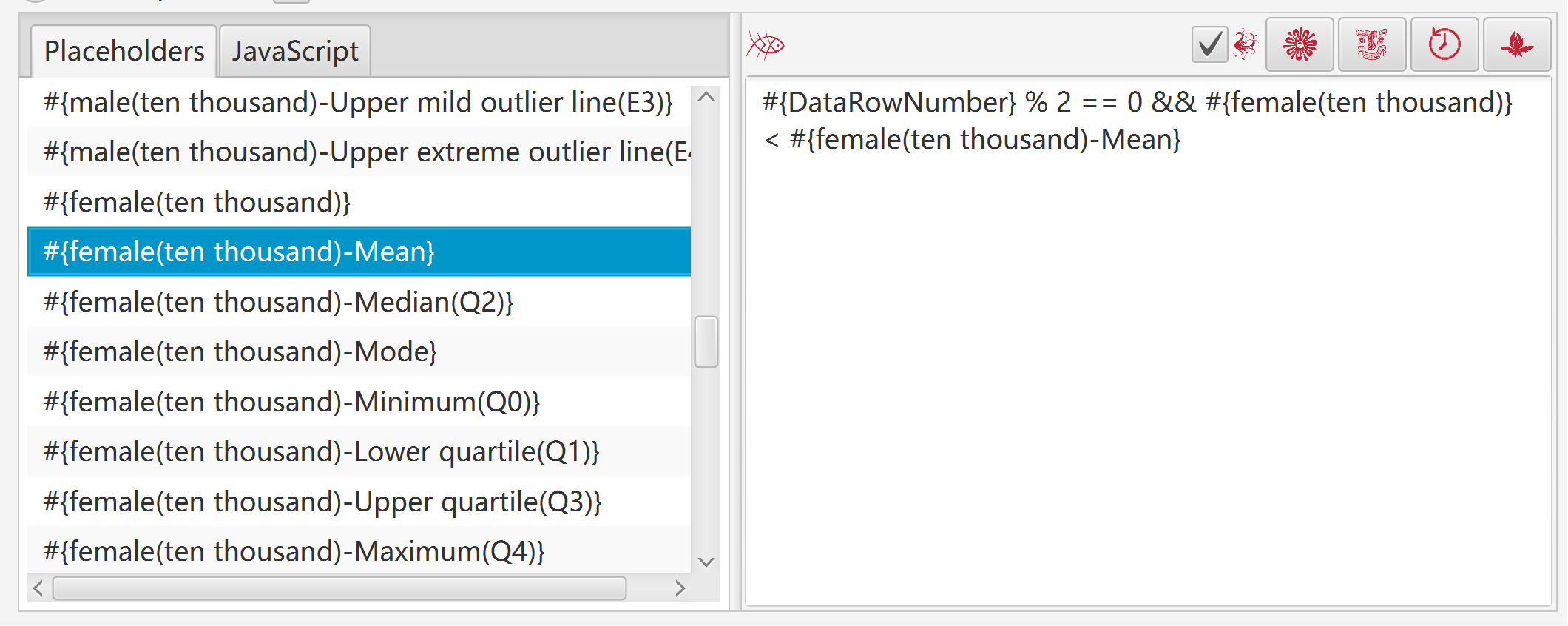
Examples:
|
expression |
meaning |
|---|---|
|
#{DataRowNumber} % 2 == 0 |
data row number is even |
|
#{TableRowNumber} % 2 == 1 |
odd rows in current page |
|
Math.abs(#{v1}) + Math.PI * Math.sqrt(#{v2}) |
calculation |
|
'#{v1}'.replace(/hello/ig, 'Hello') |
replace all “hello”(case-insensitive) as “Hello” in column “v1” |
|
'#{v1}'.toLowerCase() |
lower case of value of column “v1” |
|
'#{v1}'.split(‘,’) |
split value of column “v1” by comma |
|
#{v1} - #{v1-Mean} |
difference between value of column “v1” and mean of column “v1” |
“Row Filter” is special “Row Expression”, and can be condition to filter data rows.
It should return boolean value("true" or "false") finally.
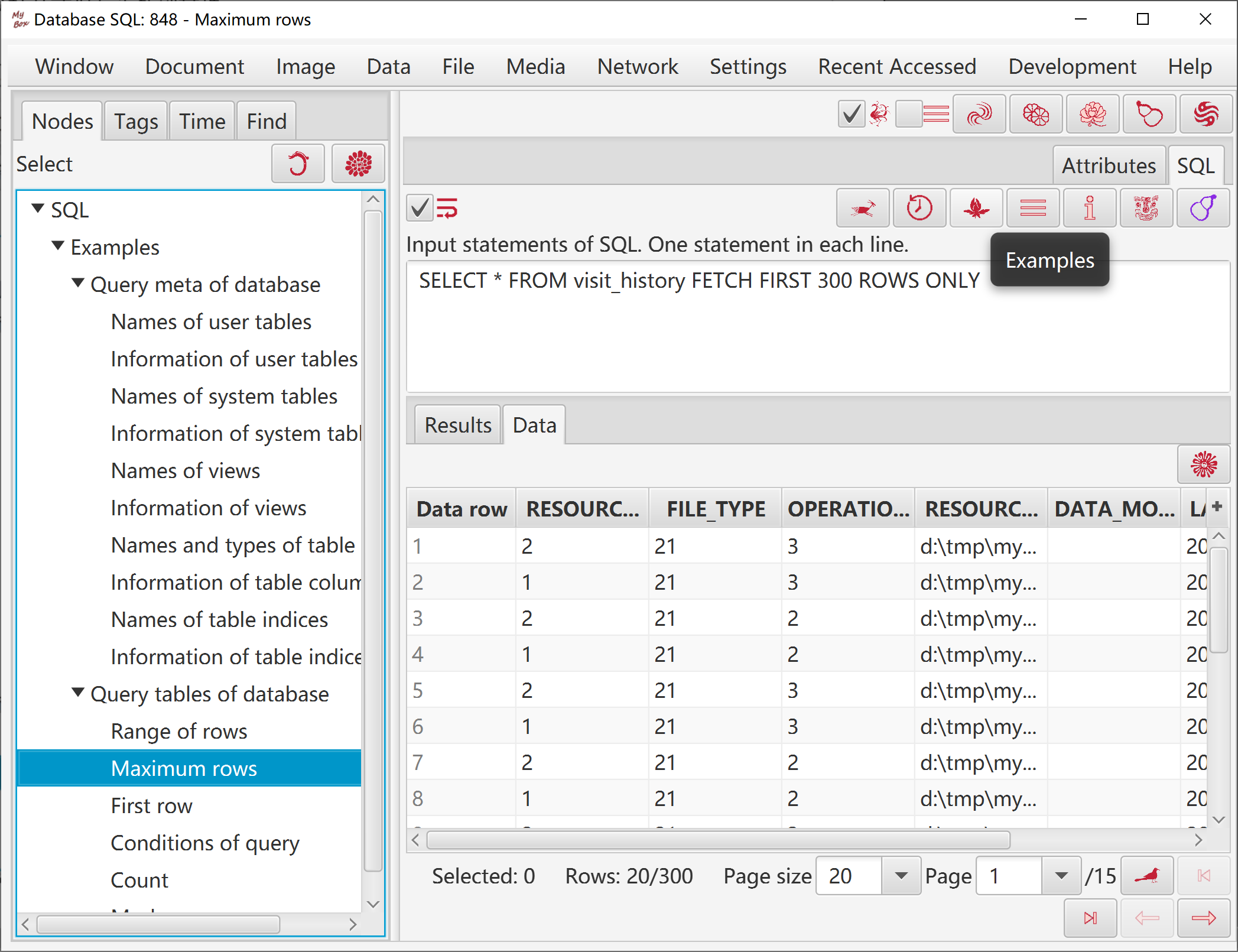
Can set maximum rows.
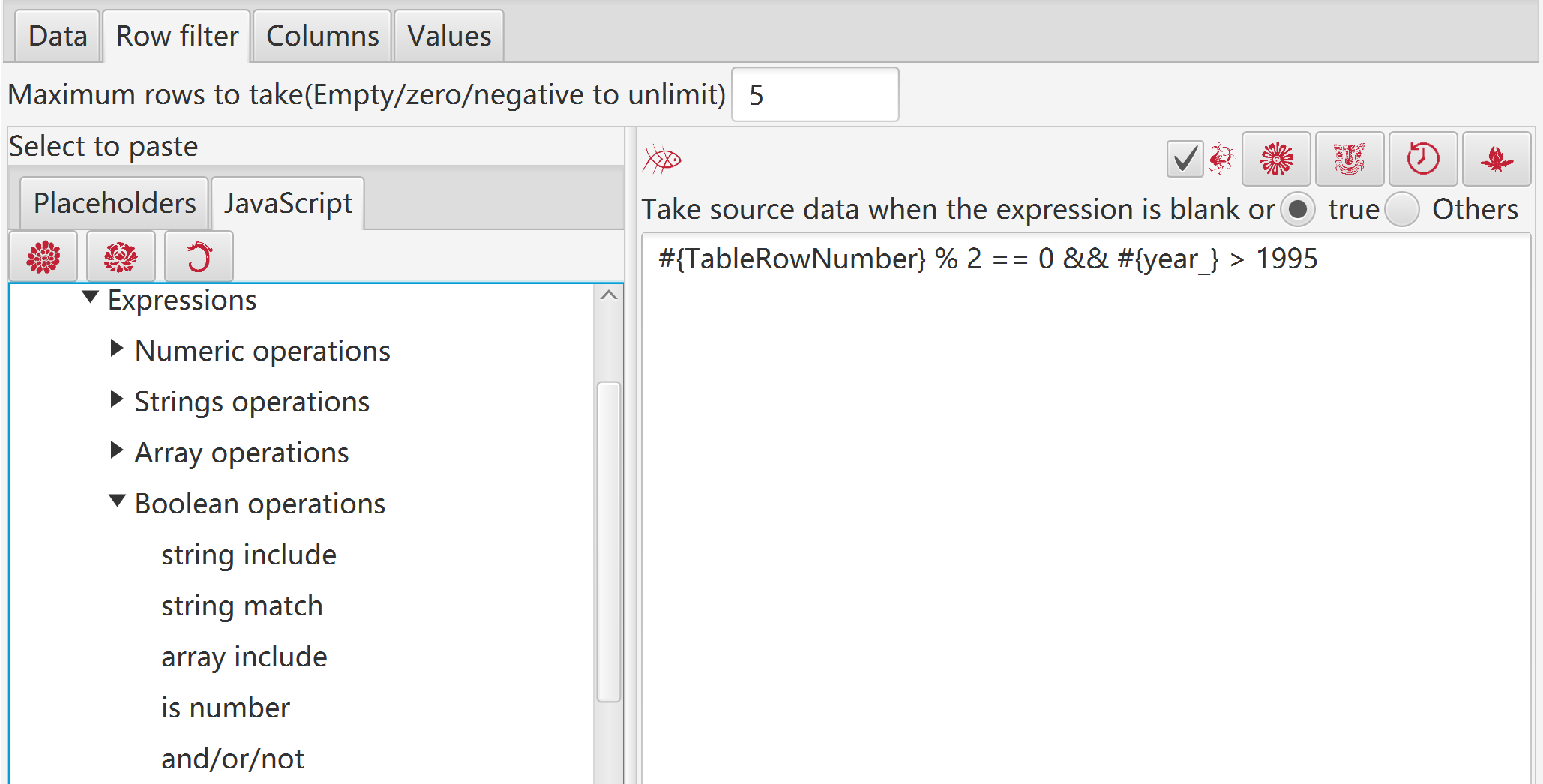
Exmaples:
|
Expression |
meaning |
|---|---|
|
#{DataRowNumber} % 2 == 0 |
data row number is even |
|
#{TableRowNumber} % 2 == 1 |
odd rows in current page |
|
Math.abs(#{v1}) >= 0 |
value of column “v1” is number |
|
#{v1}) > 0 |
value of column “v1” is larger than zero |
|
#{v1} - #{v2} < 100 |
difference between values of “v1” and “v2” is less than 100 |
|
'#{v1}'.length > 0 |
value of column “v1” is not empty |
|
'#{v1}'.search(/Hello/ig) >= 0 |
value of column “v1” includes “Hello”(case-insensitive) |
|
'#{v1}'.startsWith(‘Hello’) |
value of column “v1” starts with “Hello” |
|
var array = [ ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’];array.includes(‘#{v1}’) |
value of column “v1” is one of “A”, “B”, “C” |
|
#{v1} < #{v1-Mean} |
value of column “v1” is less than mean of column “v1” |
Select data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Select columns. If no column is selected, then all columns are taken.
Set row filter.
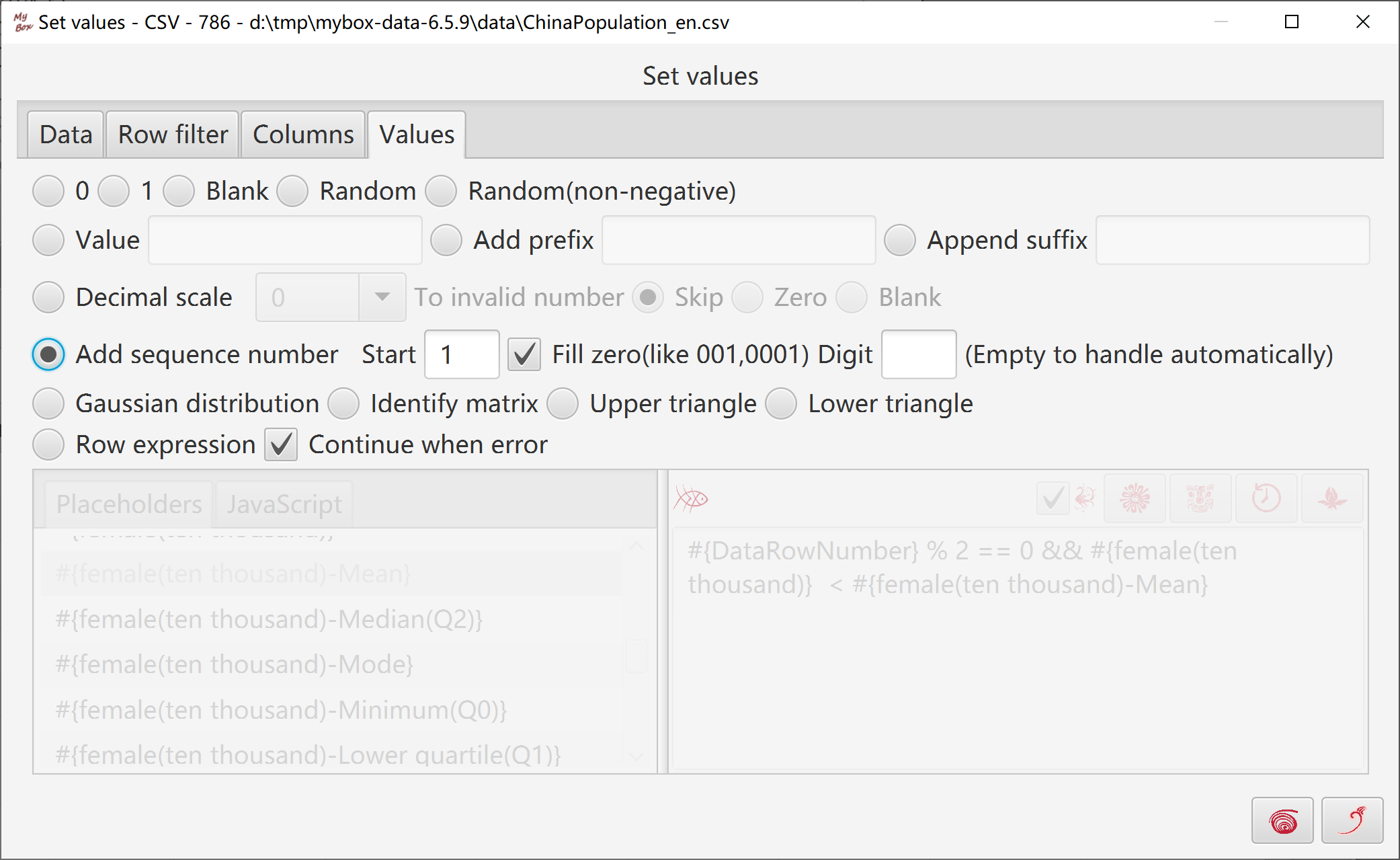
Set values of selected data as following:
Constant:0, 1, blank, or inputted value
Random, random of non-negative
Add prefix, append suffix, set decimal scale, or add sequence numbers
When selected data are sqaure, whose rows number equals to columns number, they can be set as following: gaussian distribution, identify matrix, upper triangular matrix, lower triangular matrix.
Row expression
If handle all pages of data file, then auto-backup before set values.
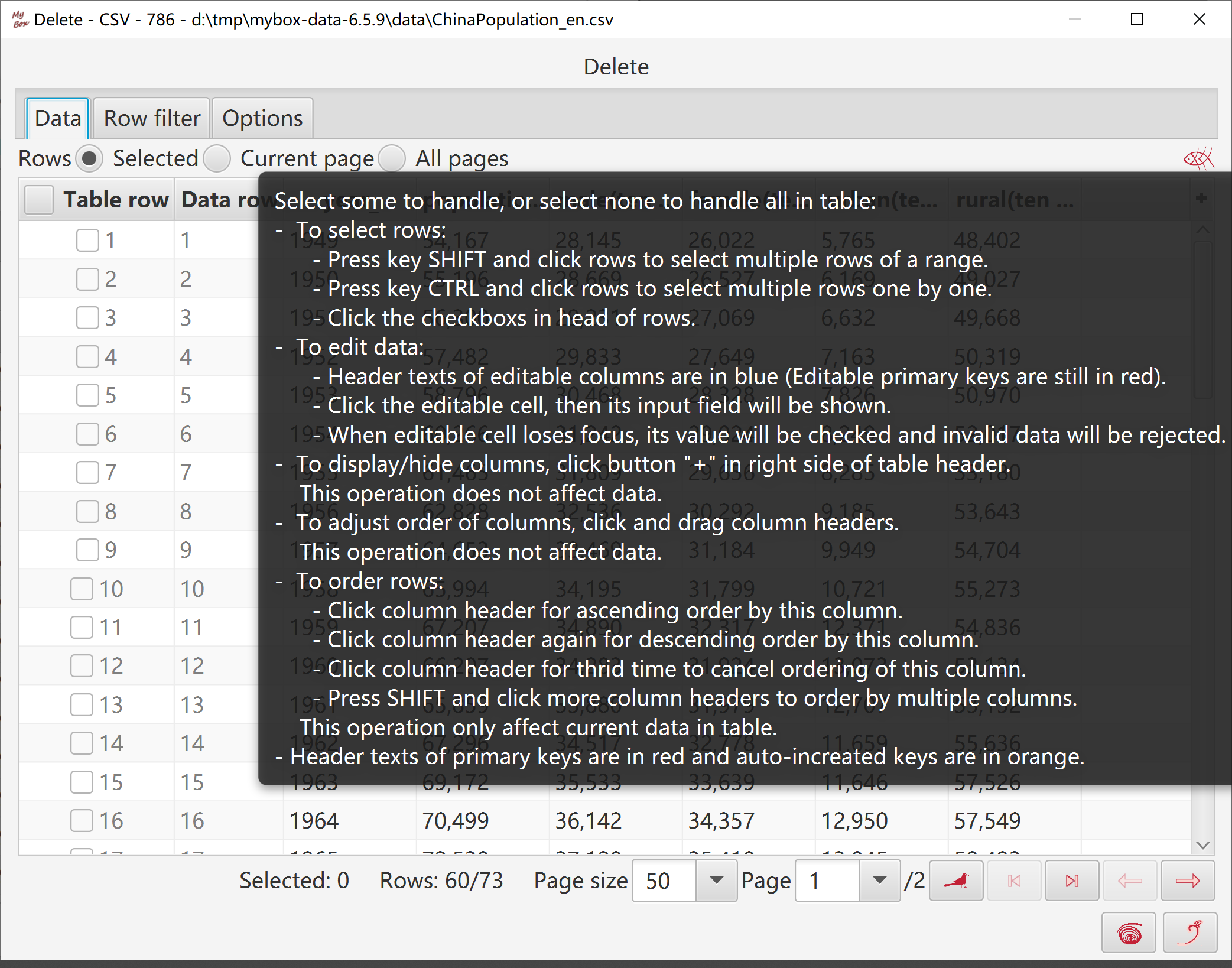
Select data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Set row filter.
Option: Whether continue when error.
If handle all pages of data file, then auto-backup before delete.
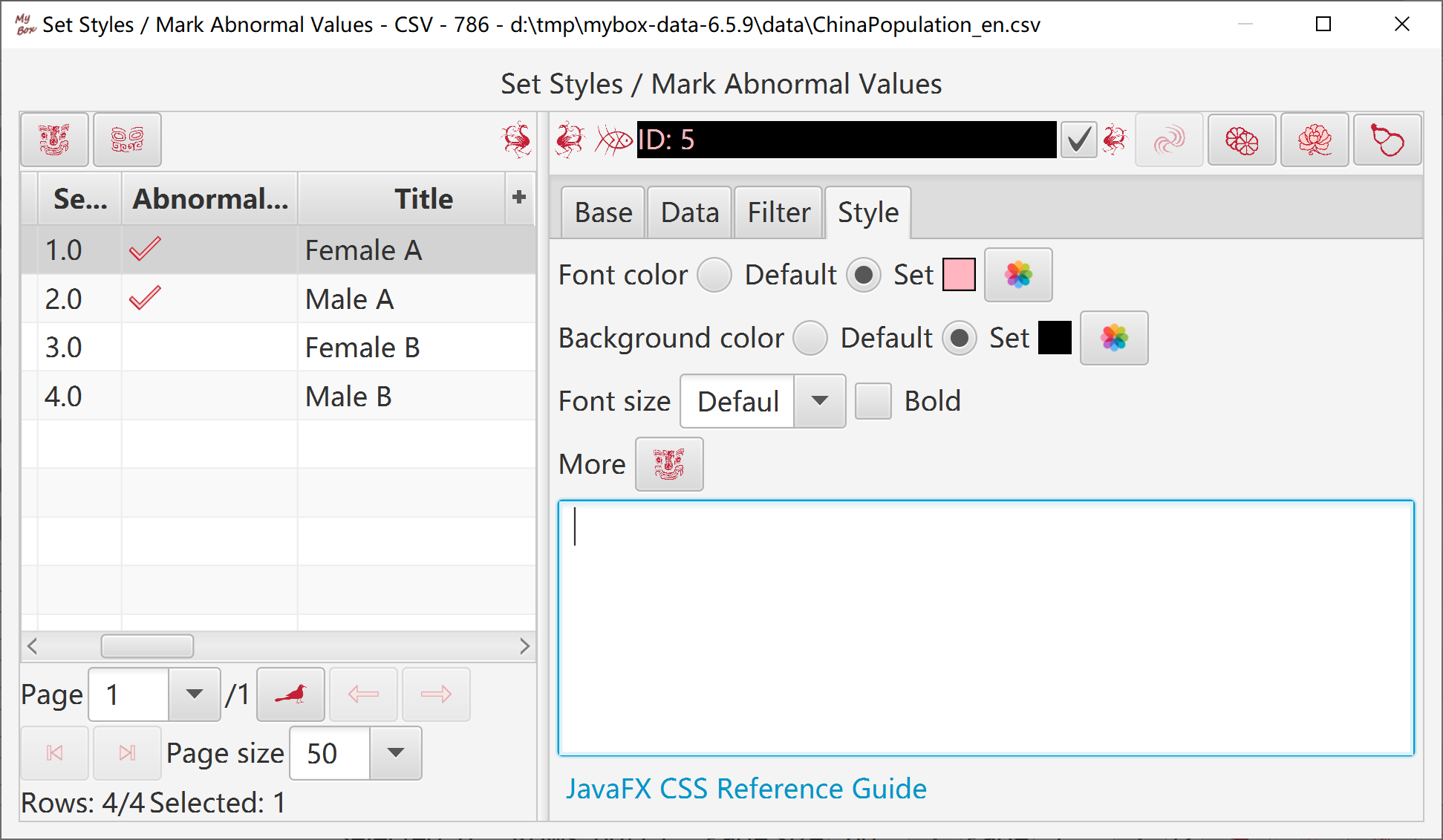
Add/Edit/Delete styles.
Define conditions to determine which data cells to apply the style:
Range of data rows
Column names.
Row filter.
Notice, data of a row number may be changed when some rows are added or deleted.
Example, when insert 2 rows before "row 6", original "row 12" becomes "row 14" while current "row 12" was "row 10".
So "row number" is not right way to locate a specific data row while rows number is changing.
A way to refer sepcial rows is the expression composed of column values.
Define style values:
Font color, font size, background color, bold, etc.
More values in format of JavaFx CSS.
Define title and sequence number of the style.
Set whether the style marks abnormal values.
All styles are applied to the data one by one in order of their sequence number.
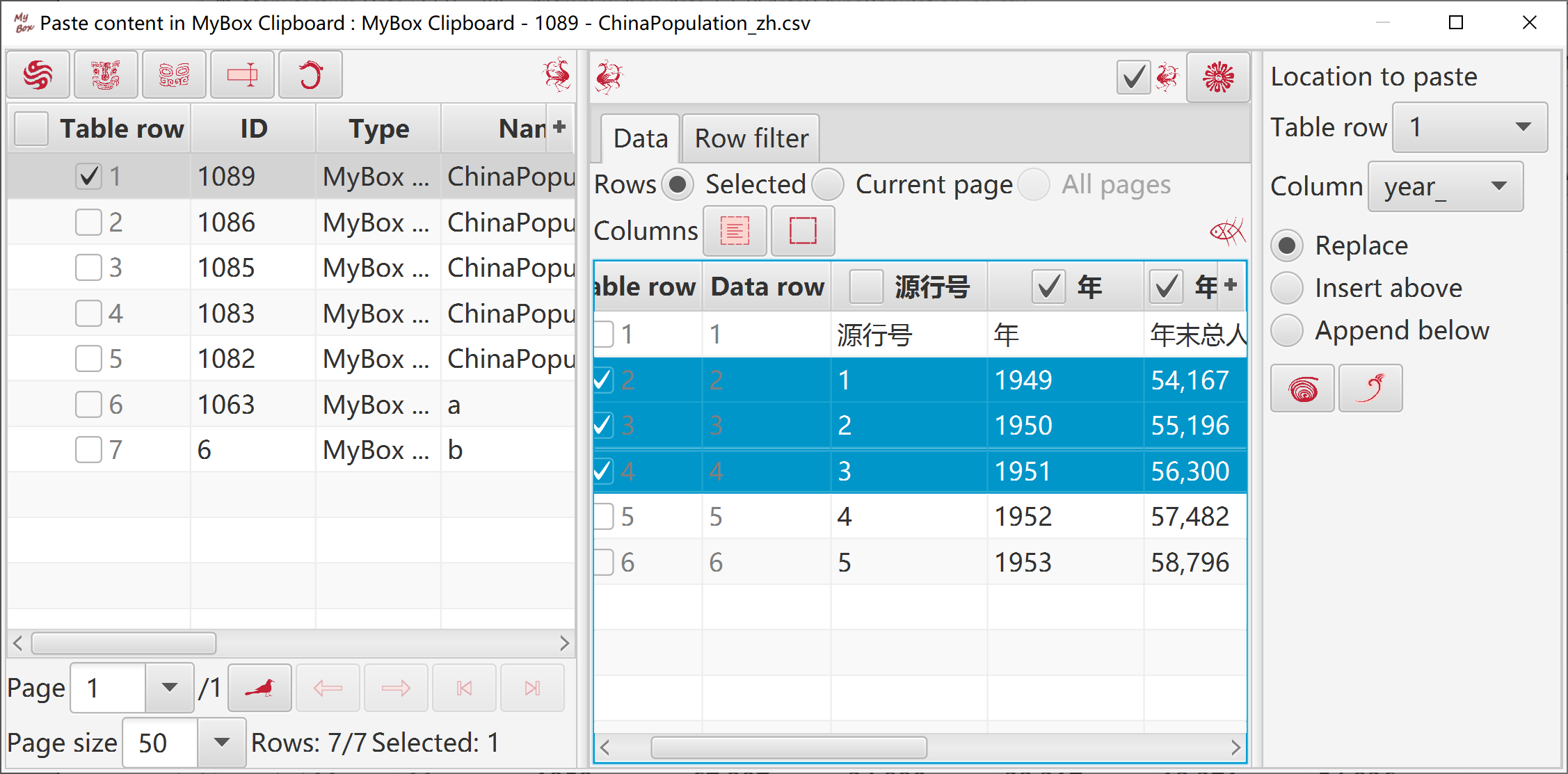
Select data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Select columns. If no column is selected, then all columns are taken.
Set row filter.
Target can be following: new csv/excel/text file, matrix, system clipboard, MyBox clipboard, database table.
When rows are current page or selected ones, target can be defined location in table to insert/append/replace.
Select data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Select columns. If no column is selected, then all columns are taken.
Set row filter.
Calcuate:
Select the column to sort and whether descending.
Data type of column affects sorting results.
Maximum rows number of results can be set.
Target can be following: new csv/excel/text file, matrix, system clipboard, MyBox clipboard, database table.
When rows are current page or selected ones, target can be defined location in table to insert/append/replace.
Select data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Select columns. If no column is selected, then all columns are taken.
Set row filter.
Calcuate: Options to set first column as column names.
Target can be following: new csv/excel/text file, matrix, system clipboard, MyBox clipboard, database table.
When rows are current page or selected ones, target can be defined location in table to insert/append/replace.
Select data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Select columns. If no column is selected, then all columns are taken.
Set row filter.
Calcuate:
Accroding to: Columns/rows/all.
Algorithms: MinMax(Range can be set), sum(L1), ZScore(L2).
To non-numeric, skip or count as zero.
Target can be following: new csv/excel/text file, matrix, system clipboard, MyBox clipboard, database table.
When rows are current page or selected ones, target can be defined location in table to insert/append/replace.
Select data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Select columns. If no column is selected, then all columns are taken.
Set row filter.
Calcuate:
Input name of values.
Input row expression.
Target can be following: new csv/excel/text file, matrix, system clipboard, MyBox clipboard, database table.
When rows are current page or selected ones, target can be defined location in table to insert/append/replace.
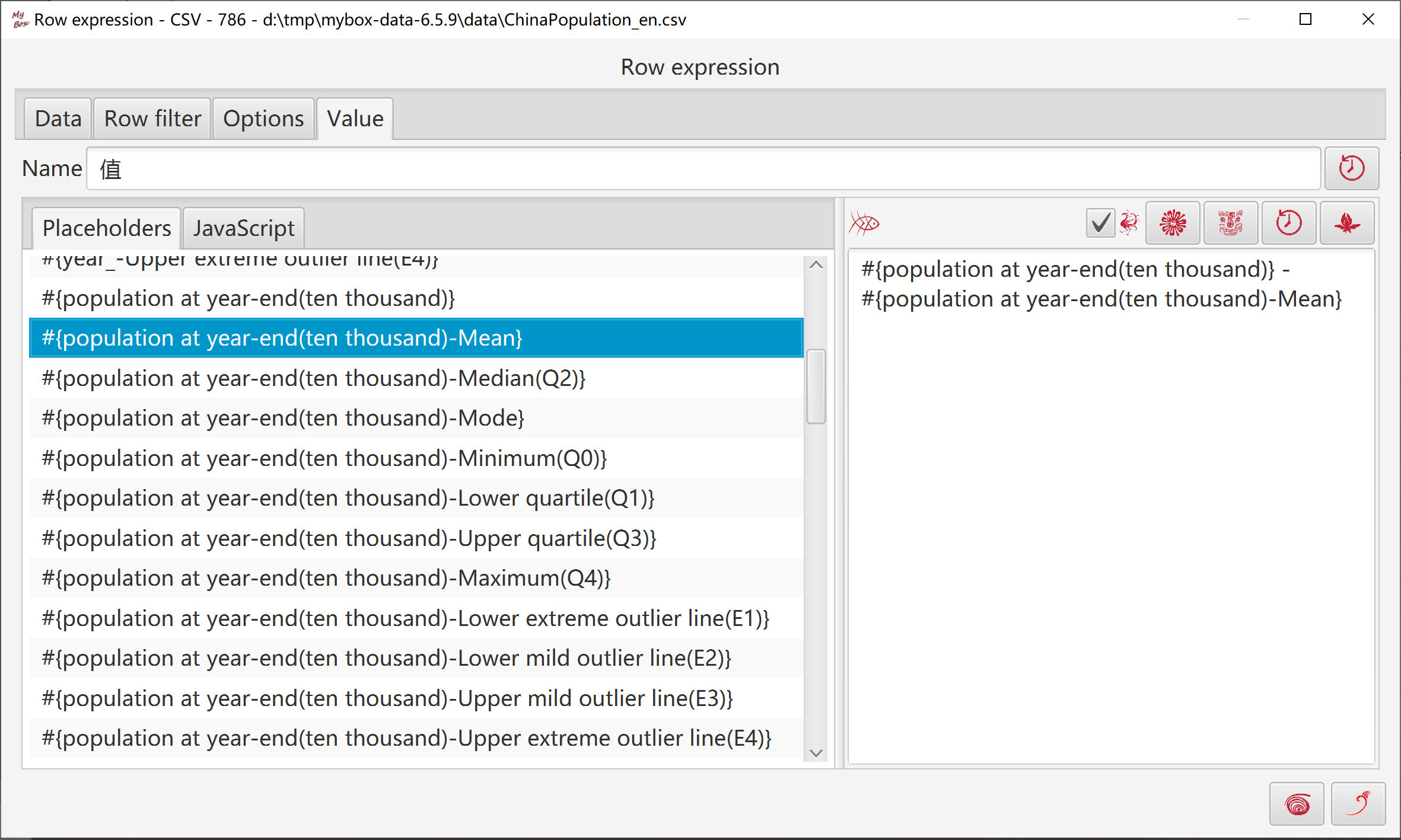
Select data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Select columns. If no column is selected, then all columns are taken.
Set row filter.
Calcuate:
Following values can be generated:
count, sum, mean, geometric mean, sum of squares, population variance, sample variance, population standard deviation, sample standard deviation, skewness, minimum(Q0), lower quartile(Q1), median(Q2), upper quartile(Q3), maximum(Q4), upper extreme outlier line(E4), upper mild outlier line(E3), lower mild outlier line(E2), lower extreme outlier line(E1), mode
Accroding to: Columns/rows/all.
Set decimal scale.
To non-numeric, skip or count as zero.
Target can be following: new csv/excel/text file, matrix, system clipboard, MyBox clipboard, database table, or defined location in table to insert/append/replace.
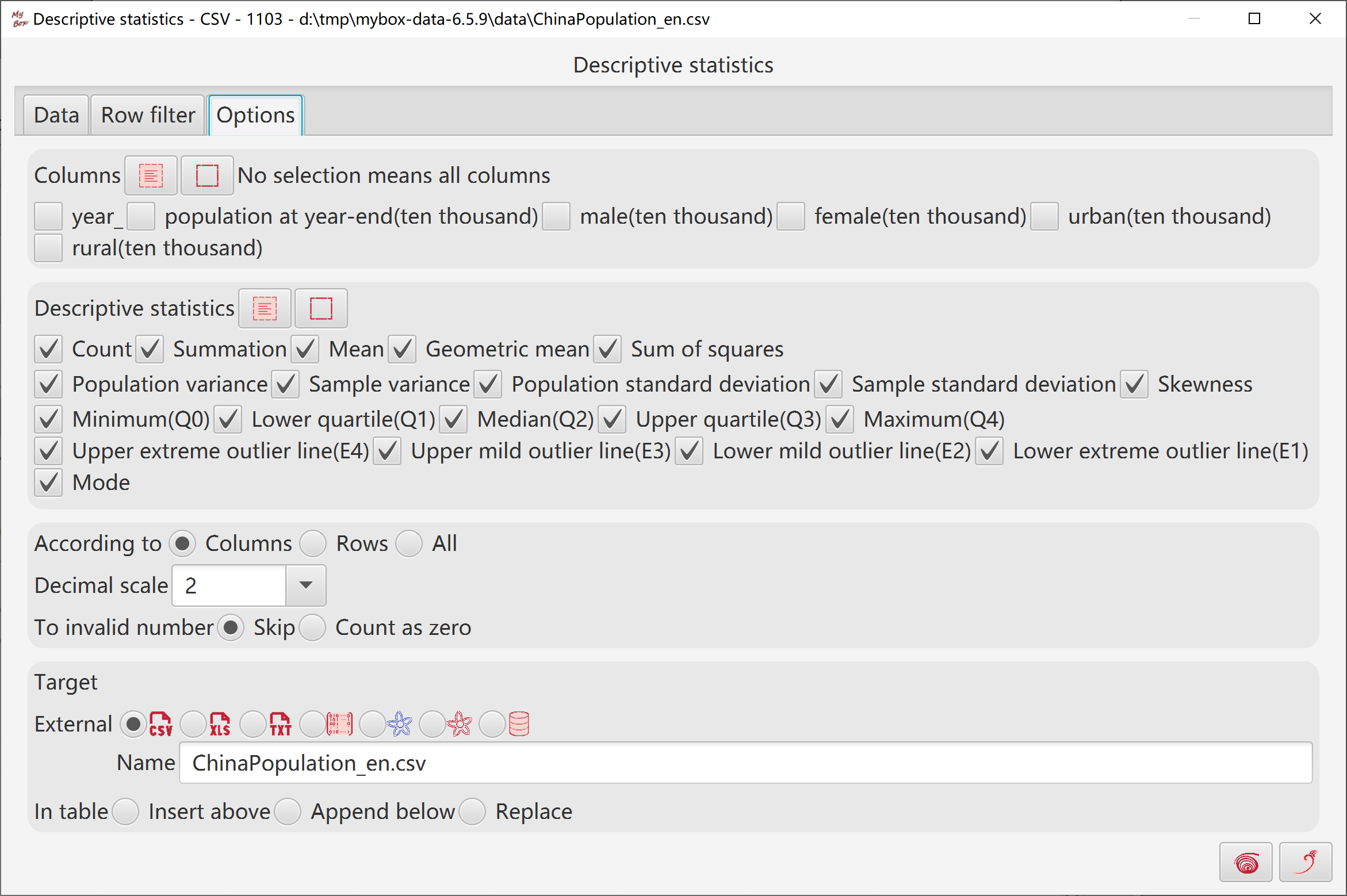
Select data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Set row filter.
Calcuate:
Select some columns as "group by". Need not be numbers.
Select some aggregate values to be calculated:
Like avarage, max, min, variance, standard deviation, etc.
"count" is always calcualted, and not in the list.
Multiple items can be selected. None selection is permitted.
Involved values should be numbers.
Select some values as "order by". Multiple items can be selected. None selection is permitted
Input maximum number of result rows. Blank/zero/negative means no limitation.
To invalid numbers, option to set as blank or zero.
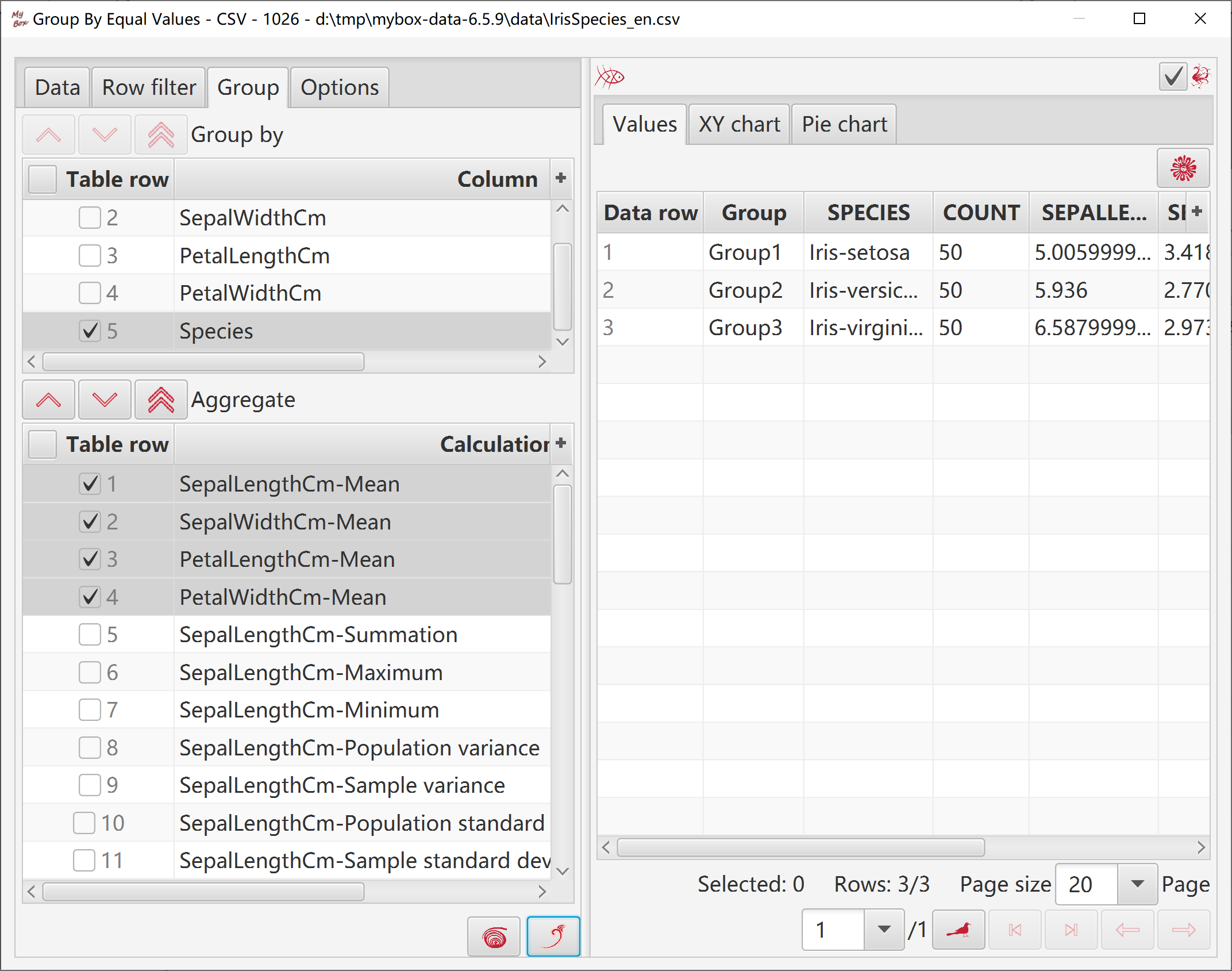
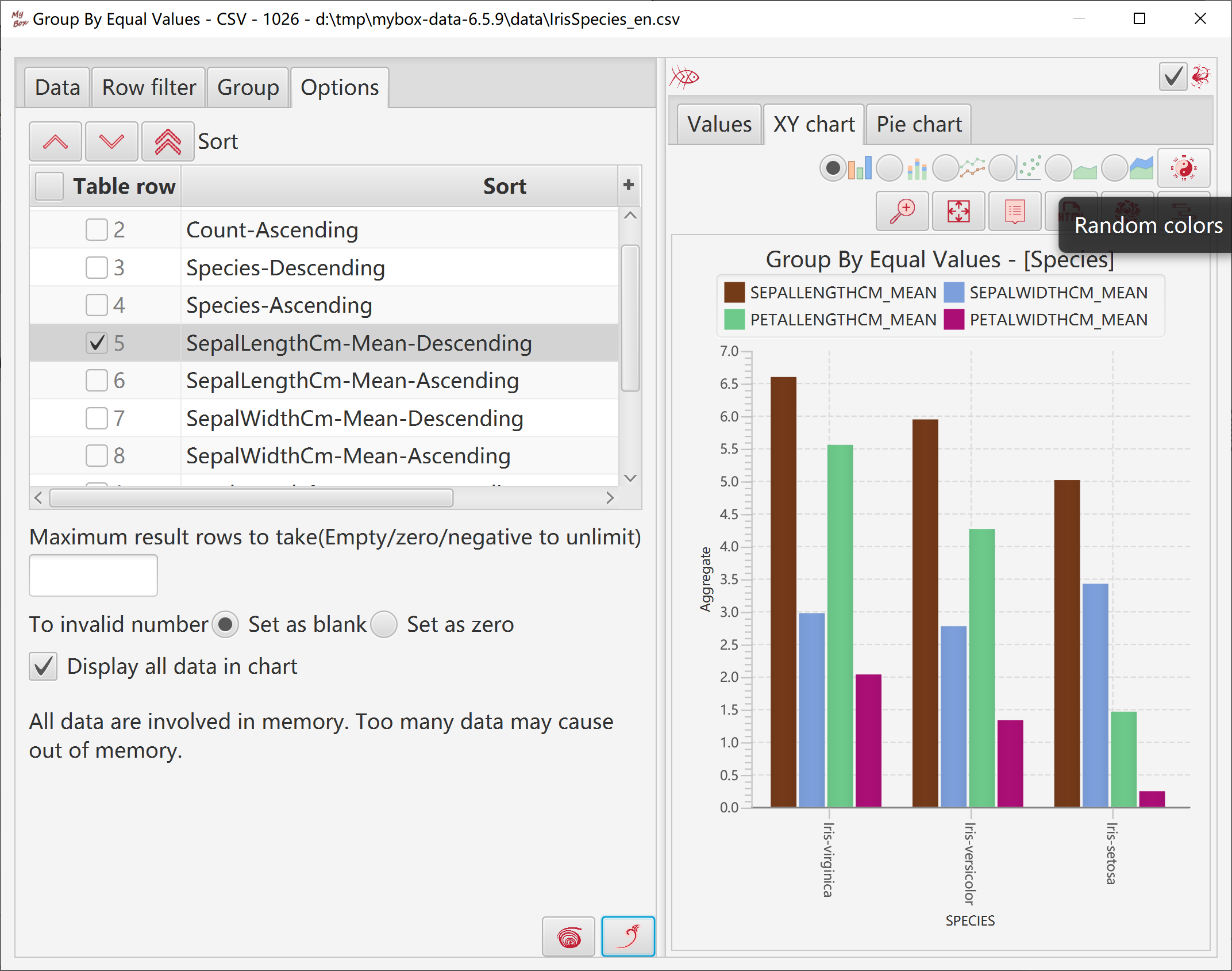
Calculated groups and their aggregate values are displayed in XY chart.
Calculated groups and their count are displayed in Pie chart.
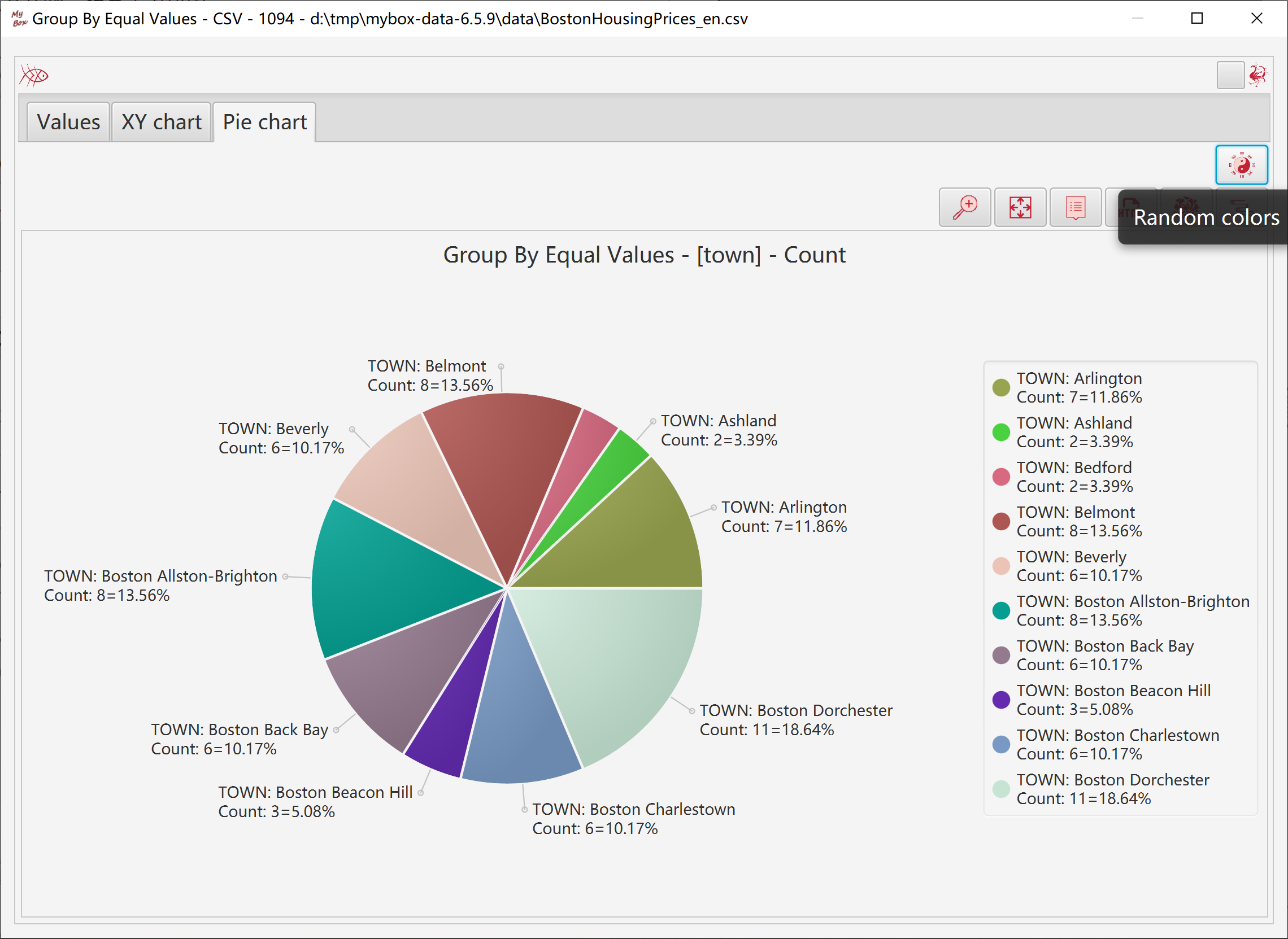
In charts:
If only one column in group, category values are values of this column.
If multiple columns in group, category values are names of groups.
Option to display all data in charts:
If yes, lots of data may cause out of memory.
If no, only current page of results are display in charts.
Data overflow may happen.
This tool is based on Apache Commons Math.
The regression does not store data, so calculation itself has not memory limitation when handle lots of rows.
Select data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Select columns. If no column is selected, then all columns are taken.
Set row filter.
Calcuate:
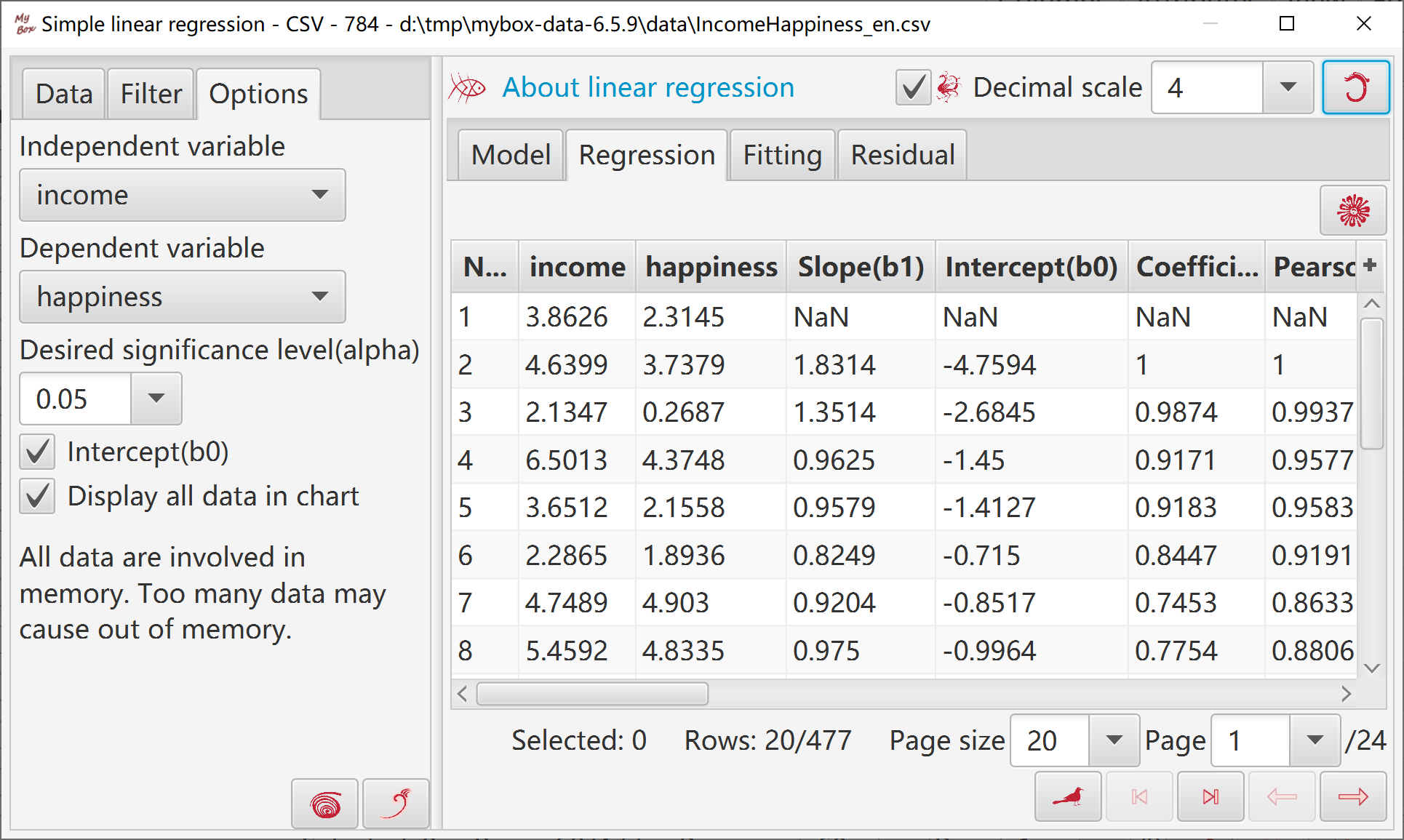
Select one column as independent variable.
Select another column as dependent variable.
Option whether includes intercept.
Set decimal scale.
Display values status of regression steps in table, including number of observations, slope, intercept, coefficient of determination(R-Square), correlation coefficient(R), mean of squared error(MSE) , sum of squared errors(SSE), total sum of squares(SSTO), sum of squares about regression(SSM/SSR), etc.
Display fitted liear model.
Display data status of last regression step.
Input value fo independent variable, and generate predicted value.
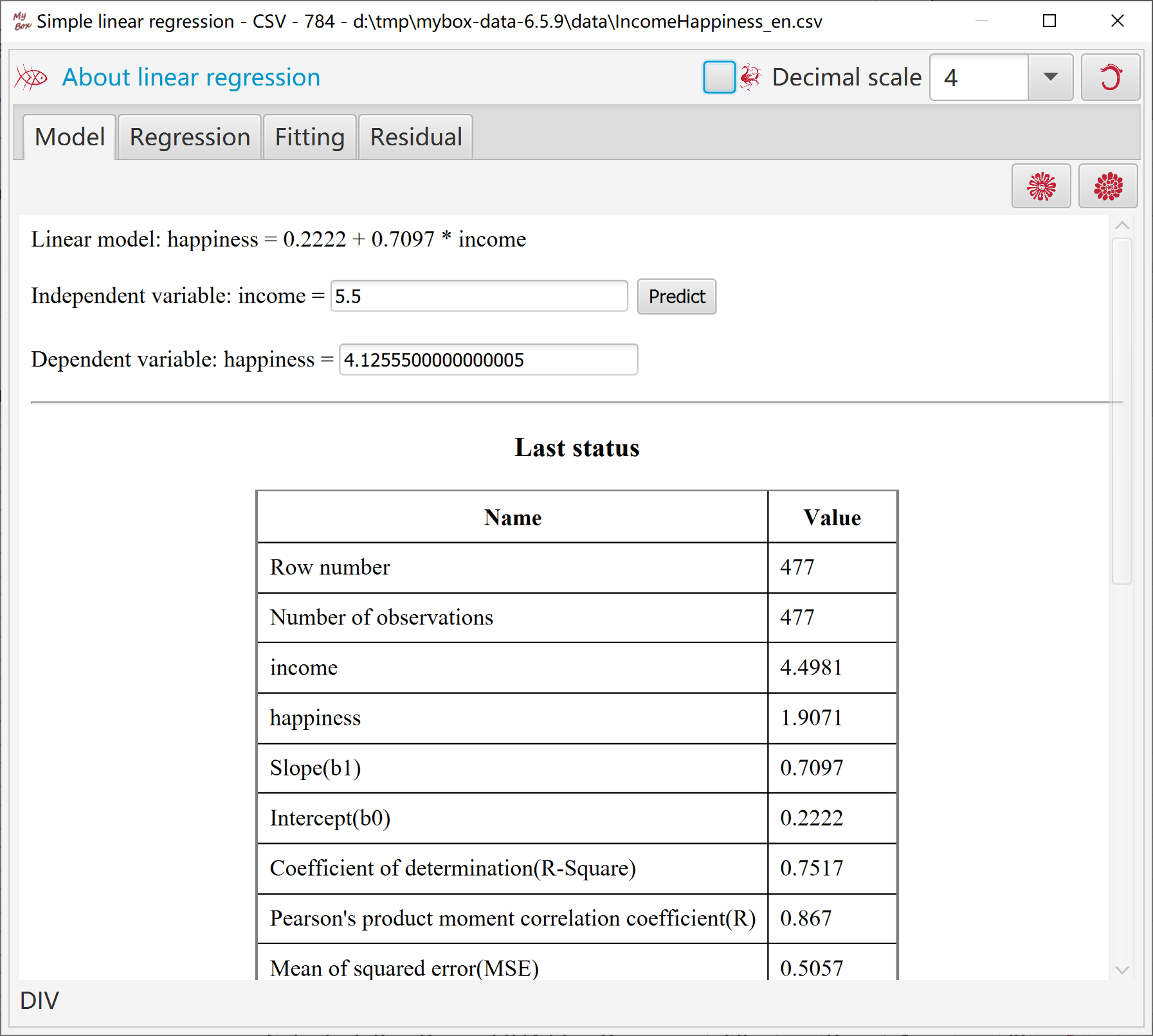
When handle all data rows(all pages), option to display all values in chart.
When display all values in chart, need concern memory limitation when load lots of data.
Or else only values in current page will be displayed in chart while all pages involve regression, and no memory limitation.
Set parameters of plot, X axis and Y axis.
Options to display fitted points, fitted line, or model description in chart.
Options to display data labels.
Set random colors to fitted points/line.
Fitted chart can be popped.
Html including fitted chart and its data can be created.
Display fitted chart's data in table.
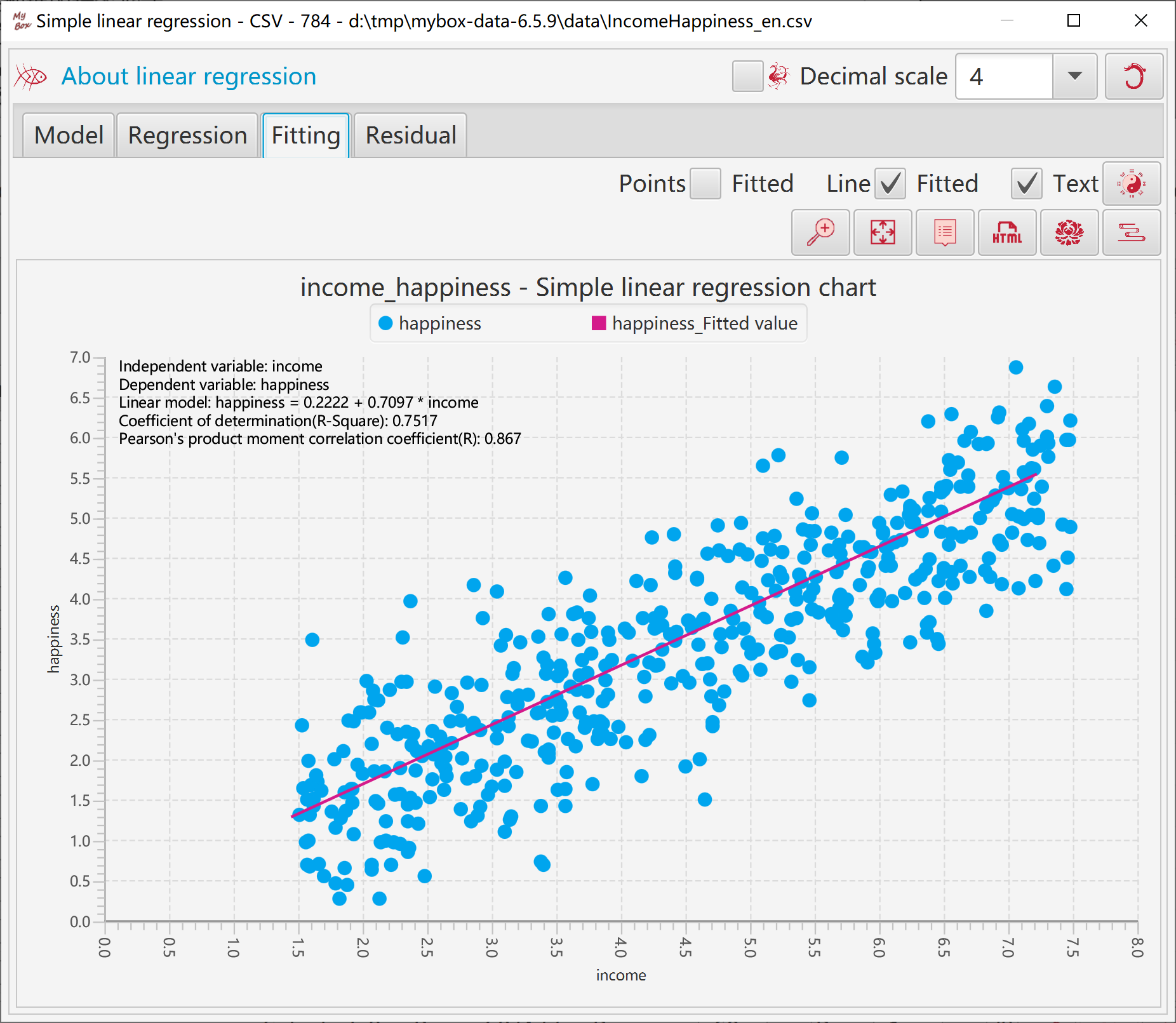
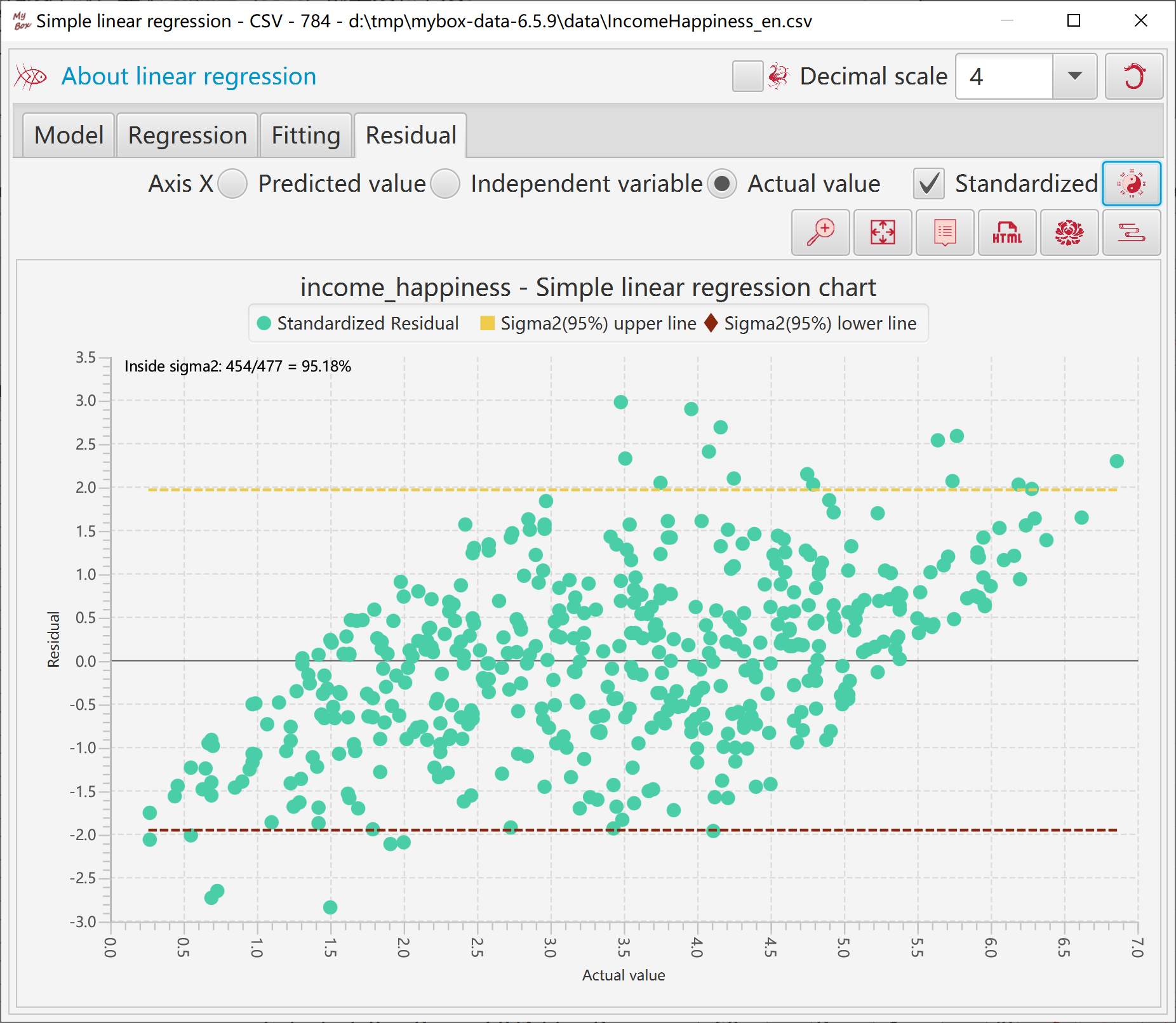
X axis can be set as: predicted value, independent varaible, or actual value.
Option whether standardize residuals.
When standardize residuals, upper line and lower line of Sigma2(95%) will be displayed.
Set random color to points and lines.
Display residual chart's data in table.
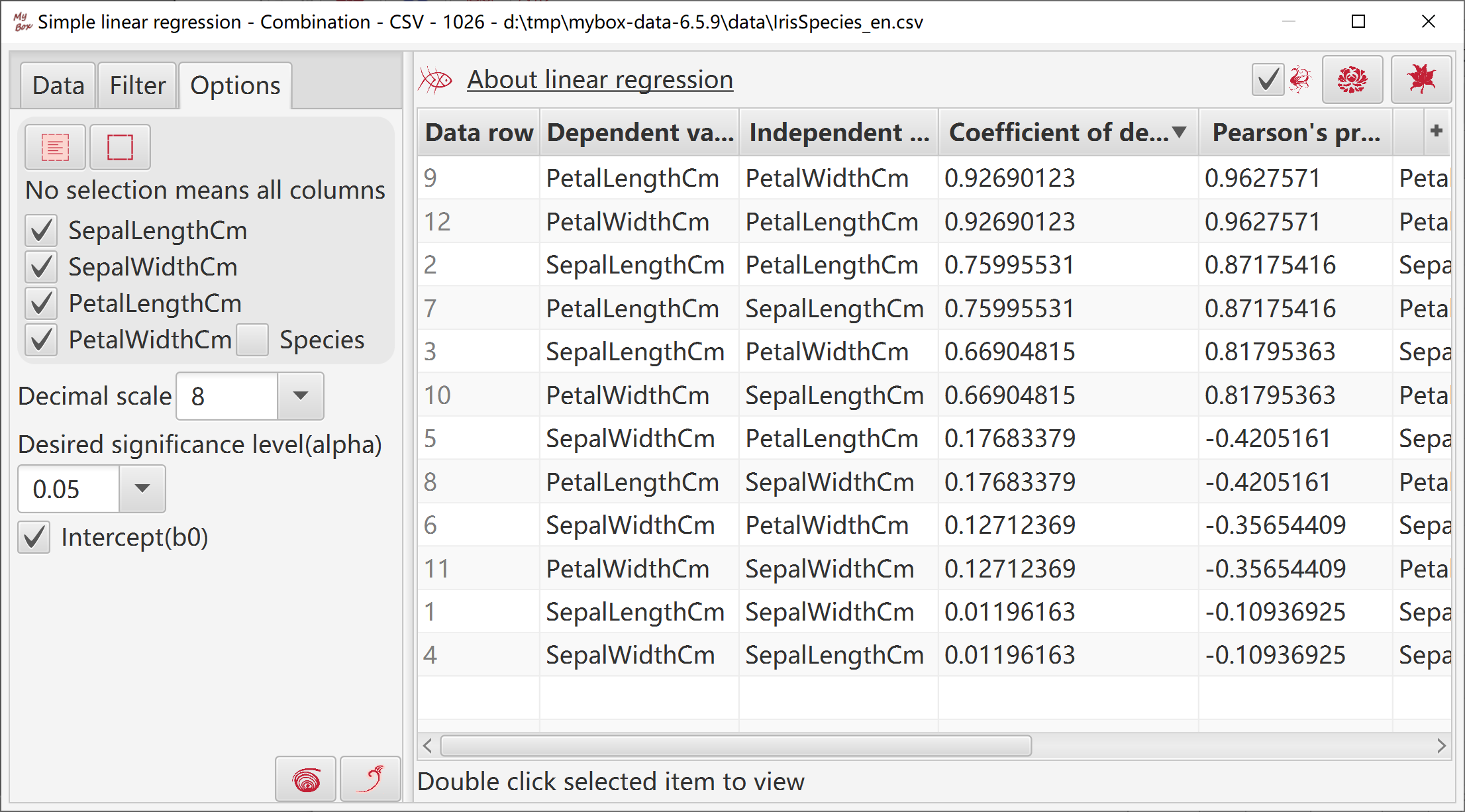
This tool helps to generate data of simple linear regression:
Select some columns.
Select options like decimal scale, alpha, whether include intercept.
When click button "OK":
Tool make pairs of columns and calculate their regression models.
Sort the modes by their coefficient of determination(R-Squre) in descending order.
Select one mode and click button "View" to view its regression data, fitting chart, and residual chart.
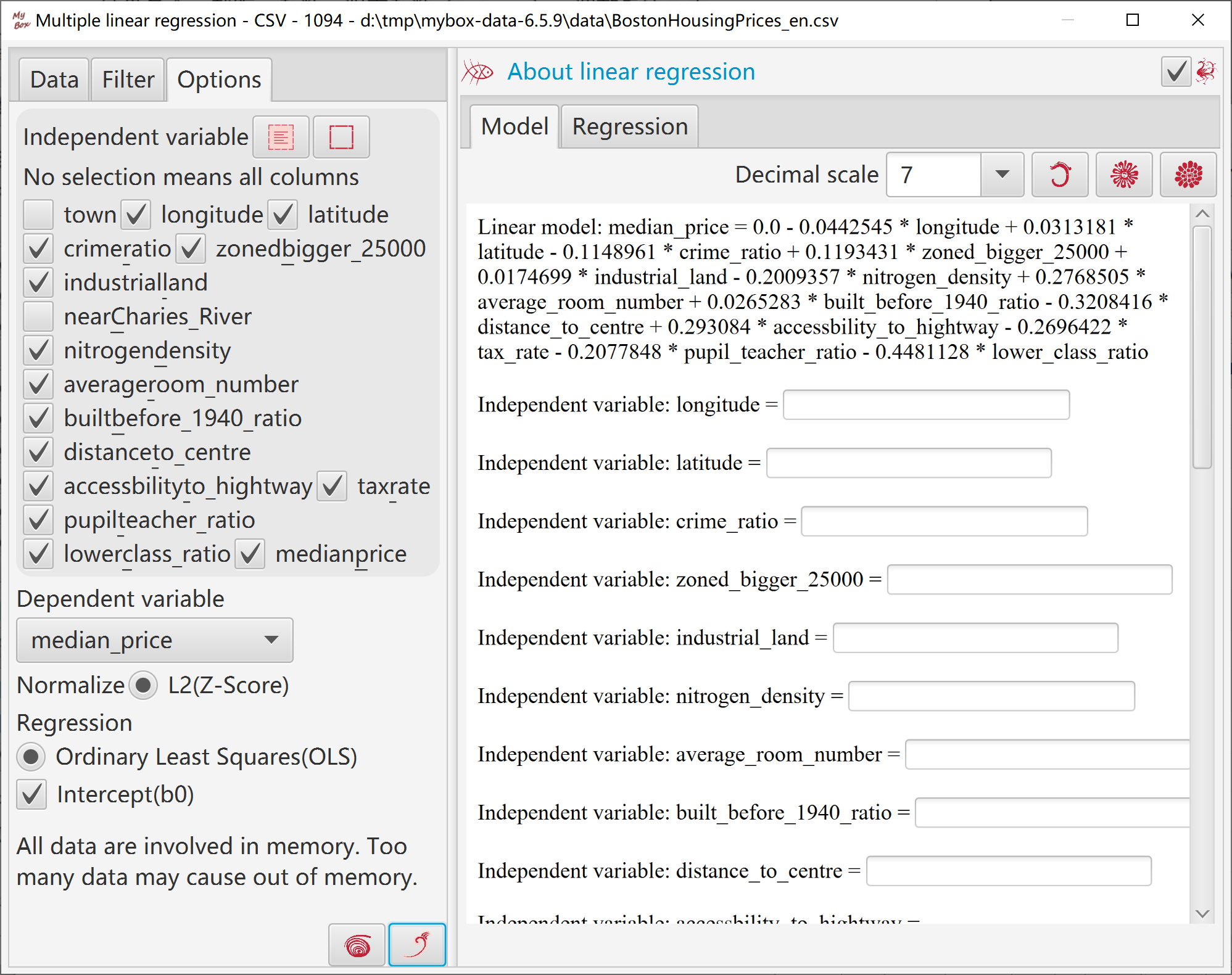
This tool helps to generate data of multiple linear regression based on Apache Commons Math:
Select some column as independent variables, whose data should be numbers.
Select a column as dependent variable, whose data should be numbers.
Select whether include intercept.
Click button "OK":
Tool normalizes involved data by Z-Score.
Tool calculates multiple linear regression by Ordinary Least Squares(OLS).
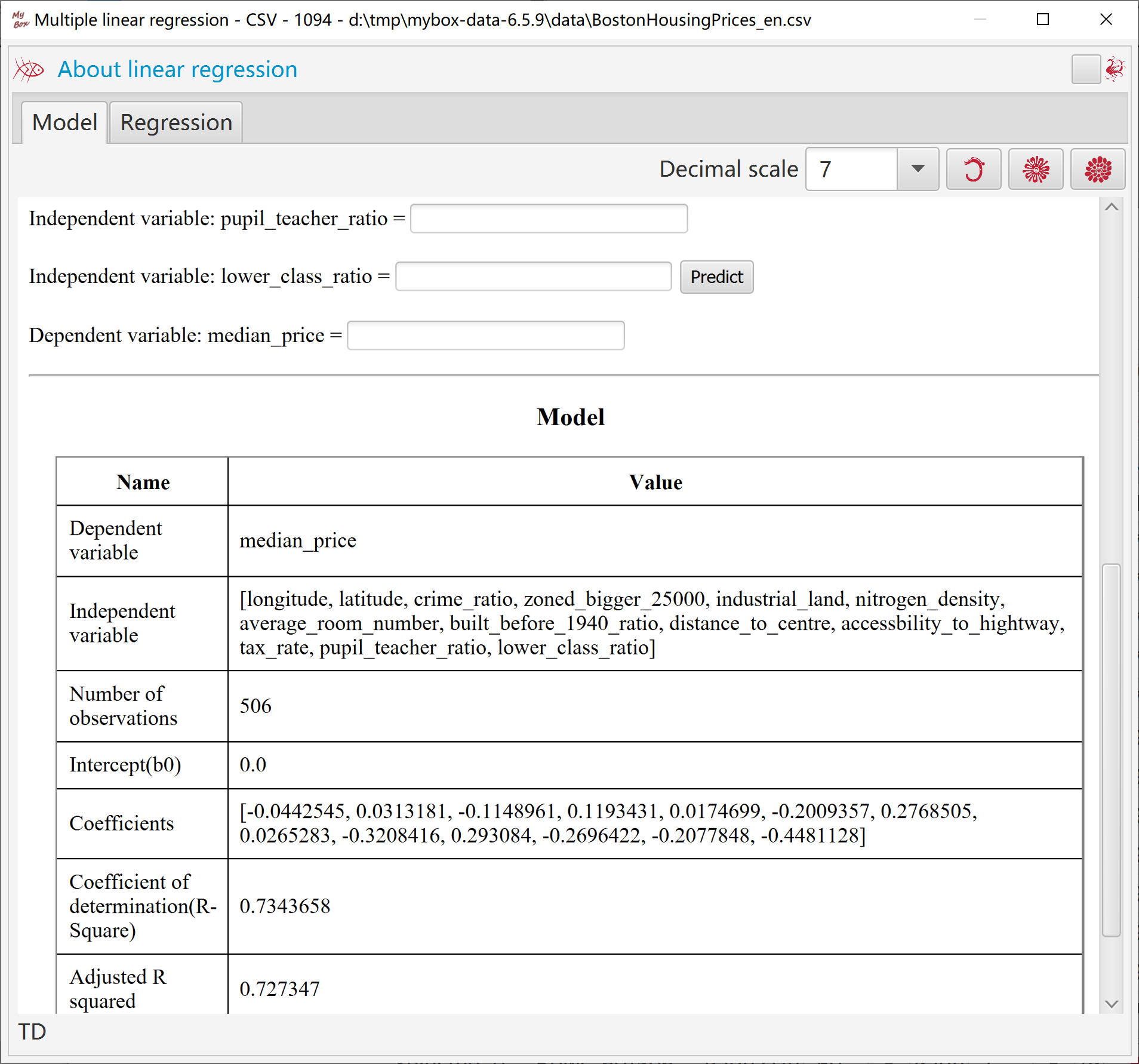
Results include intercept, coefficients, R-Squre, adjusted R-Squre.
User can input values of independent variables and predict value of dependent variable.
Select data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Select columns. If no column is selected, then all columns are taken.
Set row filter.
Calcuate:
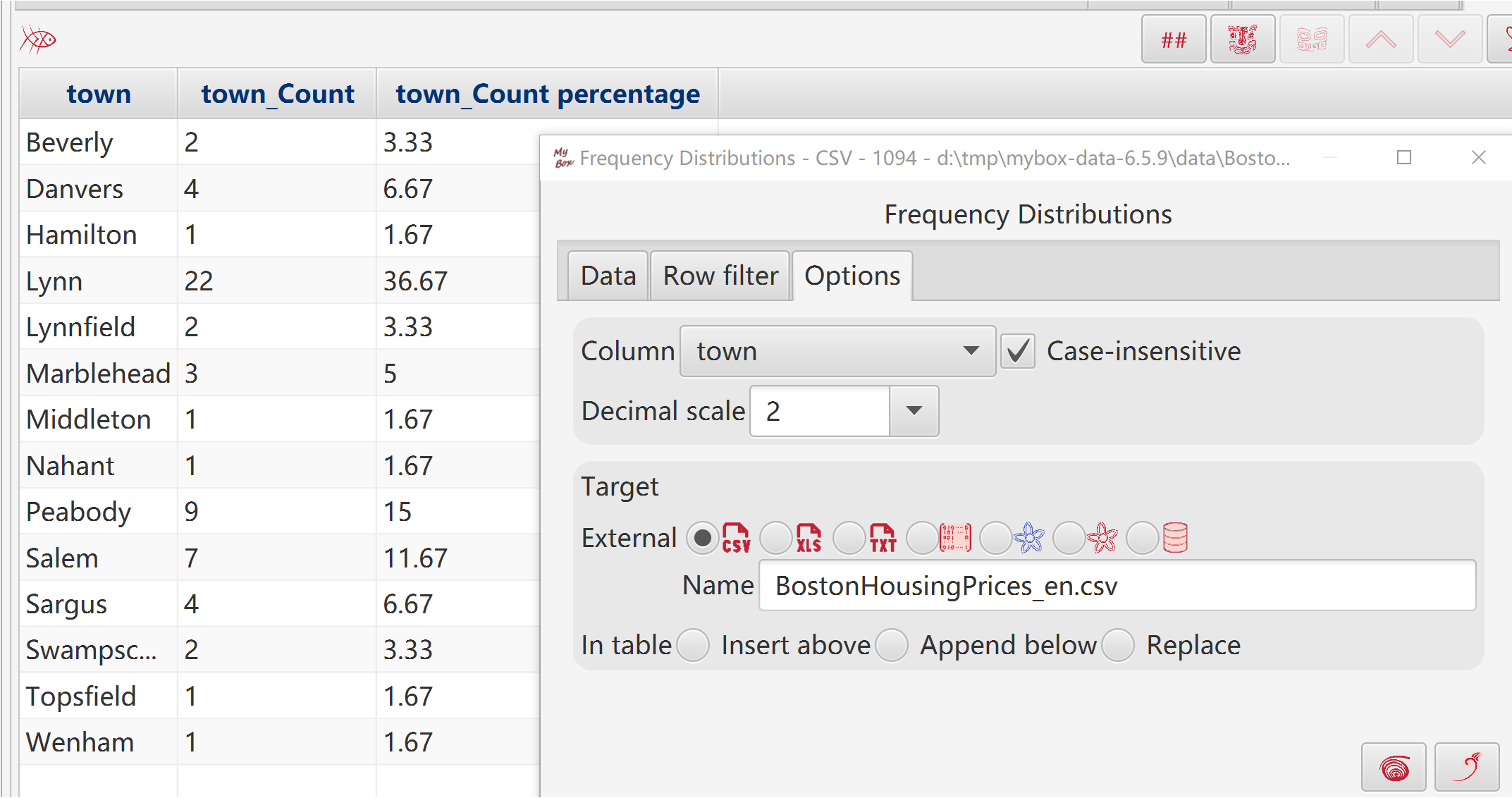
Select one column to count frequency.
Option whether case-insensitive
Set decimal scale.
Target can be following: new csv/excel/text file, matrix, system clipboard, MyBox clipboard, database table.
Select data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Select columns. If no column is selected, then all columns are taken.
Set row filter.
Calcuate:
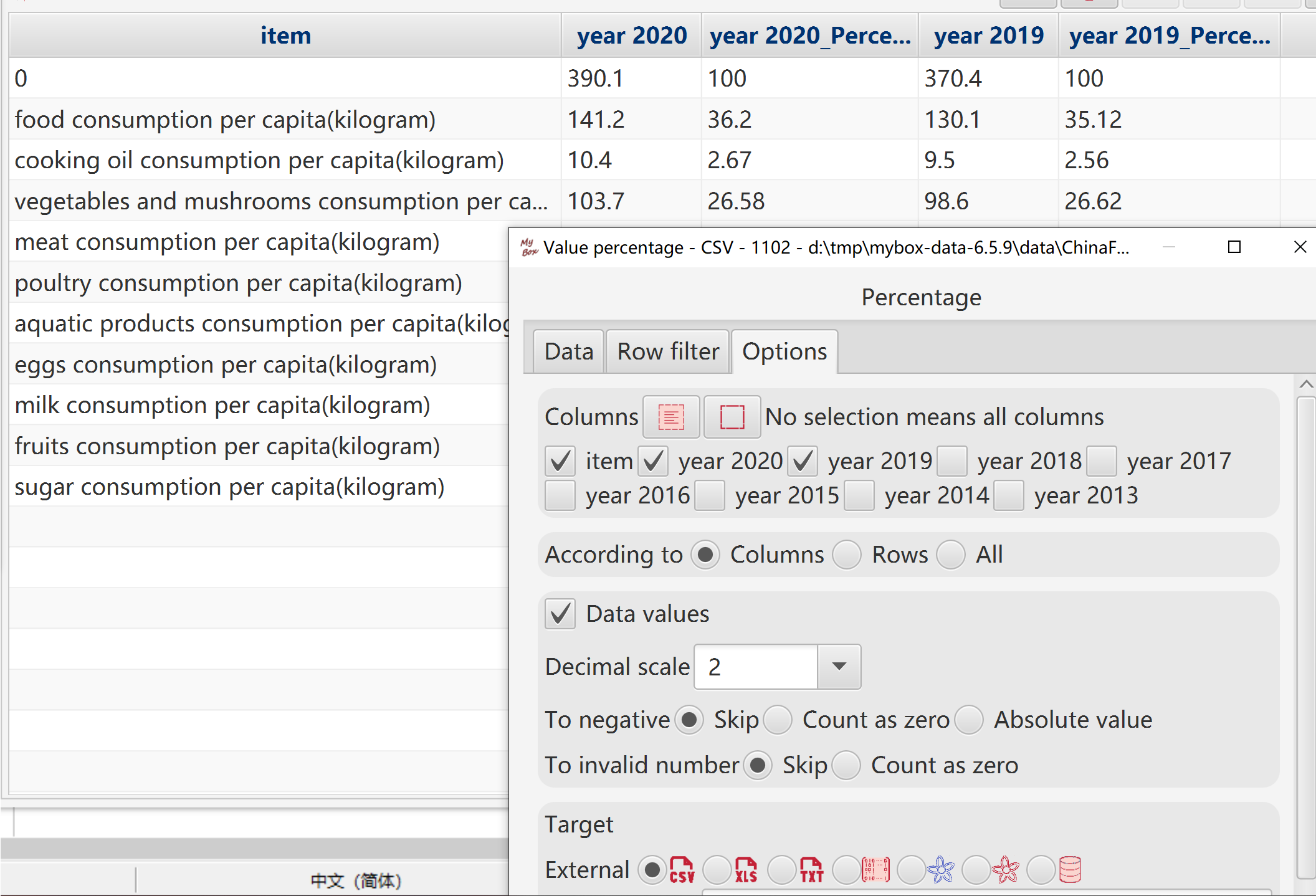
Accroding to: Columns/rows/all.
Select how to treat negative values: zero or absoluate value.
Set decimal scale.
To non-numeric, skip or count as zero.
Target can be following: new csv/excel/text file, matrix, system clipboard, MyBox clipboard, database table.
When rows are current page or selected ones, target can be defined location in table to insert/append/replace.
Select data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Select columns. If no column is selected, then all columns are taken.
Set row filter.
Calcuate:
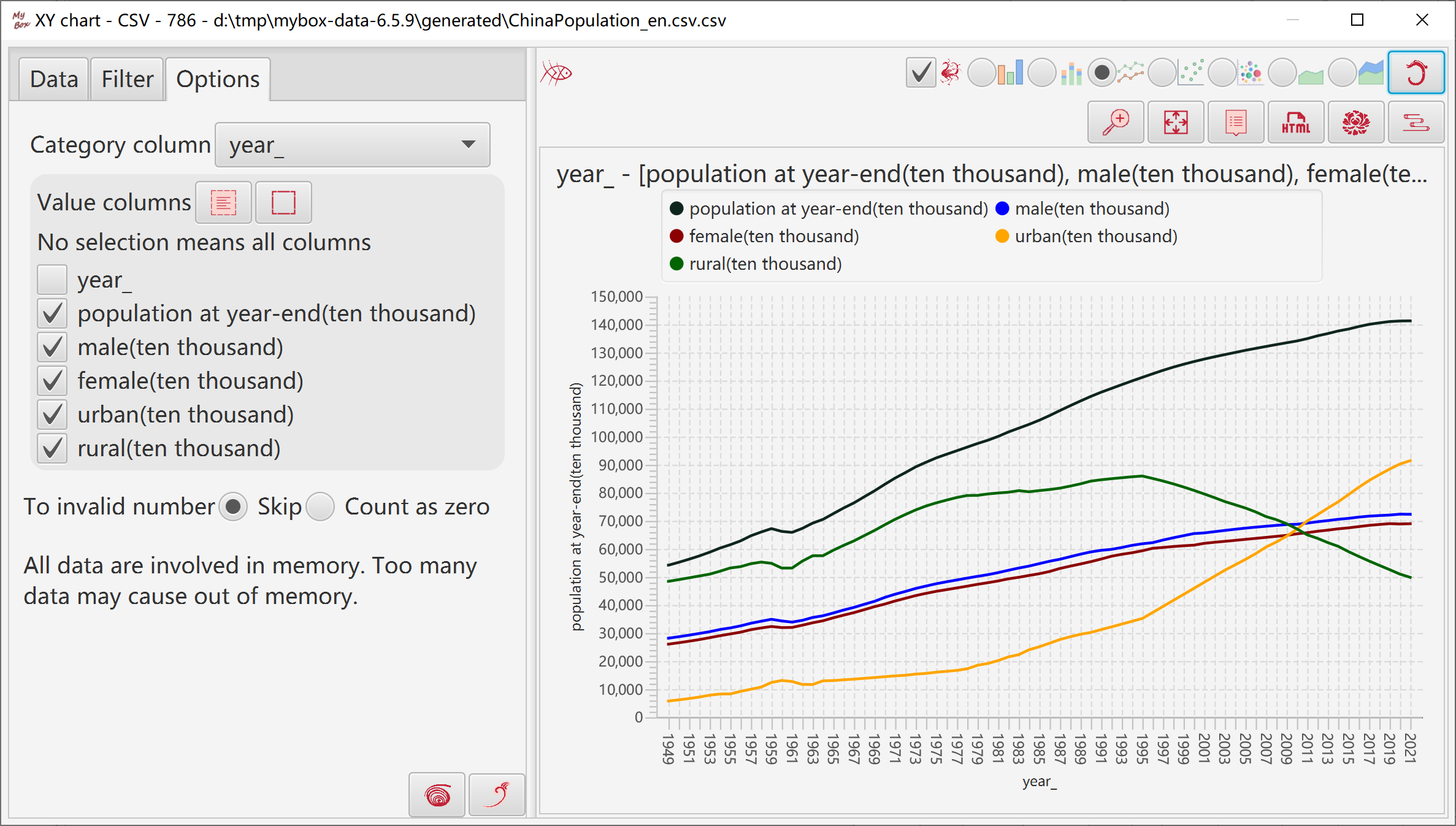
Select one column as "Category Axis", to define data names..
Multiple columns can be selected as data in direction of "Number Axis". Different value series are shown in different colors or shapes.
To non-numeric, skip or count as zero.
When display all data rows(all pages), need concern memory limitation.
By default, "Category Axis" is the horizontal axis and "Number Axis" is the vertical axis.
Select type of XY Chart.
Click button “Menu” to set parameters of chart.
Click button “Pop” to display current chart as image in popped window.
Click button “Data” to display data of the chart in data table.
Click button “Html” to display data of the chart in html page.
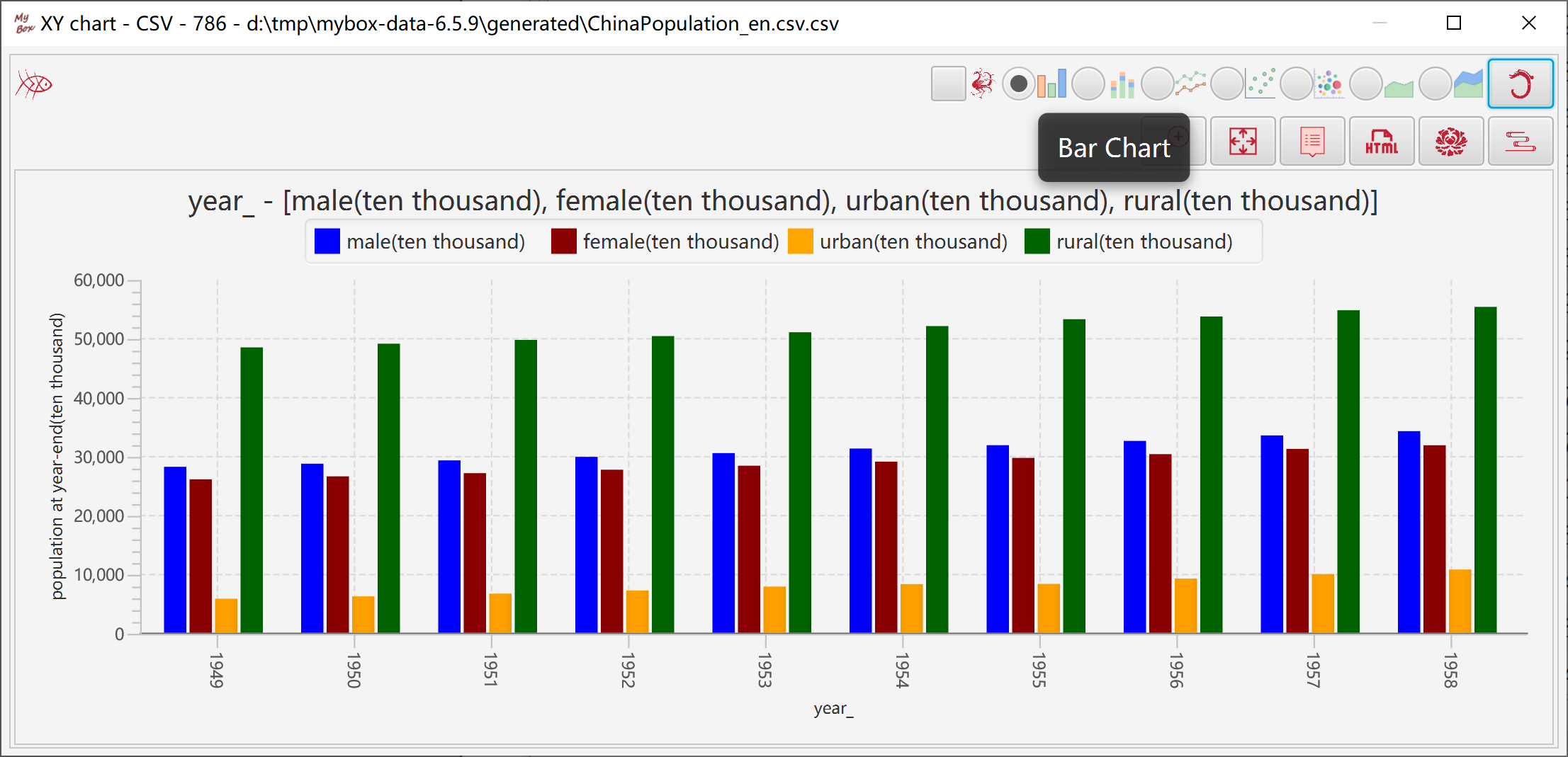
Represents data size with bars' heights.
"Category" column is always counted as strings.
Represents data size with bars' heights.
"Category" column is always counted as strings.
Represents data trend with lines connecting points.
"Category" column can be counted as strings or numbers.
Represents data distribution with symbols.
"Category" column can be counted as strings or numbers.
Represents data size with circles of different radius:
"Category Column" and "Value Column" define coordinates of data.
Select several columns as "Size Columns" to defines data size.
All columns should be numbers. Size columns should be non-negative.
Represents data size with area size.
"Category" column is always counted as strings.
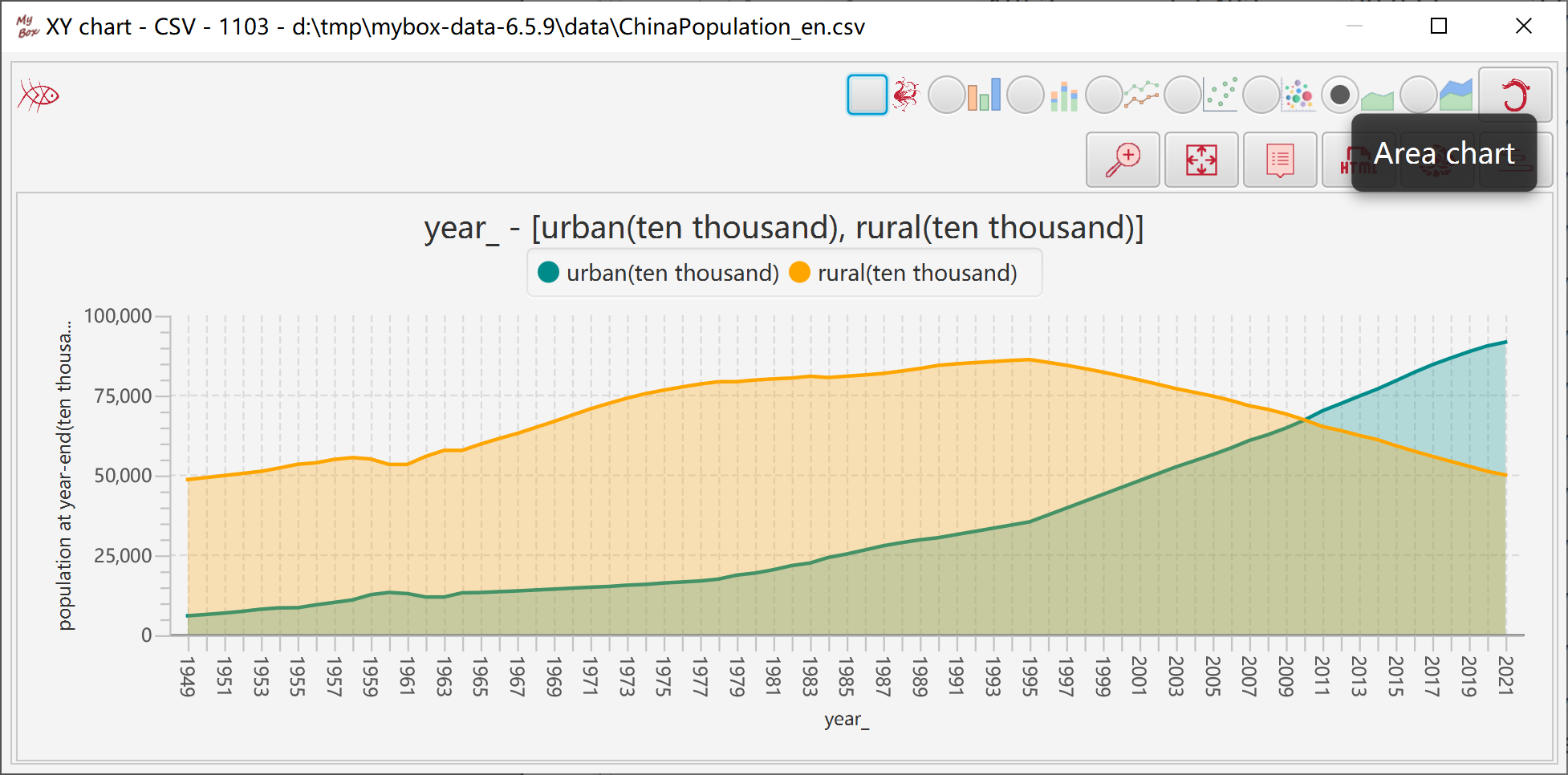
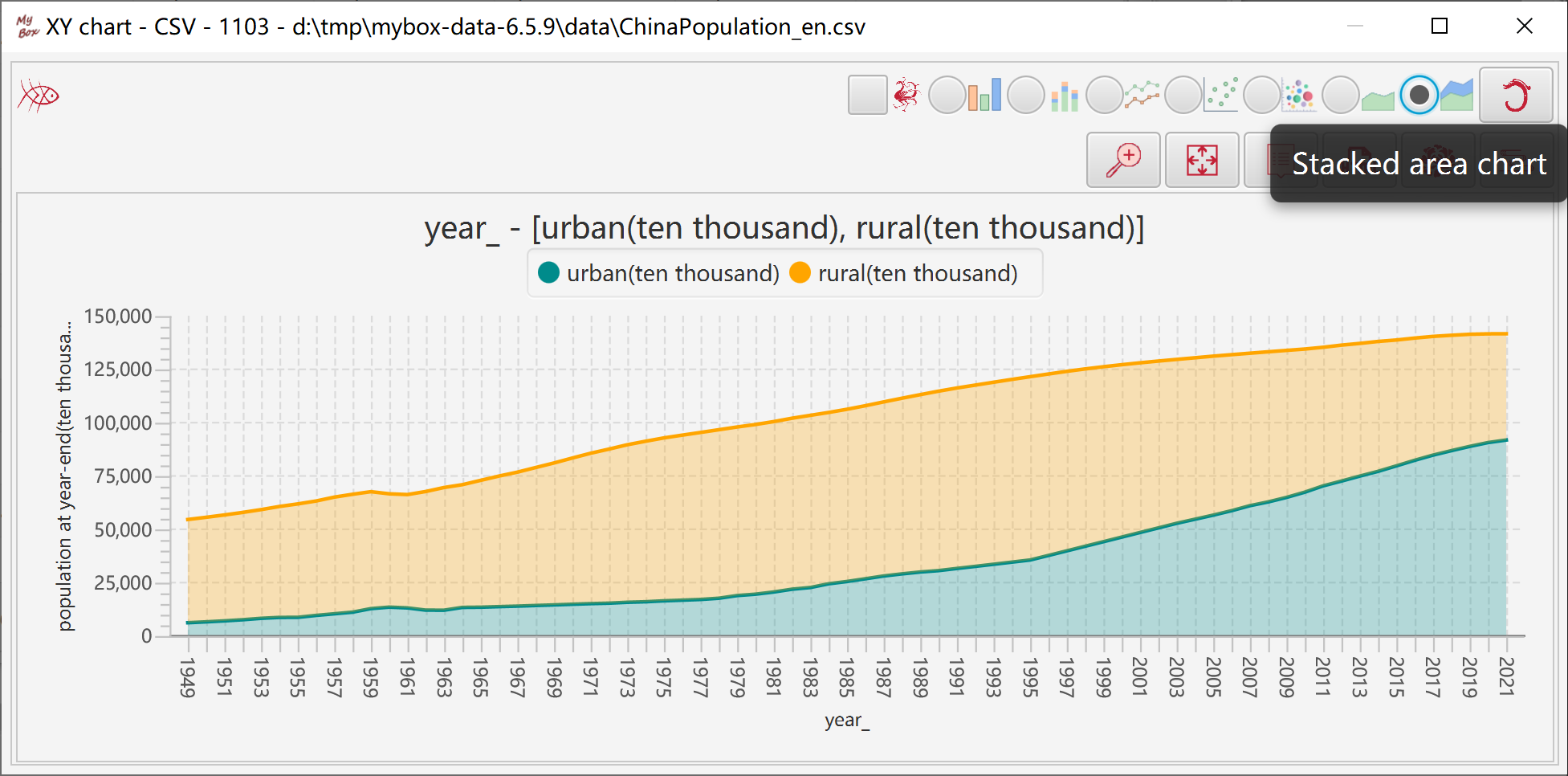
Represents data size with area size.
"Category" column is always counted as strings.
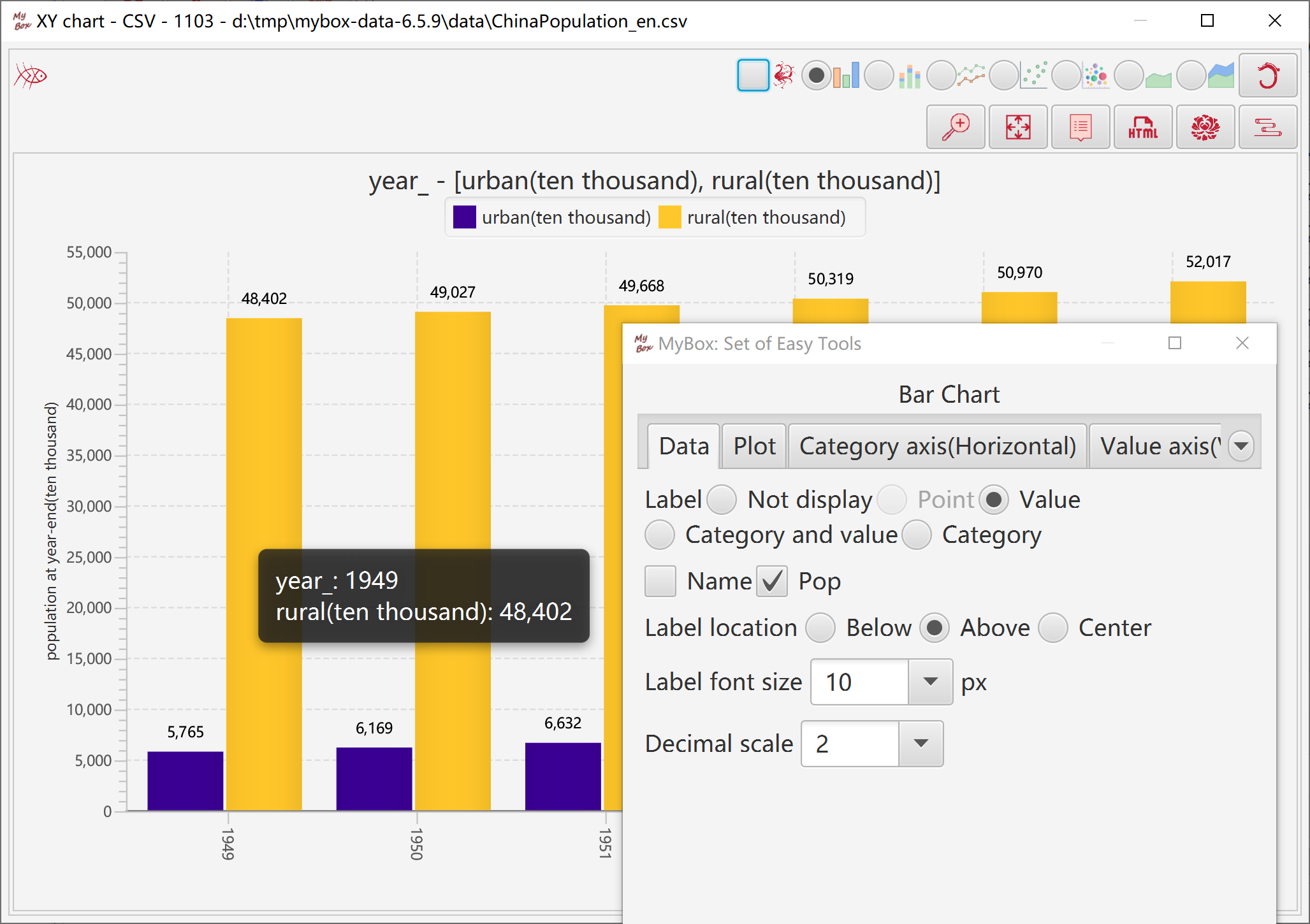
Options about label: not display, point, value, category, etc.
Location of labels.
Font size of labels.
Decimal scale.
Set parameters of plot: title, font size, location of legend, zero-lines, grid lines, line width, etc.
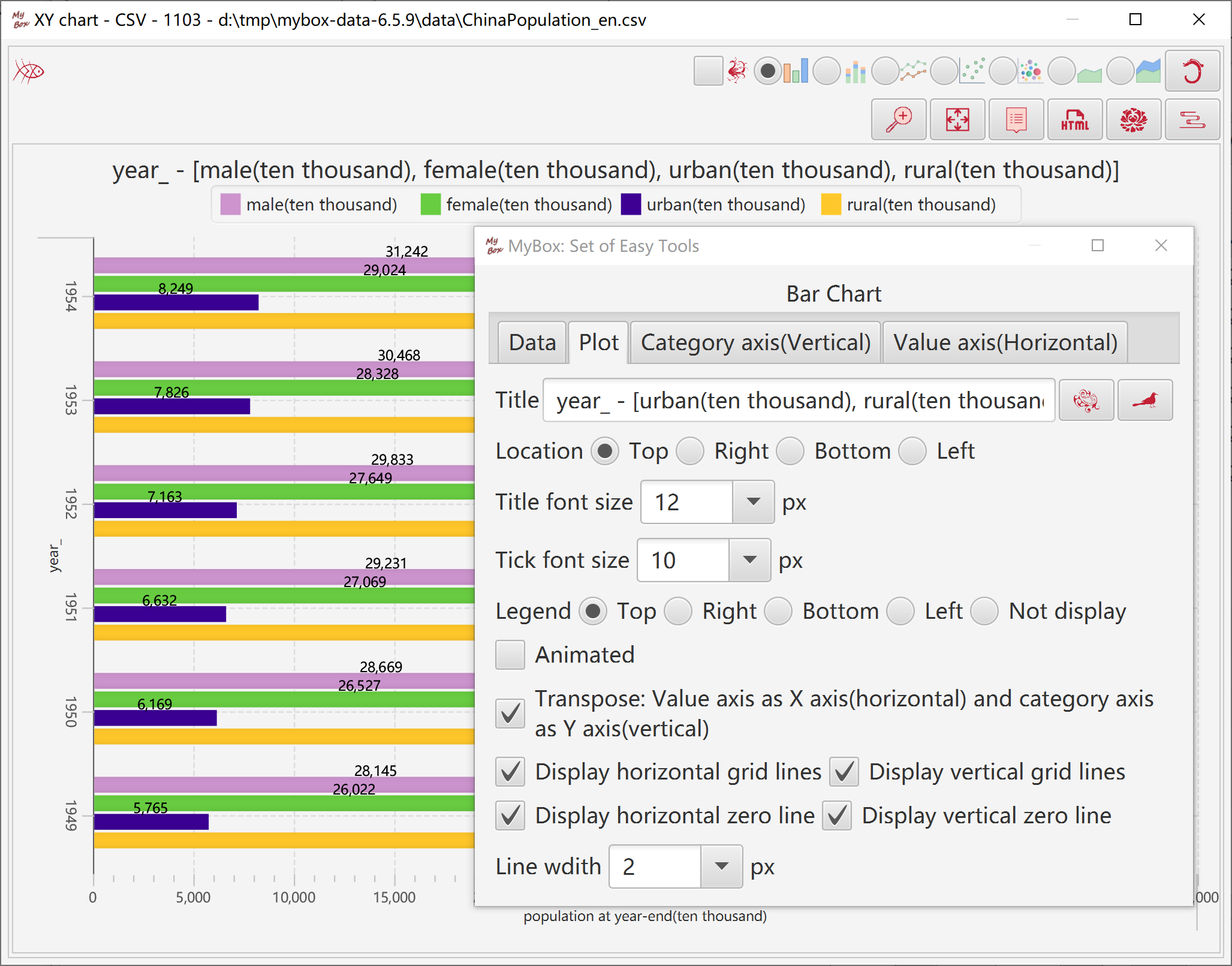
Set parameters of category axis: label, font size, location, tick, count values as string or number, coordinate, etc.
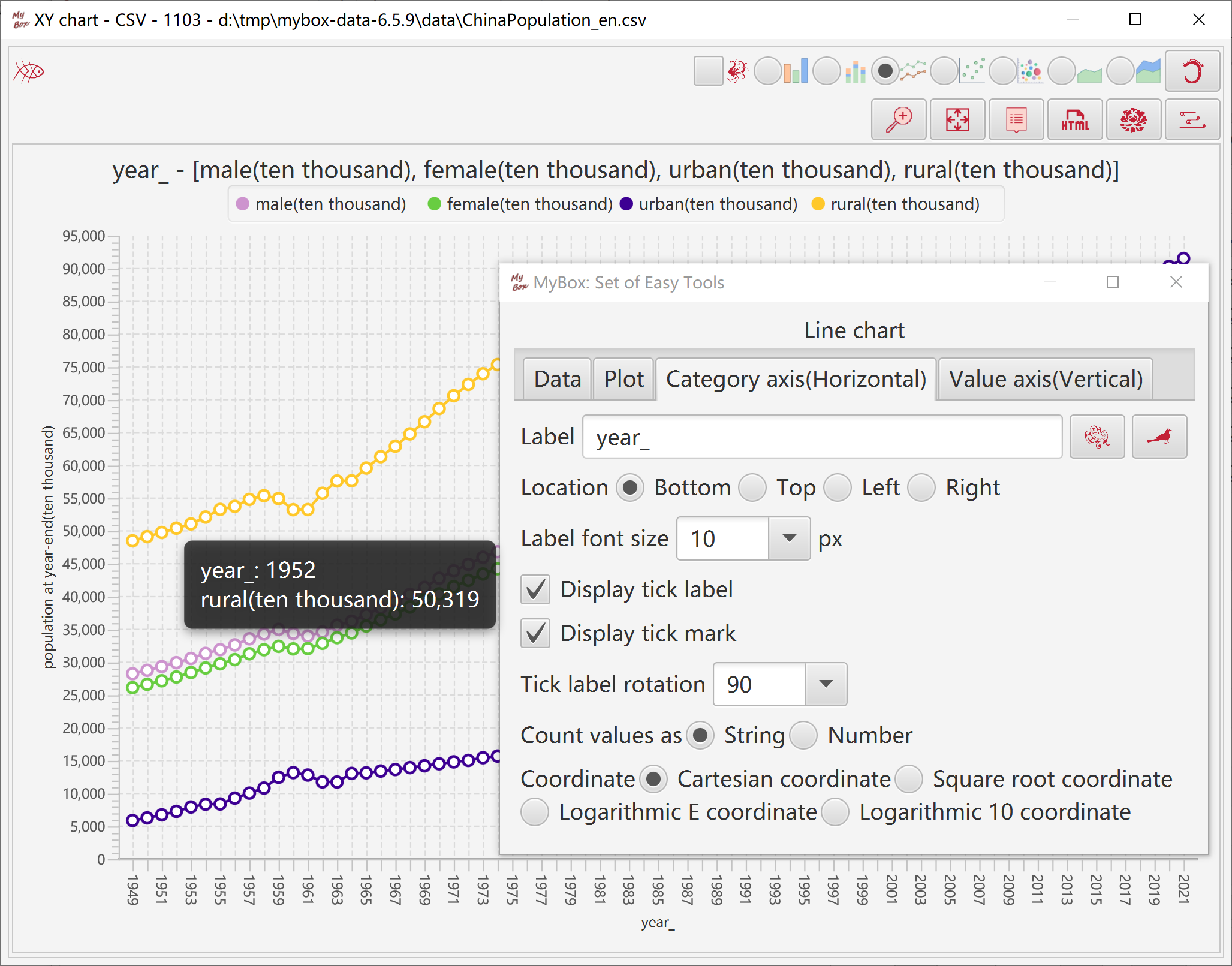
Set parameters of number axis: label, font, location, tick, coordinate, etc.
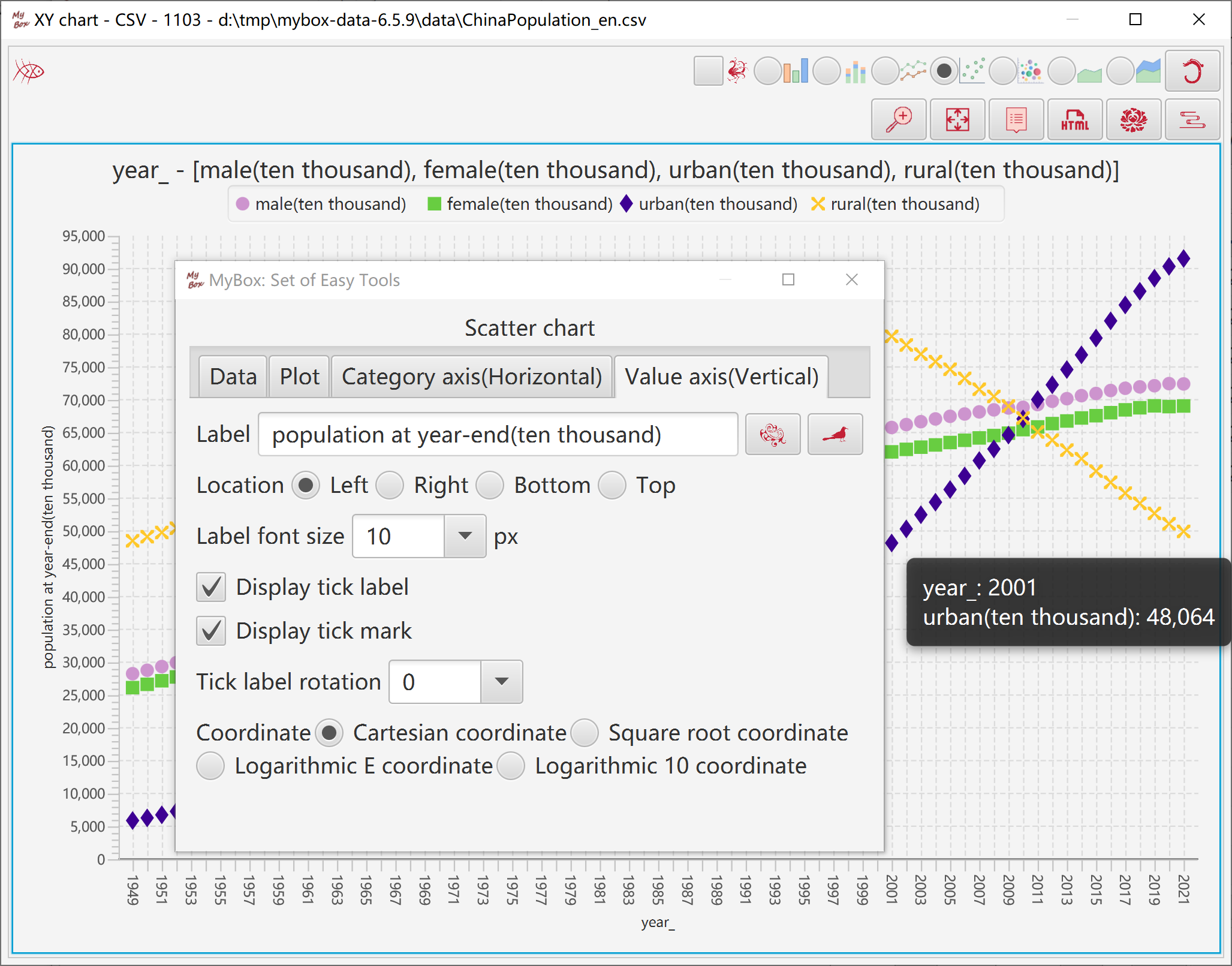
Select data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Select columns. If no column is selected, then all columns are taken.
Set row filter.
Calcuate:
Select one column as "Category Axis", to define data names..
Select another column as "Number Axis".
Data numbers are represented as percentages with a circle divided into segments.
Value column should be non-negative.
When display all data rows(all pages), need concern memory limitation.
Click button “Menu” to set parameters of chart.
Click button “Pop” to display current chart as image in popped window.
Click button “Data” to display data of the chart in data table.
Click button “Html” to display data of the chart in html page.
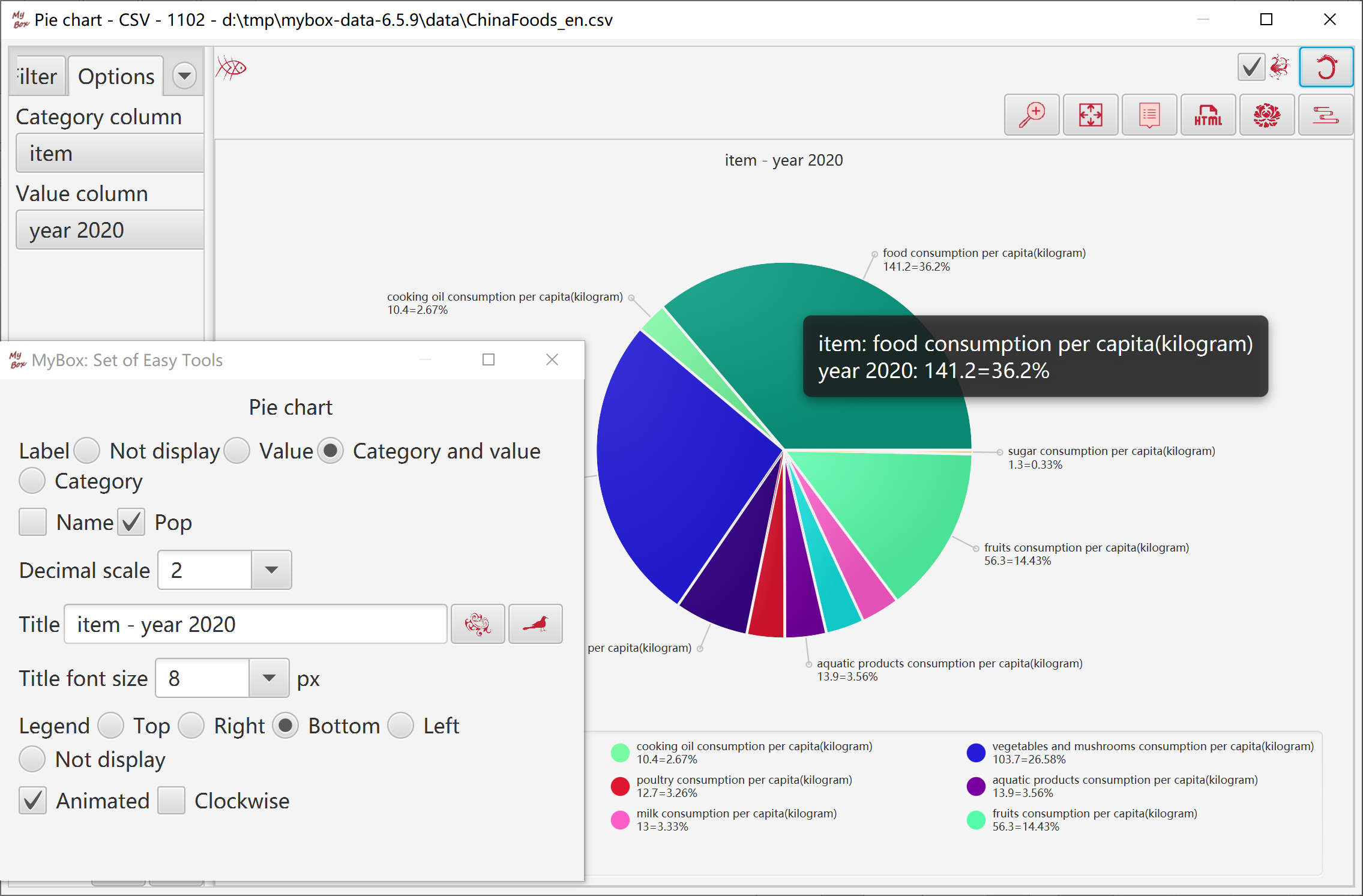
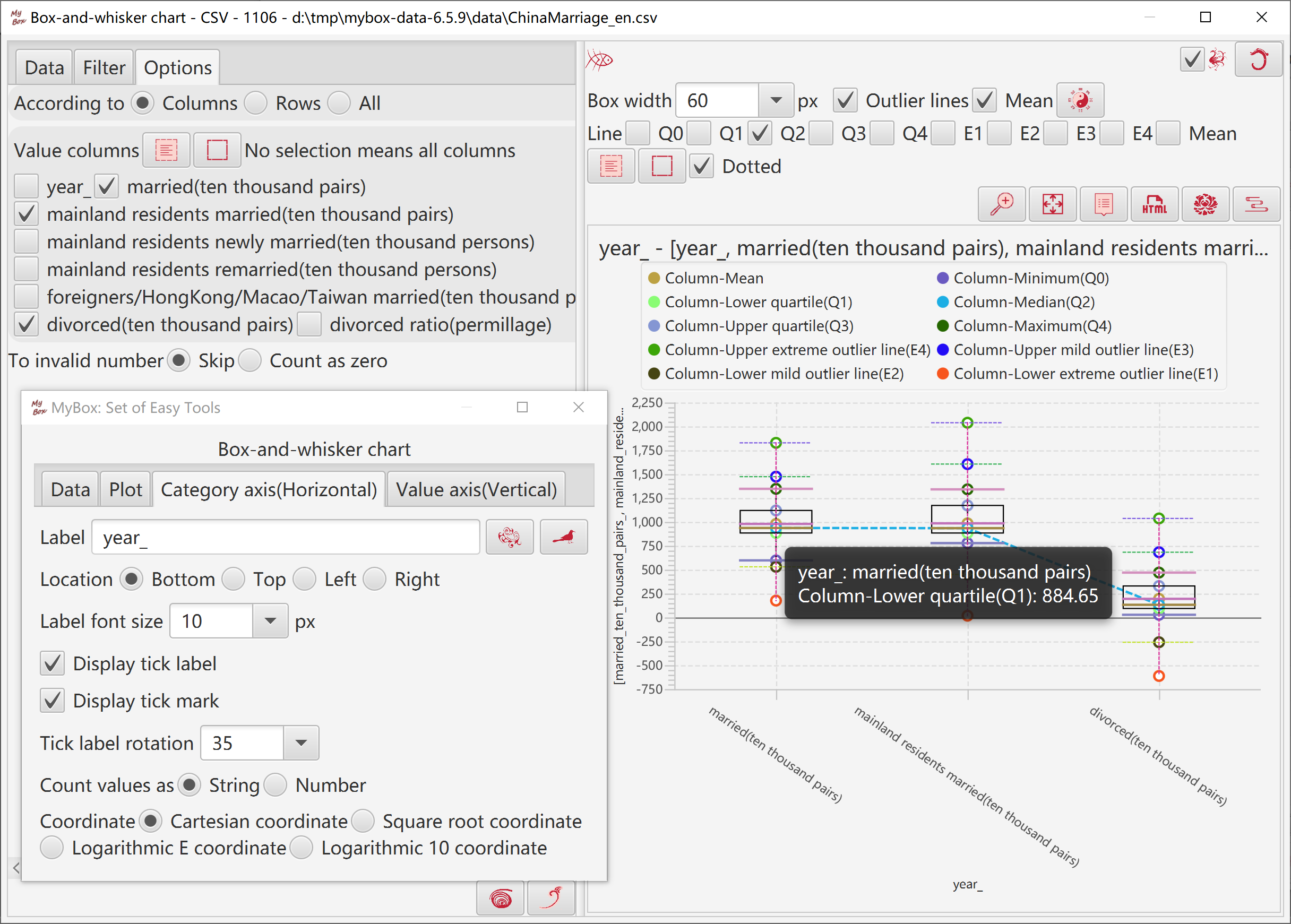
Box-and-whisker chart represents data distribution:
Sort data according to column/row/all in ascending order.
Following items can show aggregation and discreteness of data:
Minimum Q0 = in 0%(start) of the data list
Lower quartile Q1 = in 25% of the data list
Median Q2 = in 50%(middle) of the data list
Upper quartile Q3 = in 75% of the data list
Maximum Q4 = in 100%(end) of the data list
Following values can be used to mark ourliers of data:
Lower extreme outlier line E1 = Q1 - 3 * ( Q3 - Q1 )
Lower mild outlier line E2 = Q1 - 1.5 * ( Q3 - Q1 )
Upper mild outlier line E3 = Q3 + 1.5 * ( Q3 - Q1 )
Upper extreme outlier line E4 = Q3 + 3 * ( Q3 - Q1 )
Following values can be referred for discreteness:
Mean = avarage of the data list
Calcuate:
Based on line chart.
According to: columns, rows(select category column), or all.
Set or select:
Box width.
Whether display outliers lines or mean.
Whether display connection lines of values, and whether dotted lines.
Random colors.
Click button “Menu” to set parameters of chart.
Click button “Pop” to display current chart as image in popped window.
Click button “Data” to display data of the chart in data table.
Click button “Html” to display data of the chart in html page.
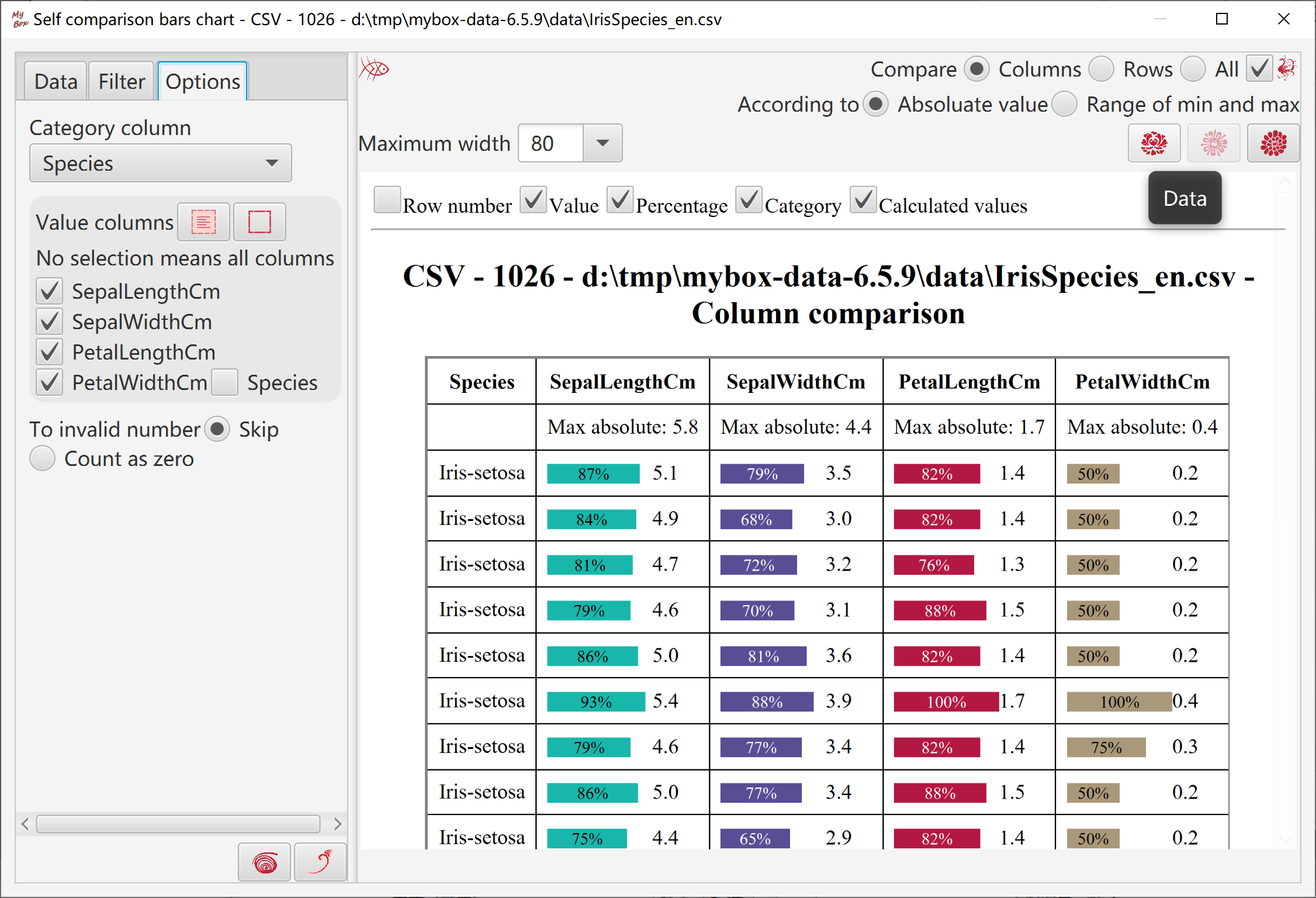
Self comparison bars show difference between data and reference values.
Bars are calculated by following rulers:
If value is zero, no bar
When compare as absoluate values:
maximum_value = maximum_absolute_value_of_column/row/all
precentage = absolute_value / maximum_value
width = maximum_width * precentage
color = If value is larger than zero, color_of_column.
If value is less than zero, inverted_color_of_column
When compare as range of minimum and maximum:
maximum_value = maximum_value_of_column/row/all
minimum_value = minimum_value_of_column/row/all
precentage = (value - minimum_value) / (maximum_value - minimum_value)
width = maximum_width * precentage
color = color_of_column
Data: Select rows in table or select all data rows(all pages), and select columns.
Calcuate:
Select one column as category column(unnecessary)
Compare: columns/rows/all.
According to: absoluate values, or range of minimum and maximum.
When display all data rows(all pages), need concern memory limitation.
Set or select:
Maximum width
Whether display row numbers, values, percentages, categories, calculated values.
Edit data in chart.
Edit html of chart.
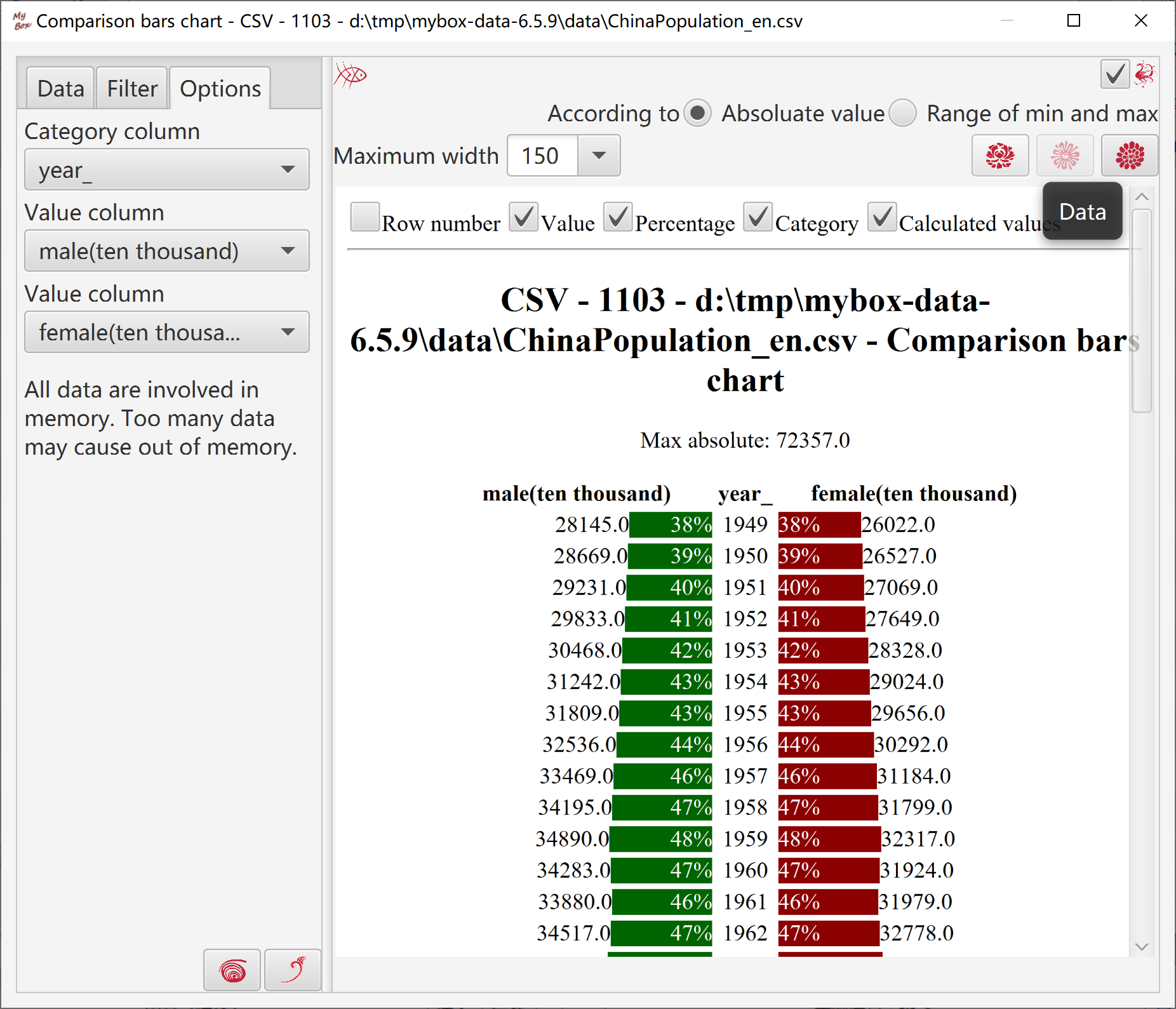
Comparison bars show difference between two series of data.
Bars are calculated by following rulers:
If value is zero, no bar
When compare as absoluate values:
maximum_value = maximum_absolute_value_of_value_columns
precentage = absolute_value / maximum_value
width = maximum_width * precentage
color = If value is larger than zero, color_of_column.
If value is less than zero, inverted_color_of_column
When compare as range of minimum and maximum:
maximum_value = maximum_value_of_value_columns
minimum_value = minimum_value_of_value_columns
precentage = (value - minimum_value) / (maximum_value - minimum_value)
width = maximum_width * precentage
color = color_of_column
Data: Select rows in table or select all data rows(all pages), and select columns.
Calcuate:
Select one column as category column(unnecessary)
Select tow value columns
According to: absoluate values, or range of minimum and maximum.
When display all data rows(all pages), need concern memory limitation.
Set or select:
Maximum width
Whether display row numbers, values, percentages, categories, calculated values.
Edit data in chart.
Edit html of chart.
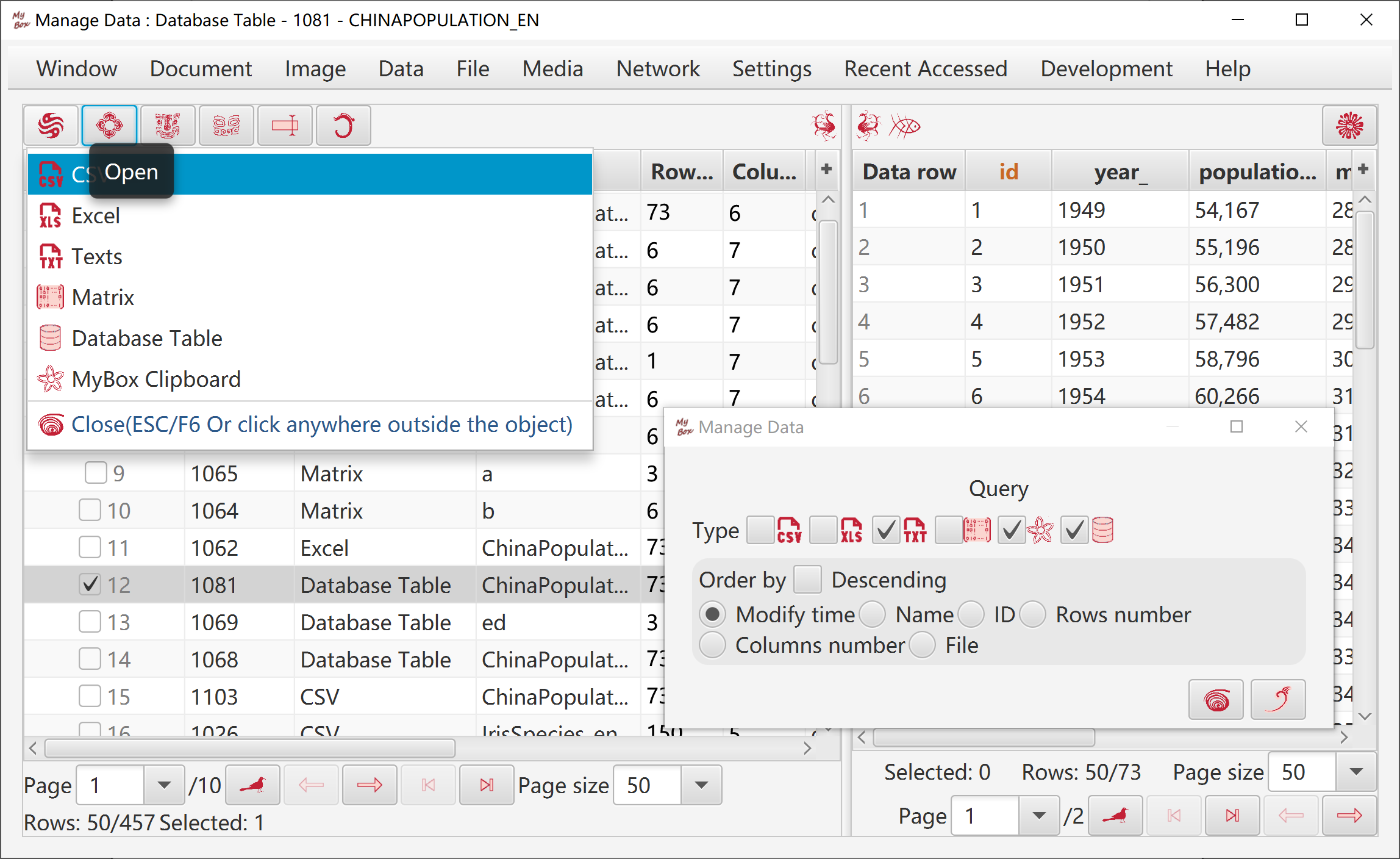
This tool manages following objects:
Data Files
Record is created/updated when csv/excel/texts data file is opened by its editor.
Data are saved in data file.
Deleting record of data file will not delete data file itself.
Data Clipboards
Record is created when data is copied into MyBox Clipboad.
Data are saved in file under MyBox internal path.
Deleting record of data clipboards will delete its internal file.
Matrices
Records are maintained by Matrices Manager.
Data are saved in MyBox database.
Deleting record of matrix will delete data of this matrix.
Data Tables
Records are maintained by Data Tables Manager.
Data are saved in MyBox database tables.
Deleting record of data table will delete data of this data table.
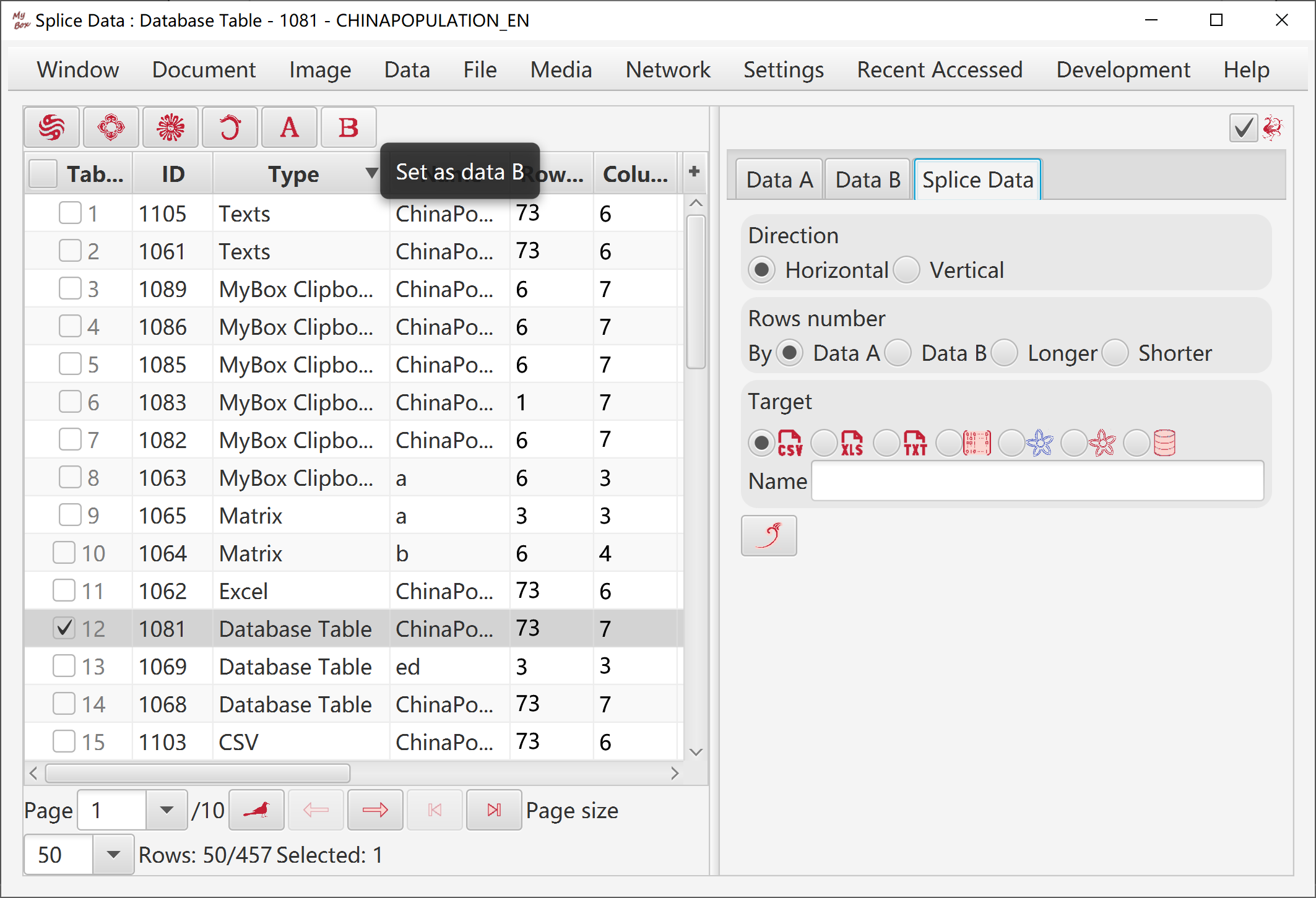
Select or open two data.
Select rows and columns from the two data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Select columns. If no column is selected, then all columns are taken.
Set row filter.
Options:
Direction: vertical, horizontal
Rows/Columns number by: Data A, Data B, longer, shorter.
Target can be following: new csv/excel/text file, matrix, system clipboard, MyBox clipboard, database table.
When file is loaded abnormally, change options and click Refresh button.
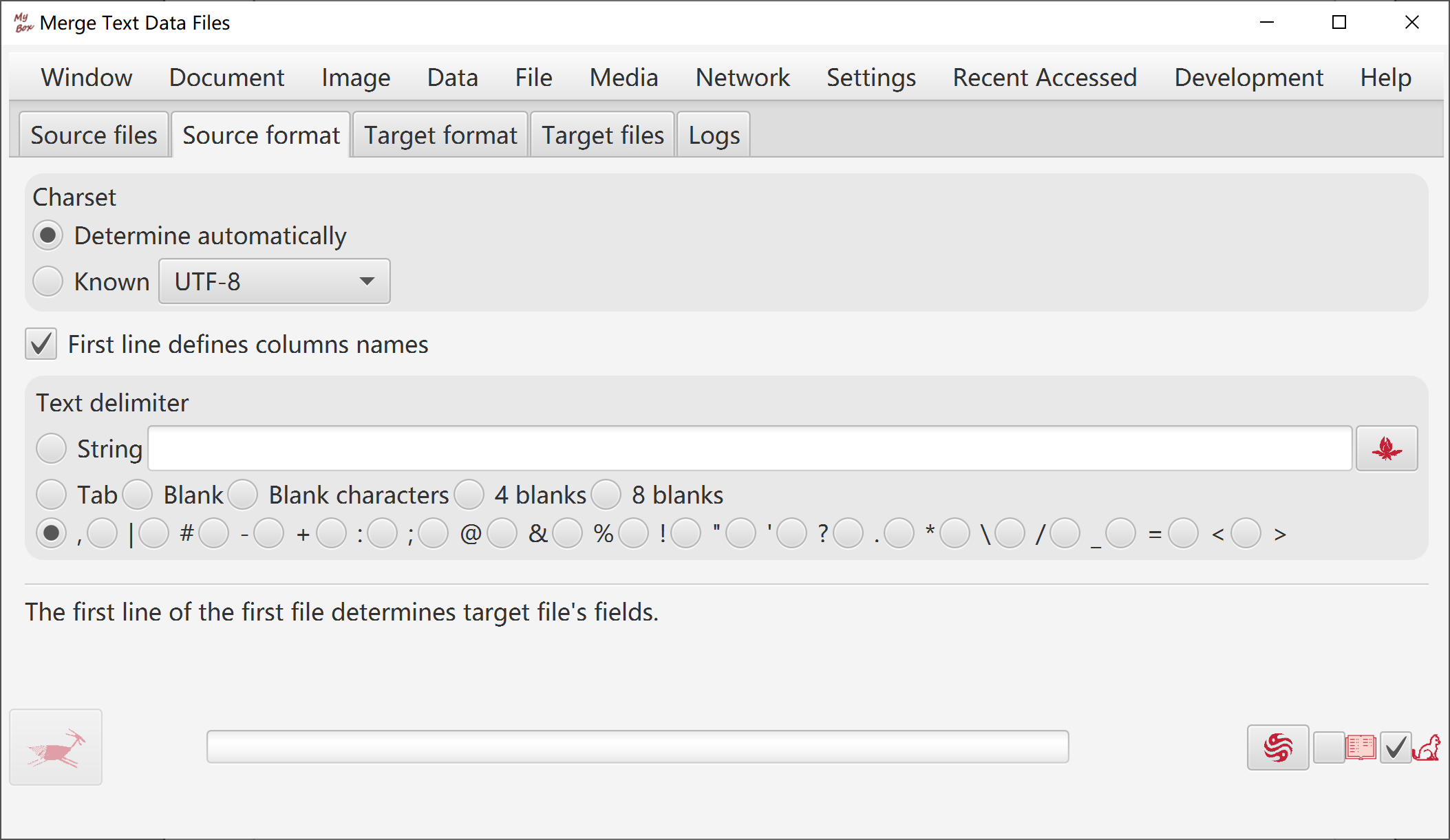
Options: charset, whether has first line as field names, and delimiter of data.
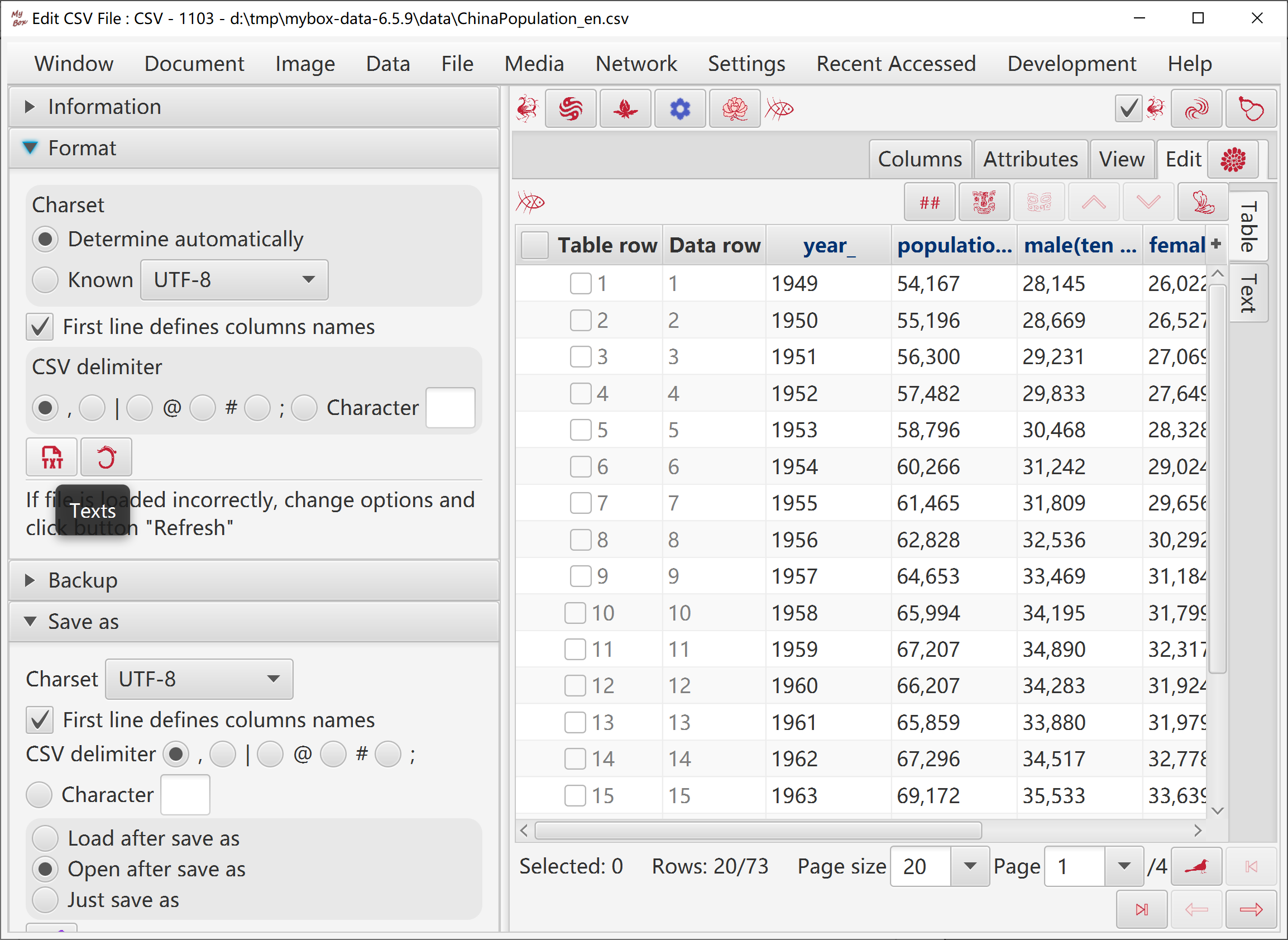
When file is loaded abnormally, change options and click Refresh button.
Options: charset, whether has first line as field names, and delimiter of data.
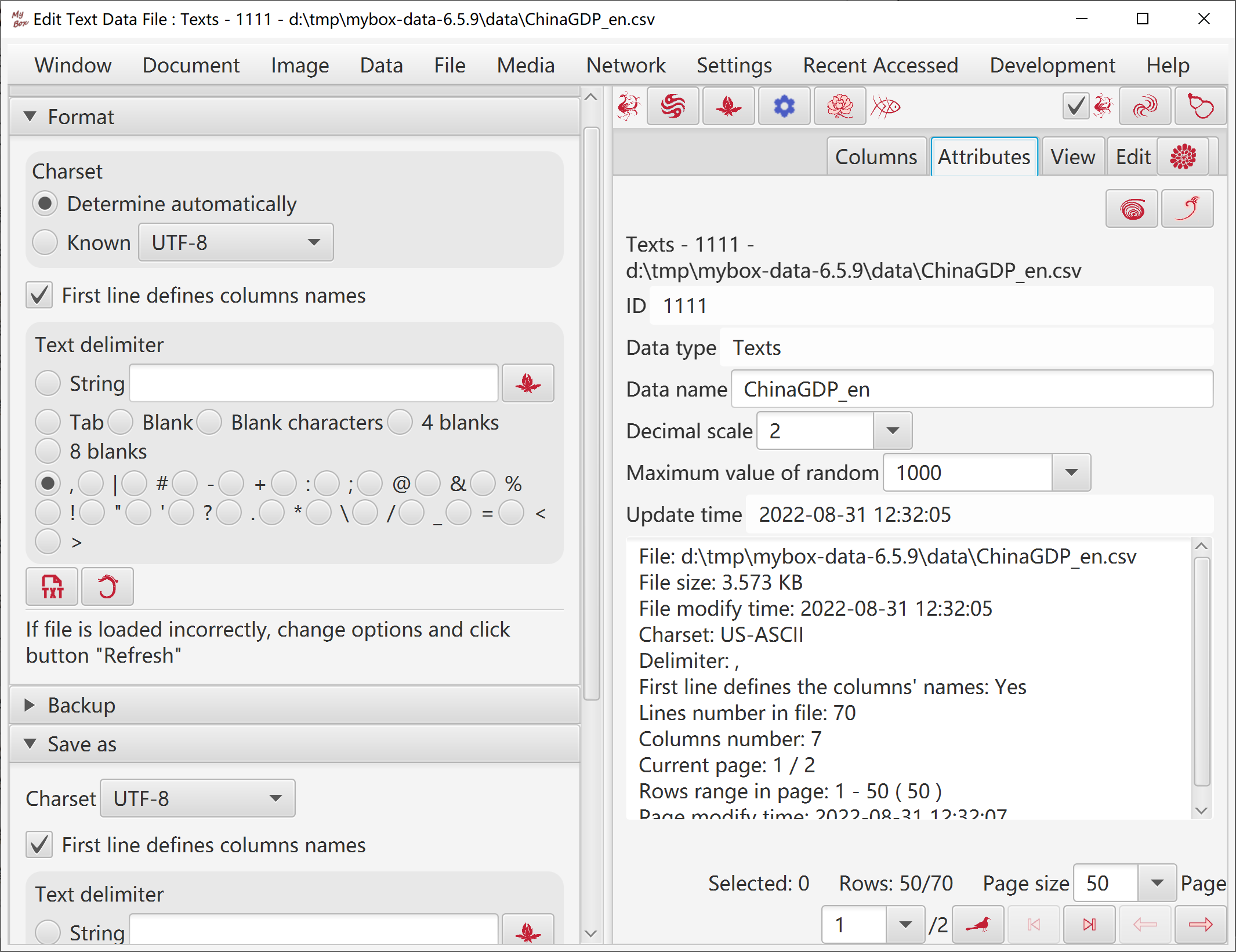
Options include sheet number and whether has first line as field names.
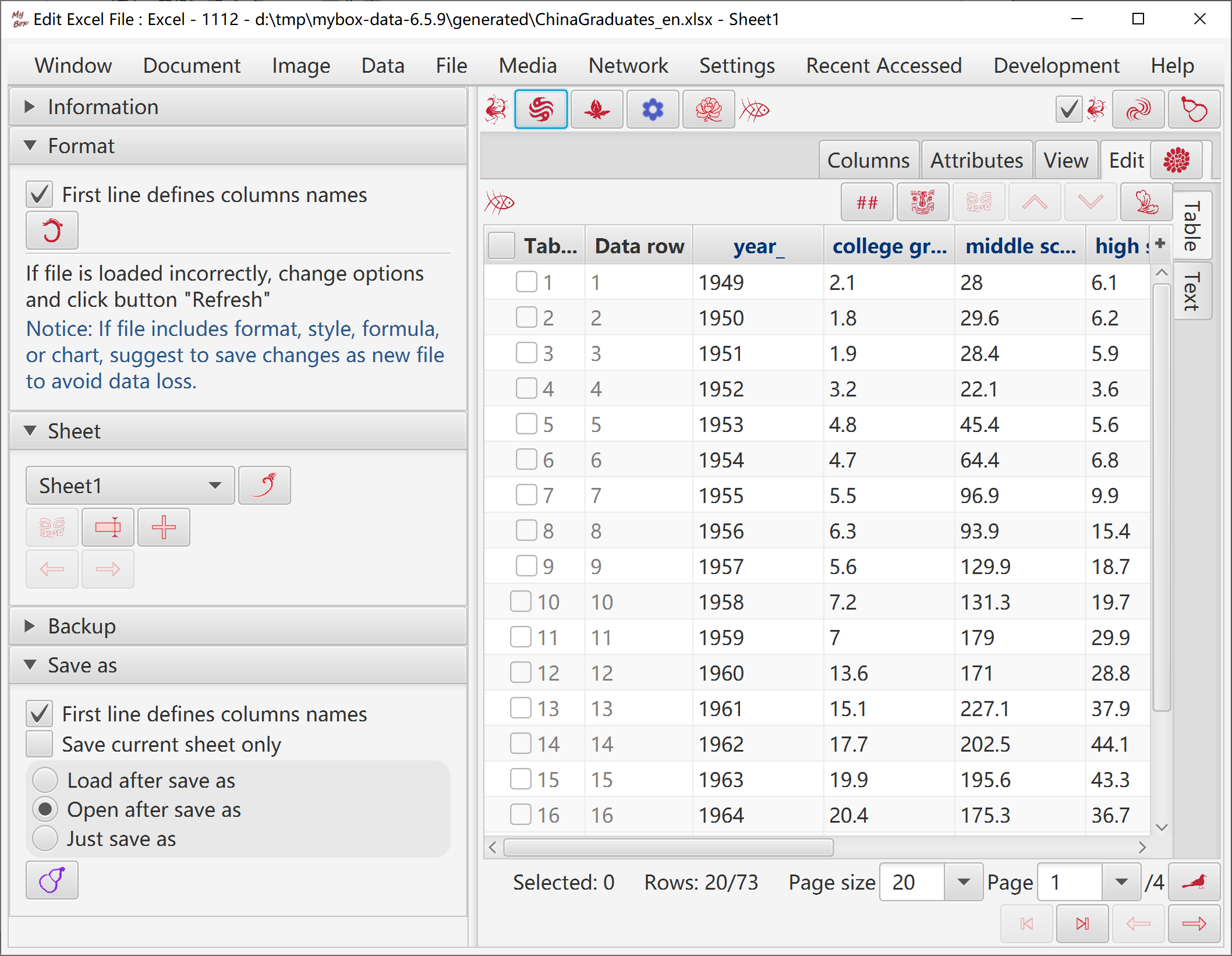
Add/Delete/Rename sheets.
Tool can only handle base data in Excel file. If file includes format, style, formula, or chart, suggest to save changes as new file to avoid data loss.
Source files' formats can be csv, excel, and text. Options of source files can be set.
Target files' formats include csv, text, excel, xml, json, html, pdf. Options of target files can be set.
Split files as maximum lines.
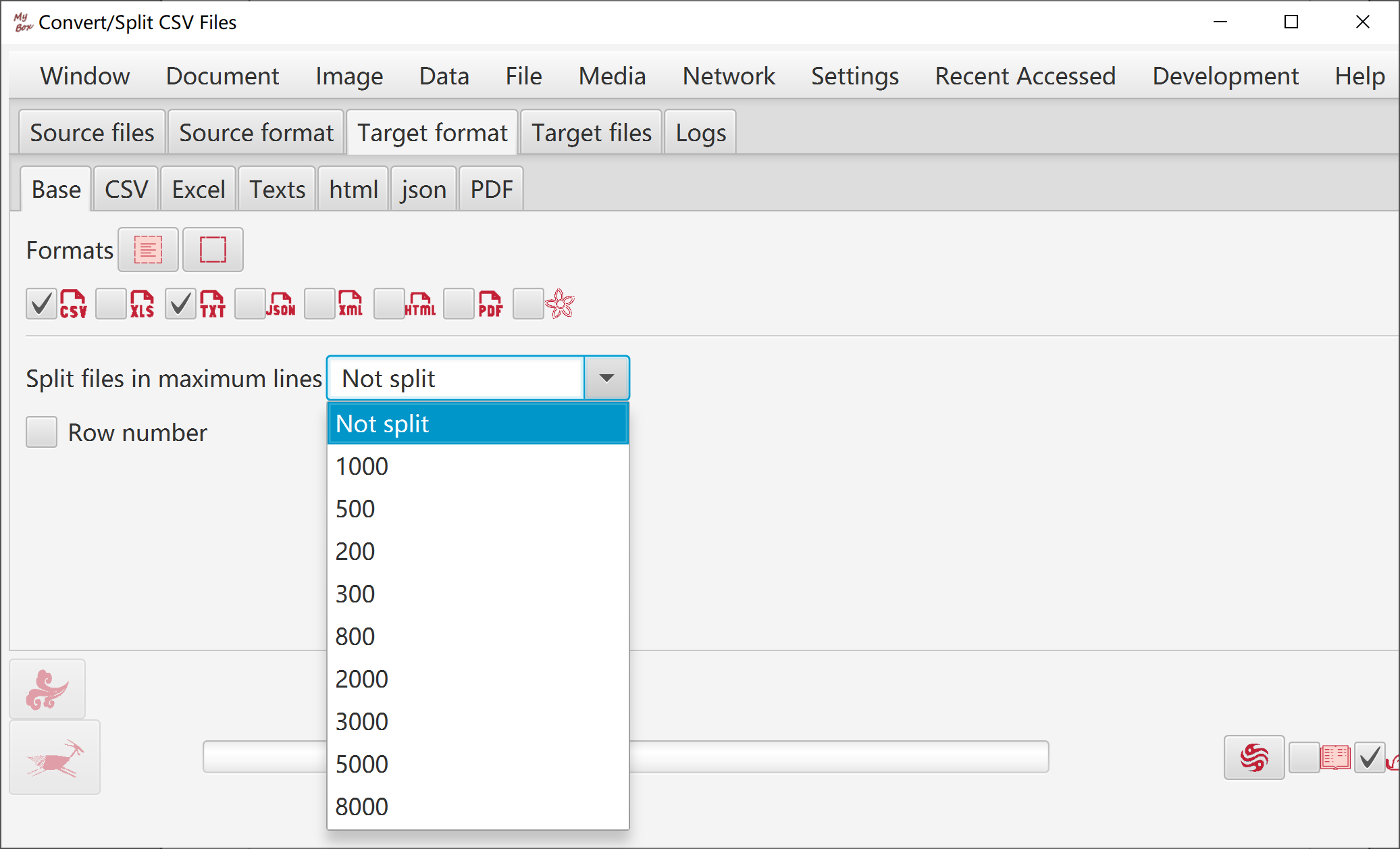
Set source format.
Set target format.
Read and parse contents in system clipboard.
Delimiter can be chosen from special characters or inputted regular expression.
First row can be set as column names.
Edit matrix.
Matrix can be saved and reused.
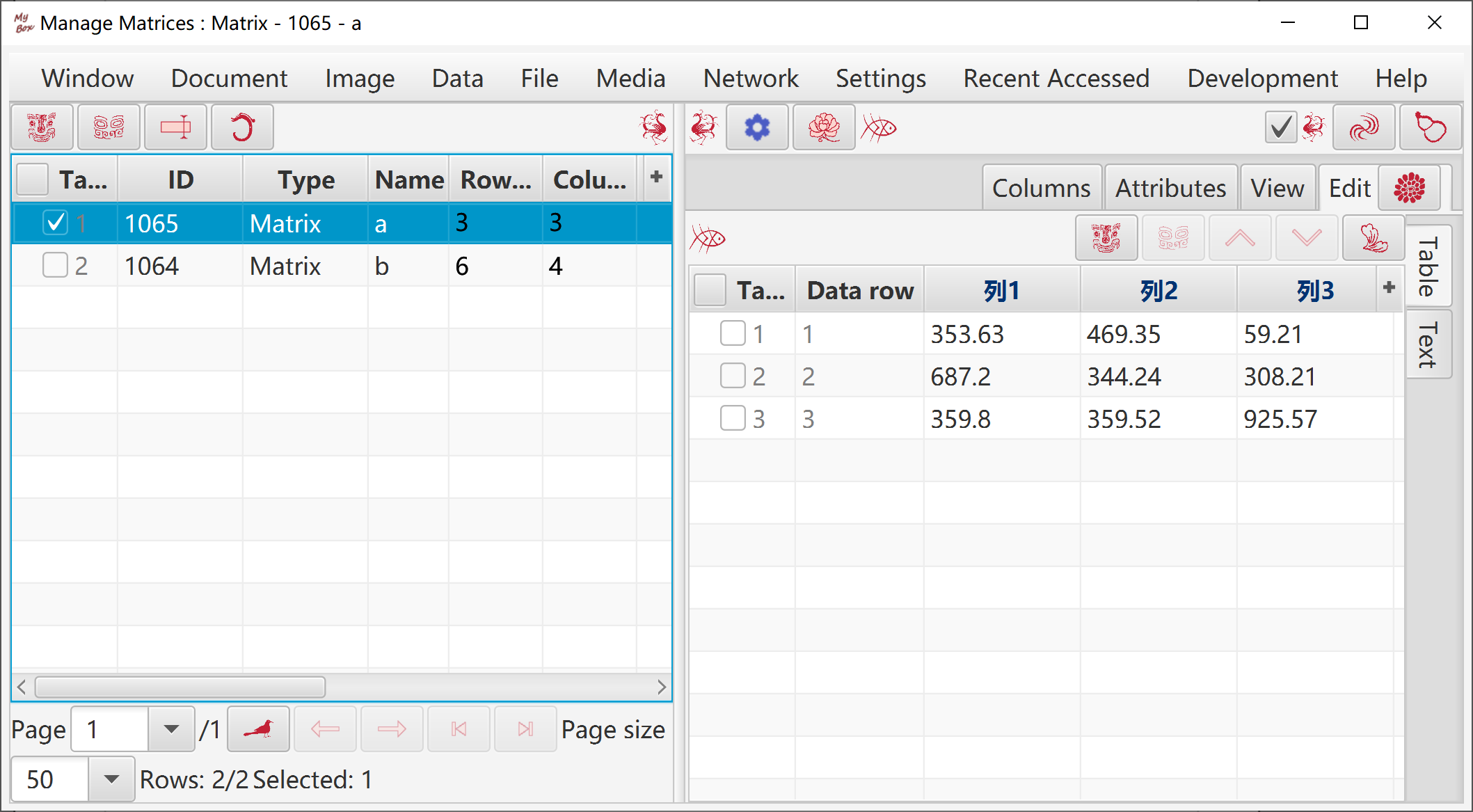
Transpose, Row Echelon Form, Reduced Row Echelon Form, Determinant By Elimination, Determinant By Complement Minor, Inverse Matrix By Elimination, Inverse Matrix By Adjoint, Matrix Rank, Adjoint Matrix, Complement Minor, Normalize, Multiply Number, Divide By Number, Power.
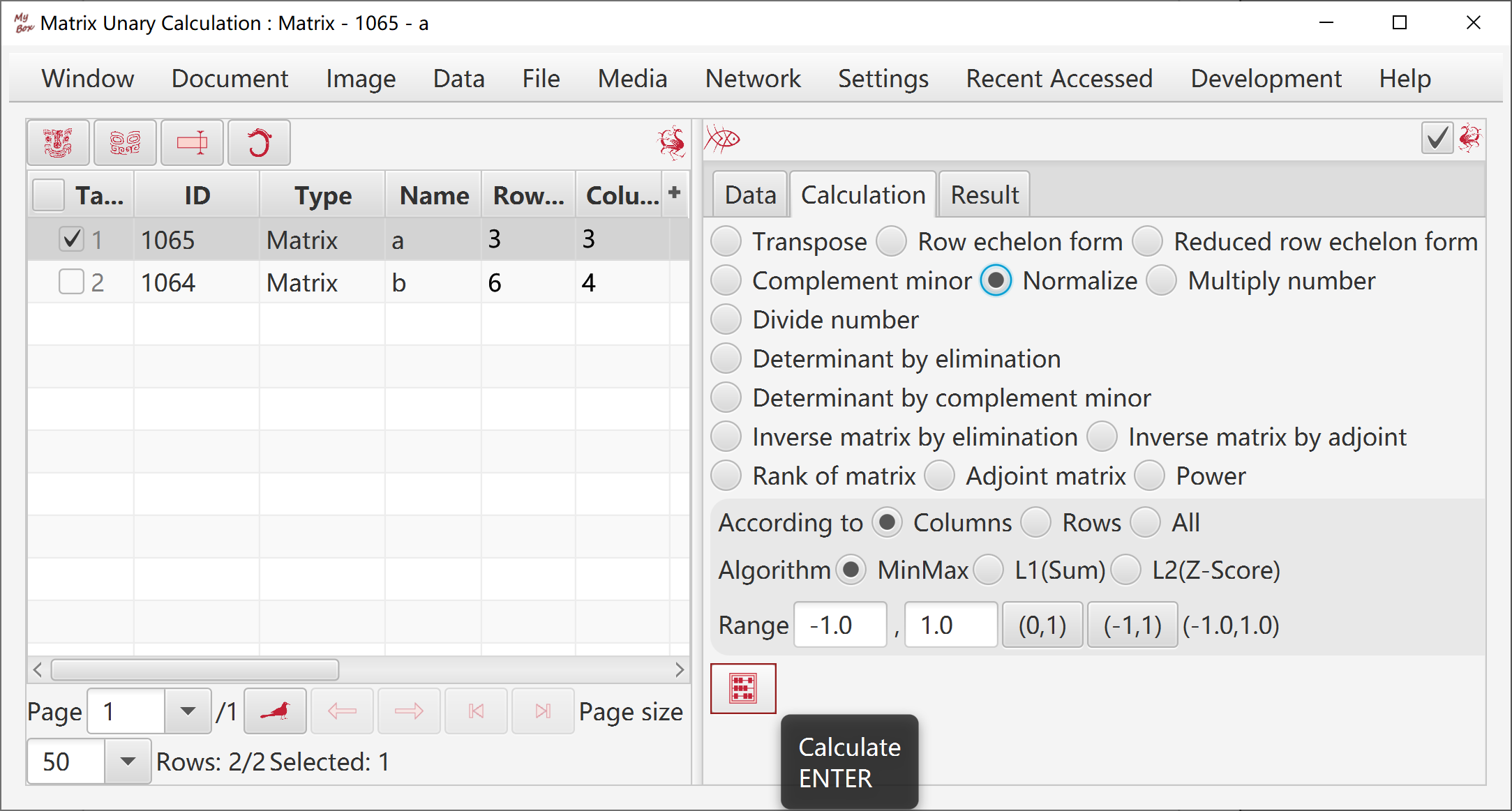
Plus, Minus, Hadamard Product, Kronecker Product, Horizontally Merge, Vertically Merge.
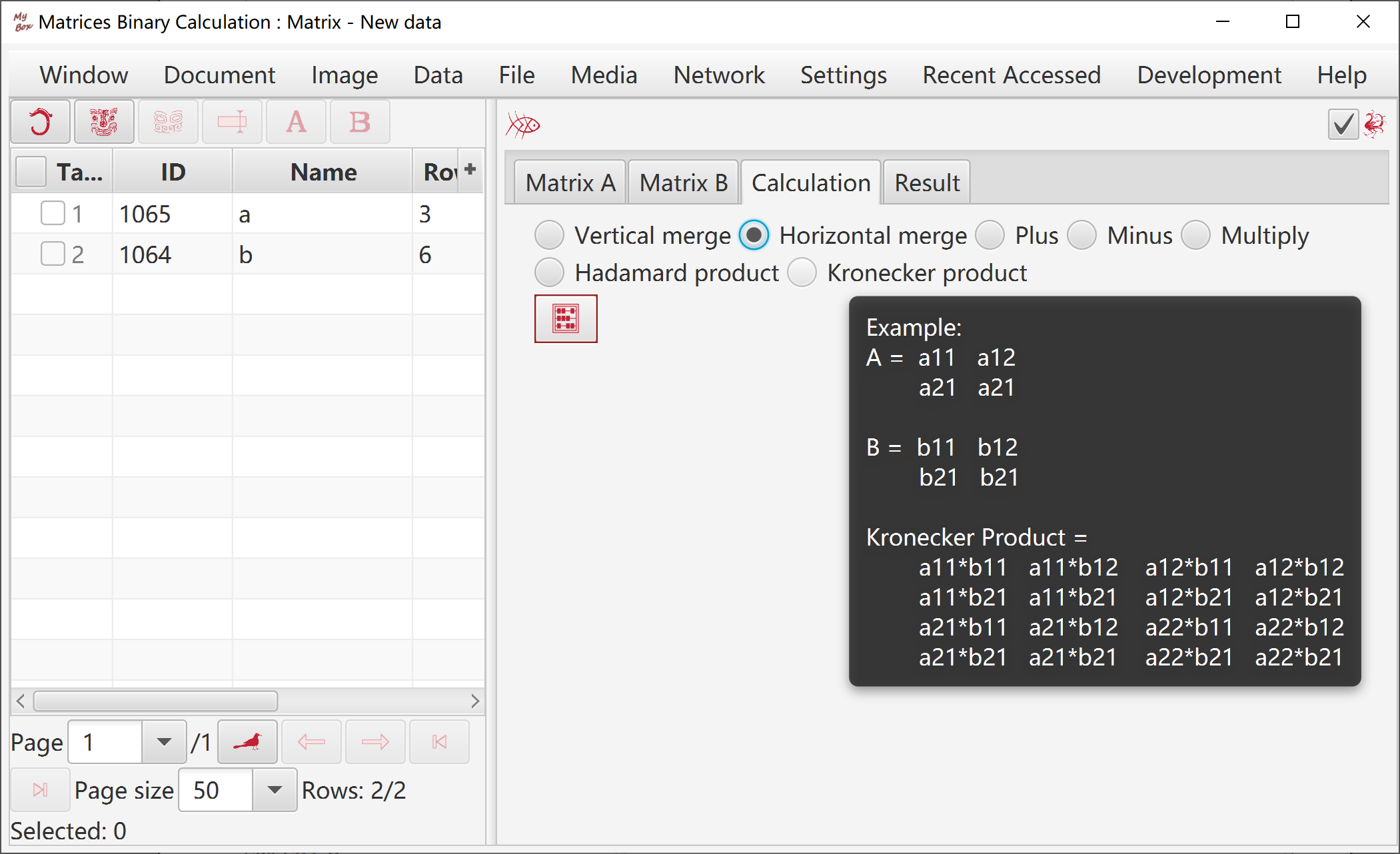
View table definition.
Execute SQL.
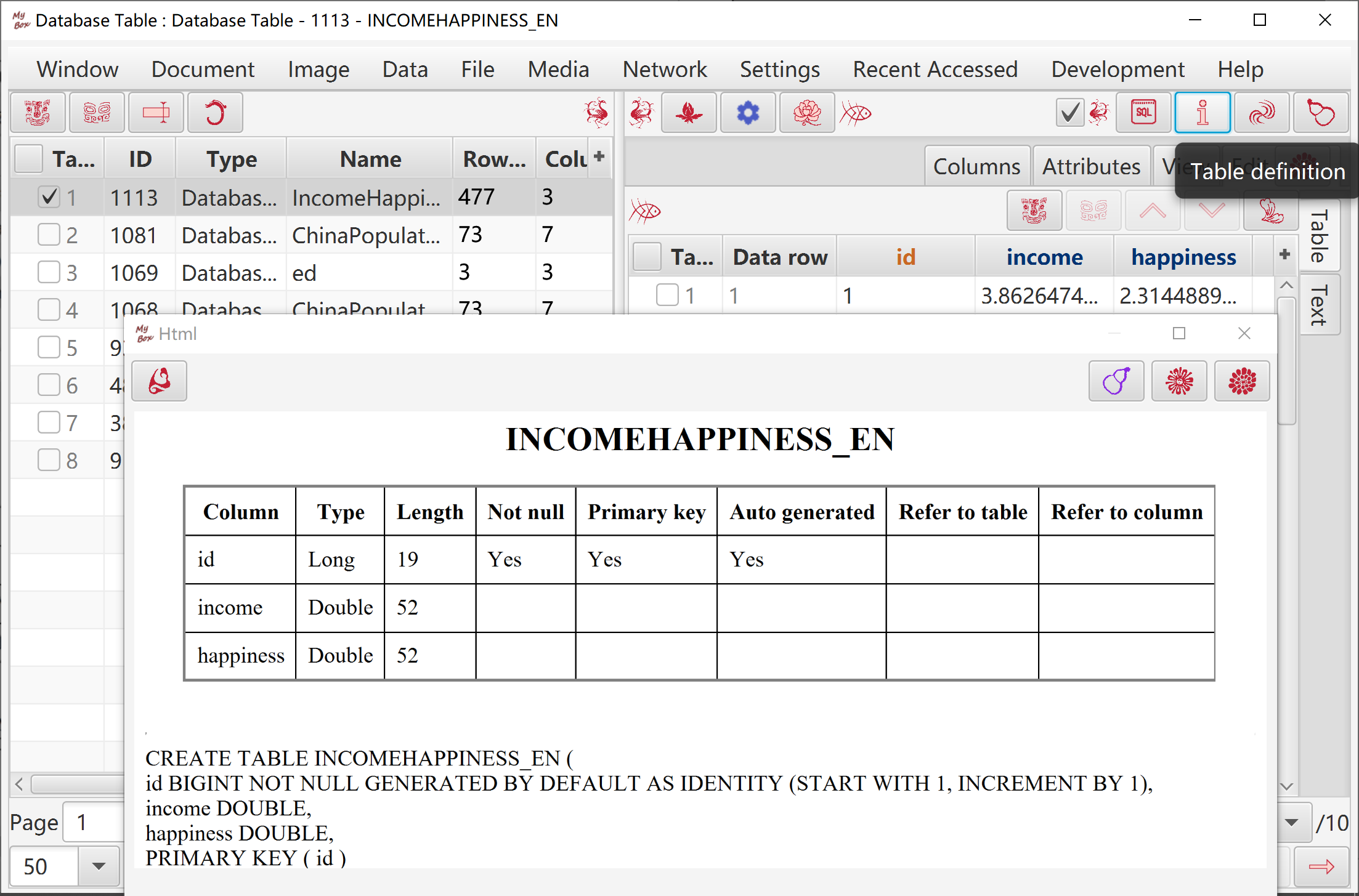
Table name and column names should satisfy "Limitations of SQL identifier":
Maximum length is 128.
"Ordinary identifier":
Not surrounded by double quotation marks.
Must begin with a letter.
Contains only letters, underscore characters (_), and digits.
Permits Unicode letters and digits.
Can not be reserved words.
It is converted as uppercase when saved in database.
It is case-insensitive when referred in SQL statement.
Example, AbC is same as abc and aBC.
"Delimited identifier":
Surrounded by double quotation marks.
Can contain any characters.
It is saved as string inside the double quotations in database.
It should be surrounded by double quotations when referred in SQL statement, except for following: It only includes upper case letters and underscores.
Example, "AbC" is different from AbC or "ABC" while "ABC" is same as ABC and abc.
After database table is created:
Definition of Primary keys can not be changed and deleted.
Definition of other columns can be added and deleted but can not be changed.
When MyBox create name of table/column:
Invalid characters are converted as underscore characters.
If it does not start with a letter, character "a" is added in front of it.
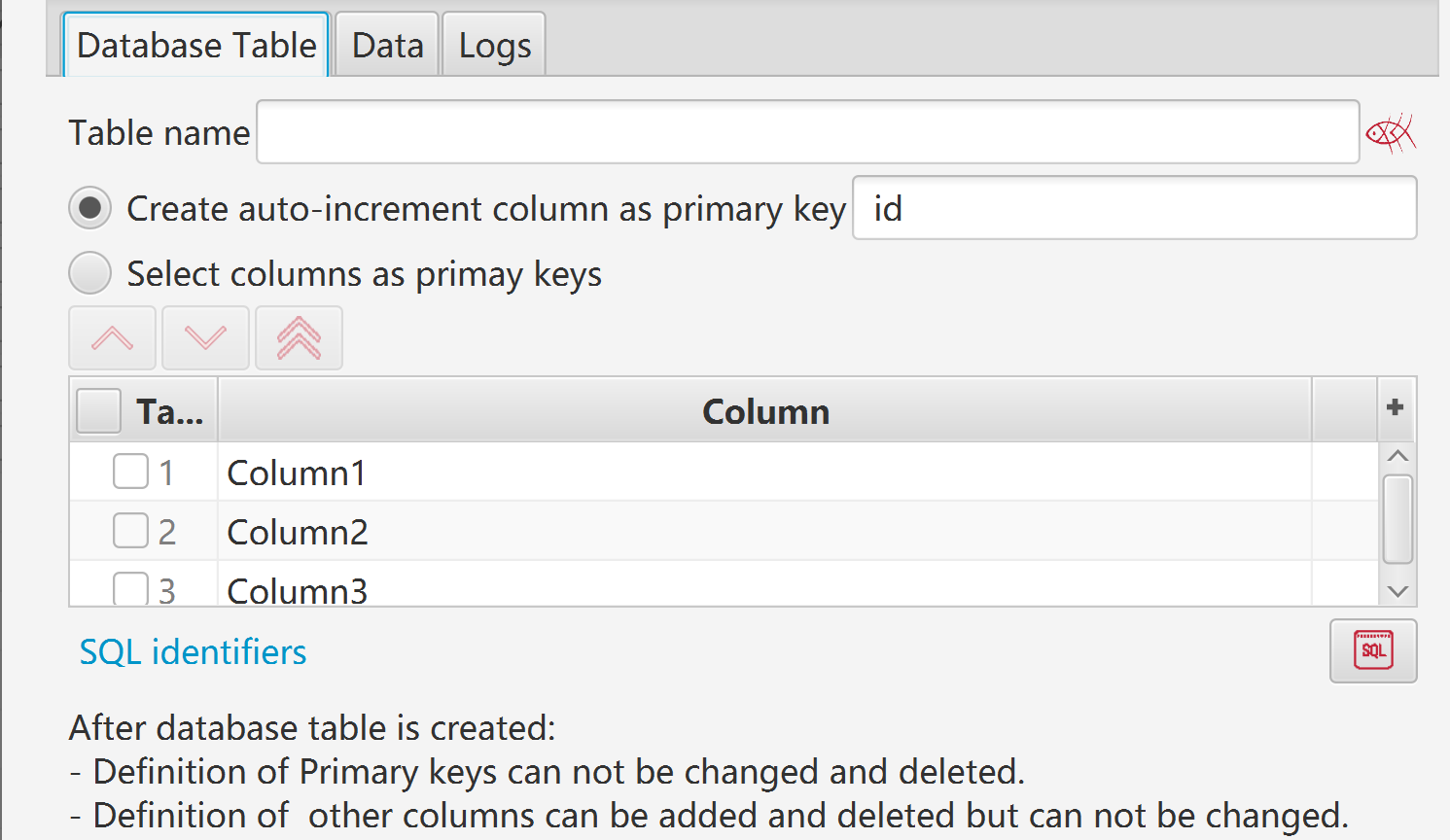
Provide examples of SQL statements.
List names of all user tables automatically.
View table definitions of all user tables.
Display outputs of execution and results of query.
SQL codes can be organized as information of tree.
Can load or save as external files.
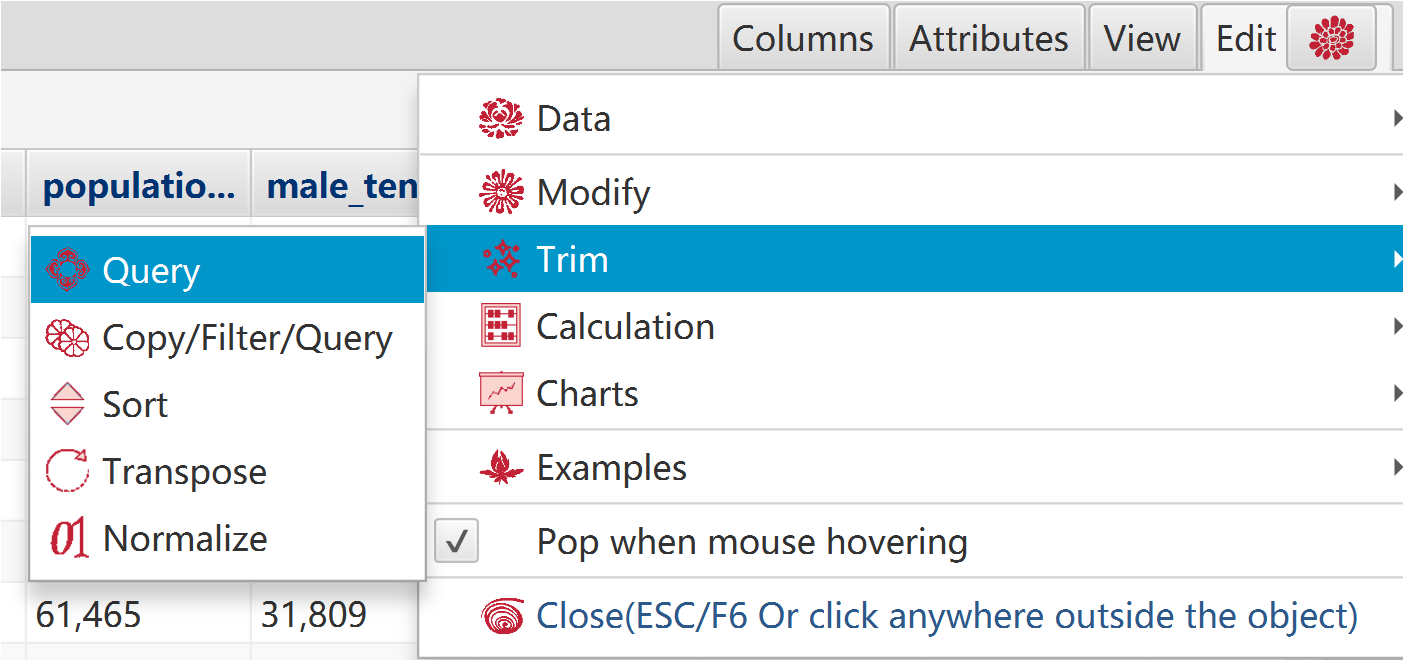
Database table has a special function menu: “Functions” - “Trim” - “Query”, which can help to input and execute SQL query:
Names of table and columns are listed in left.
Provide examples and record histories.
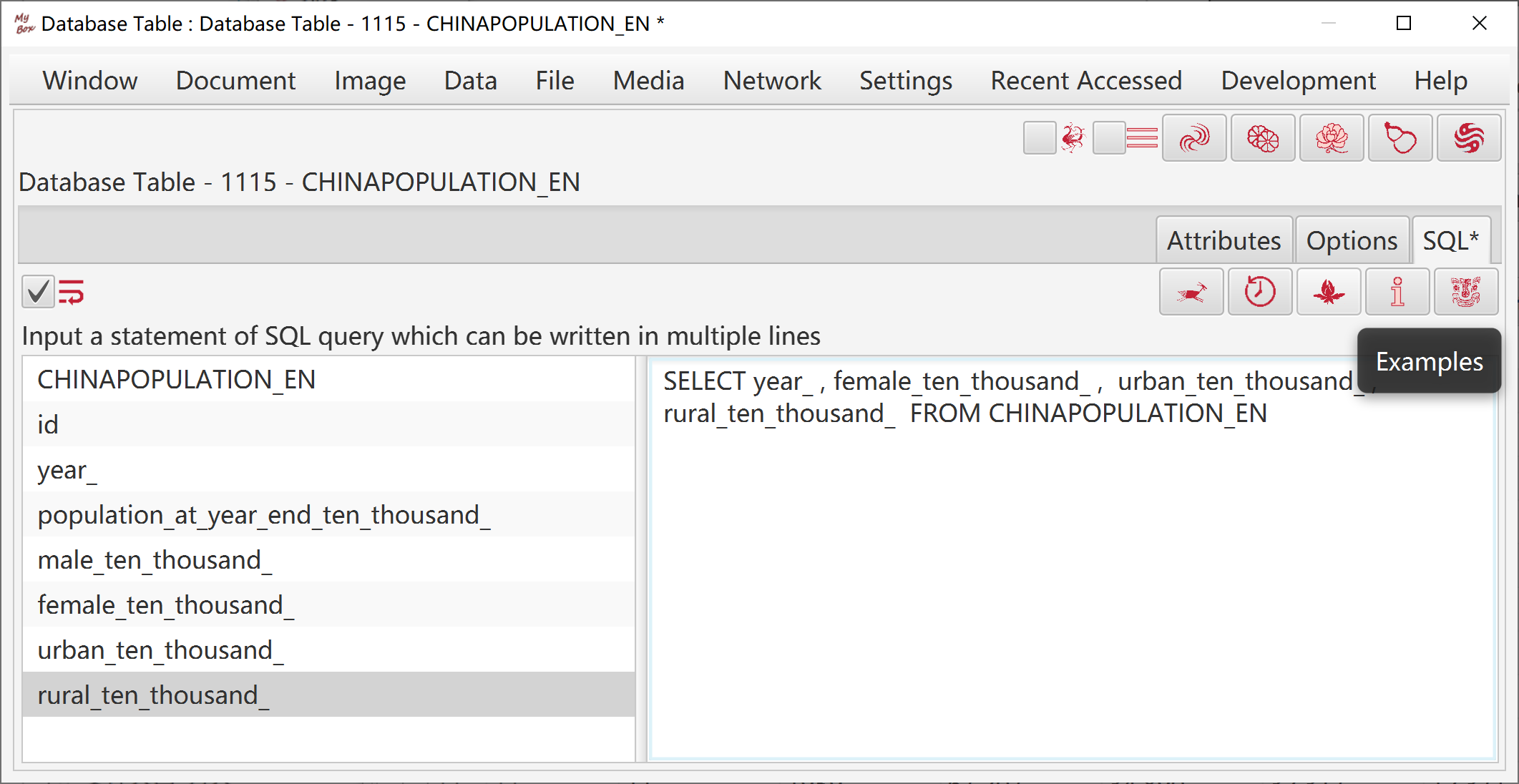
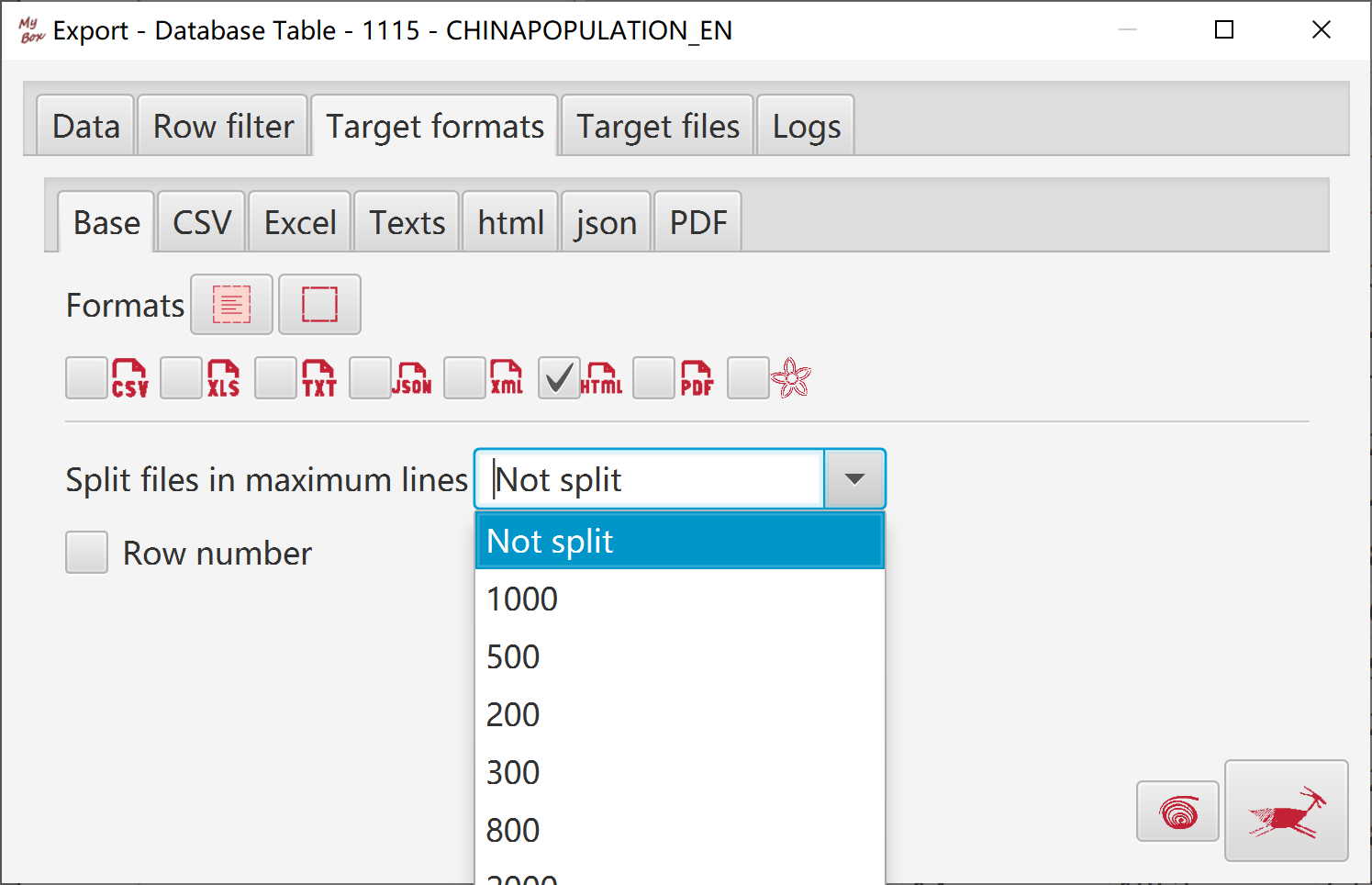
Select data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Select columns. If no column is selected, then all columns are taken.
Set row filter.
Select targets and their formats: csv, texts, excel, xml, json, html, pdf, MyBox Clipboard.
Split files in maximum lines.
Select data:
Rows can be: current page, selected rows, or all pages.
Select columns. If no column is selected, then all columns are taken.
Set row filter.
Create auto-increment column, or select some columns as primary key.
Option to import data.
JShell is one of tools in JDK:
JShell provides capability to interactively evaluate "snippets", as Read-Eval-Print Loop (REPL).
"Snippet" is a single expression, statement, or declaration of Java programming language code:
Semicolons should be in the end of statement while expression need not it.
Variables and methods can be defined and called later.
Extrenal Java classes should be accessible:
JShell picks "CLASSPATH" of system environment.
Other jar files or paths can be appended to "CLASSPATH".
Except for base classes, most of Java classes should be imported before call them.
JShell can be used for scientific computation and Java codes debug.
This tool helps to run JShell in GUI:
Input several snippets and click button "Start" to run them:
Snippets are evaluated one by one.
Results of snippets will affect later snippets, like "an execution environment".
Attributes of all evaluated snippets will be shown in a table.
Click button "Delete" or "Clear" to drop some or all snippets from current environment.
Click button "Reset" to empty JShell and environment becomes blank.
Press "CTRL+1" to pop list of code completion suggestions.
If added MyBox class paths, all methods of MyBox can be referred.
JShell codes are organized in tree. Examples are provided.
JEXL(Java Expression Language) is a library to generate values dynamically with variables and scripts.
JEXL has different syntax from Java. It is more like javascript.
Before run expression/script, all variables in it should have values held by JexlContext.
Refer to Java classes by creating their instances as local variables. Full package name is required.
JEXL can be used for scientific computation and data manufacture.
This tool helps to run JEXL in GUI:
Input JEXL expression/script.
Notice: Use single quotes instead of double quotes to surround strings.
Input Java codes of setting JexlContext like following:
jexlContext.set("name", value);
Example, set following to use Math.PI in expression/script:
jexlContext.set("Math", Math.class);
Input parameters of JEXL script if any. Separate values by comma.
Click button "Start" to evaluate the expression/script.
MyBox does following in JShell enrionment automatically:
Add MyBox library paths to CLASSPATH.
Import necessary JEXL packages.
Execute codes of JexlContext.
Calculate expression/script with parameters(if any).
If all variables and paramters have valid values, result is shown in right pane.
JEXL codes are organized in tree. Examples are provided.
This tool helps to edit, run, save Javascript codes.
Javascript codes are organized in tree. Examples are provided.
Null value of integer/long/short is the minimum value(MIN_VALUE)
Null value of double is the maximum value(Double.MAX_VALUE)
CGCS2000(China Geodetic Coordinate System), real locations and approximate to WGS-84(GPS).
GCJ-02(China encrypted coordinate), encrypted data with offsets of real locations.
WGS-84(GPS), real locations.
BD-09(Baidu encryted coordinate), based on GCJ-02.
Mapbar coordinate, based on GCJ-02.
When coordinate is unknown or invalid, the default value is CGCS2000.
Decimal values of longitude and latitude, instead of Degrees Minutes Seconds(DMS), are used when data handled.
MyBox provides "Location Tools" to convert coordinate values between decimal and DMS.
Valid range of longitude is `-180~180`, and valid range of latitude is `-90~90`.
Date and Time, like: 2014-06-11 13:51:33
Date, like: 2014-06-11
Year, like: 2014
Month, like: 2014-06
Time, like: 13:51:33
Time with Milliseconds, like: 13:51:33.261
Date and Time with Milliseconds, like: 2014-06-11 13:51:33.261
Date and Time with zone, like: 2020-09-27 12:29:29 +0800
Date and Time with Milliseconds and zone, like: 2020-09-27 12:29:29.713 +0800
"T" can be written or omitted between date and time. "2014-06-11T13:51:33" equals to "2014-06-11 13:51:33".
"0 AD" = "1 BC" = "0" = "-0" = "0000" = "-0000" = "0001-01-01 00:00:00 BC" = "公元前1" = "公元前0001-01-01 00:00:00"
"1 AD" = "1" = "0001" = "0001-01-01 00:00:00" = "0001-01-01 00:00:00 AD" = "公元1" = "公元0001-01-01 00:00:00"
"202 BC" = "-203" = "-0203" = "-0203-01-01 00:00:00" = "0202-01-01 00:00:00 BC" = "公元前202" = "公元前0202-01-01 00:00:00"
"202 AD" = "202" = "0202" = "0202-01-01 00:00:00" = "0202-01-01 00:00:00 AD" = "公元202" = "公元0202-01-01 00:00:00"
2020-07-13 11:30:59
-2020-07-13 11:30:59
-581-01-23
960
公元960
公元前770-12-11
公元前1046-03-10 10:10:10
202 BC
960-01-23 AD
1046-03-10 10:10:10 BC
Add/Delete/Edit/Copy/Clear/Refresh data.
Query data:
Define and manage query conditions.
Current query conditions is displayed on tab "information".
Data satisfying current query condition are displayed in tab "Data" in pages.
Data rows can be displayed in different colors as values of some column.
Import data in csv format:
File encoding is UTF-8 or ASCII.
The first line defines data headers which are delimited by English commas.
Followed each line defines one data row. Data fields are delimited by English commas.
The order of fields is not cared.
Necessary fields must occupy their locations, but need not have valid values(related to data).
Select whether replace existed data. Predefined data or example data always replace existed values.
Export data:
Define and manage export conditions.
Export data fields can be selected.
Export file format can be selected: csv, xml, json, xlsx, html, pdf.
Select maximum lines to split files.
Can export current data page.
Delete/Clear data:
Define and manage delete conditions.
Predefined data can not be deleted.
Referred data(like foreign keys) can not be deleted.
Define, manage, and use "Conditions":
"Conditions" are used to execute querying, deleting, or exporting.
Set conditions in panes:
Data conditions are organized as trees. Multiple nodes can be selected.
Multiple data fields can be selected as sorting conditions, and their orders can be changed.
Edit condition: Title, where, order by, fetch. They will be merged as final conditon.
Manage conditons: Add/delete/edit/copy.
Conditions ever executed are saved automatically.
Recently visited conditions are listed in pop window of the buttons.
Kinds of data can be presented in map, including Geography Codes, Location Data, and Coordinate Querying.
Data in map can be:
All data which satisfy current query condition. "Maximum number of data" can be set to avoid performance issues.
Data in current page.
TianDiTu:
Accepts coordinates of CGCS2000 and display them at correct locations without offsets.
When display other coordinates, MyBox converts them to CGCS2000 to show correct locations.
Projection can be selected: EPSG:900913/3857(Web Mercator) or EPSG:4326(Geodetic).
Controls can selected: Zoom, Scale, Map Type, Symbols.
Map Types: Standard, Satellite, Mixed Satellite, Terrain, Mixed Terrain.
Languages in different regions.
Range of map levels is 1-18.
GaoDe Map:
Accepts coordinates of GCJ-02 and display them at correct locations without offsets.
When display other coordinates, MyBox converts them to GCJ-02 to show correct locations.
Projection is EPSG:900913/3857(Web Mercator).
Map layers:
Can select multiples: standard, satellite, roadnet, traffic.
Roadnet layer and traffic layer are only supported for China.
Satellite layer is supported for part of foreign addresses.
Opacity can be set for each map layer.
Map language: Chinese, English, Chinese and English.
Range of map levels is 3-18
Can selected "Fit View" to adjust map level and center as best automatically while display all data.
Adjust map level by:
Scroll mouse wheel.
Click map controls.
Select "Map Size"
Marker image:
Selections: point(bubble), circle, or any image.
For Location Data, more selections: Data Set Image, Data Image. Point will be used if no valid value.
Size can be set(Same size for width and height)
Marker text:
Selections: Label, Coordinate, Address.
For Location Data, more selections: Start Time, End Time, Data Value, etc.
Multiples selections can be picked. Each selection will be showns in a line.
Size can be set.
Can select whether text is bold.
Color can be set. For Location Data, "Data Color" can be chosen.
Pop information:
Detailed information can be popped when mouse is upon marker.
Can select whether pop information.
Snapshot:
DPI can be set.
Current map and data in map can be saved and displayed in html.
Keys of map can be changed in "Settings". The default keys are free and shared by all MyBox users.
Basical attributes: id, level, longitude, latitude, chinese_name, english_name, 5 codes, 5 aliases,
Subordinate: owner, continent, country, province, city, county, town, village, building. ("Ancestors")
Auxiliary attributes: altitute, precision, coordinate system, area(square meters), population, comments, isPredefined.
Not null values: id, level, chinese_name or english_name.
Values of "level": global(only "Earth"), continent, country, province(state), city, county(district), town, village(neighborhood), building, point of interest.
Data is unnecessary to be subordinated level by level. Cross-over can happen. Example, a village is subordinated to Antarctica, and a city belongs to a country without province level.
Match data:
One of following can determine an address:
Match “id"(assigned by MyBox automatically). This is accurate matching.
Match "level" + ancestors + "chinese_name"/"english_name"/any one "alias". This is accurate matching.
Match "level" + "chinese_name"/"english_name"/any one "alias". This is fuzzy matching. Duplicated names in same level can cause false matching.
Matching of name or alias is case-insensitive.
Sometimes 5 "code" are useful to match data.
"subordinate" of data is set by selecting node in locations tree.
"level" of data should be lower than its ancestors.
Data must have either chinese_name or english_name.
Select or display coordinate in map.
Set as "Predefined data" or "Inputted data" against selected rows.
All geograhy codes in MyBox are organized as a Locations Tree by their subordination relationship. Multiple nodes can be selected.
Include continents, countries, Chinese provinces /cities /counties.
Countries have values of "area" and "population".
Download address:
https://github.com/Mararsh/MyBox_data/tree/master/md/GeographyCode/en
Necessary fields:
Level,Longitude,Latitude
And "Chinese Name" or "English Name"
Optional fields:
Altitude,Precision,Coordinate System,Square Kilometers,Population,
Code 1,Code 2,Code 3,Code 4,Code 5,Alias 1,Alias 2,Alias 3,Alias 4,Alias 5,
Continent,Country,Province,City,County,Town,Village,Building,Comments
Download address:
http://download.geonames.org/export/zip/
Tab-delimited text in UTF8 encoding.
Data fields:
countryCode postalCode placeName
adminName1 adminCode1 adminName2 adminCode2 adminName3 adminCode3
latitude longitude accuracy
Coordinate system is WGS_84.
Same address is written only once even when it has multiple "postal code" or coordinates.
Customize colors of data rows.
Provide "Default" and "Random" buttons.
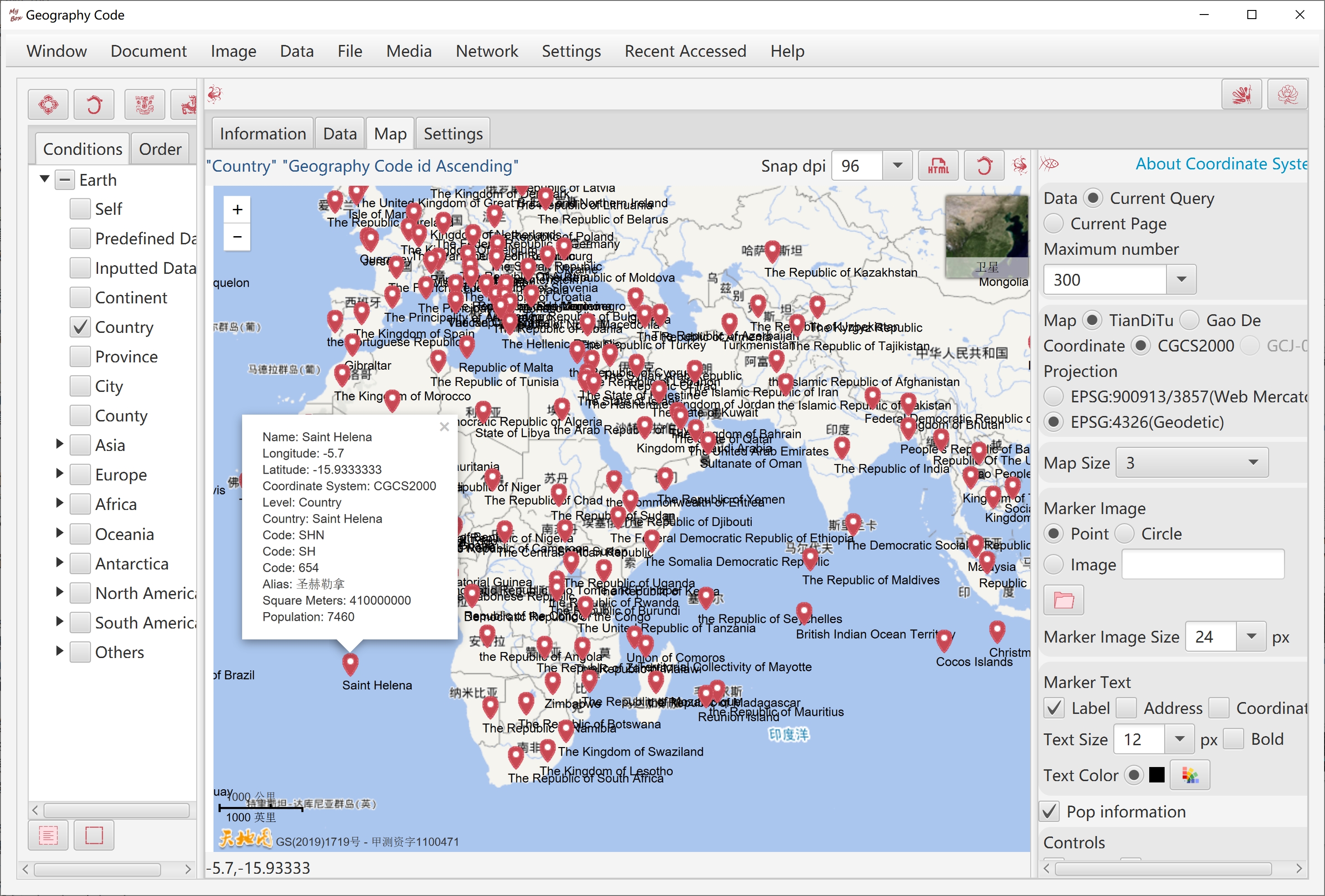
Query geography code by:
Click map.
Input address.
TianDiTu supports chinese and foreign addresses in Chinese(like "伦敦") or in English(like "Paris")
GaoDe map only supports addresses in China.
Input longitude and latitude.
Query result can be saved in Geography Code table.
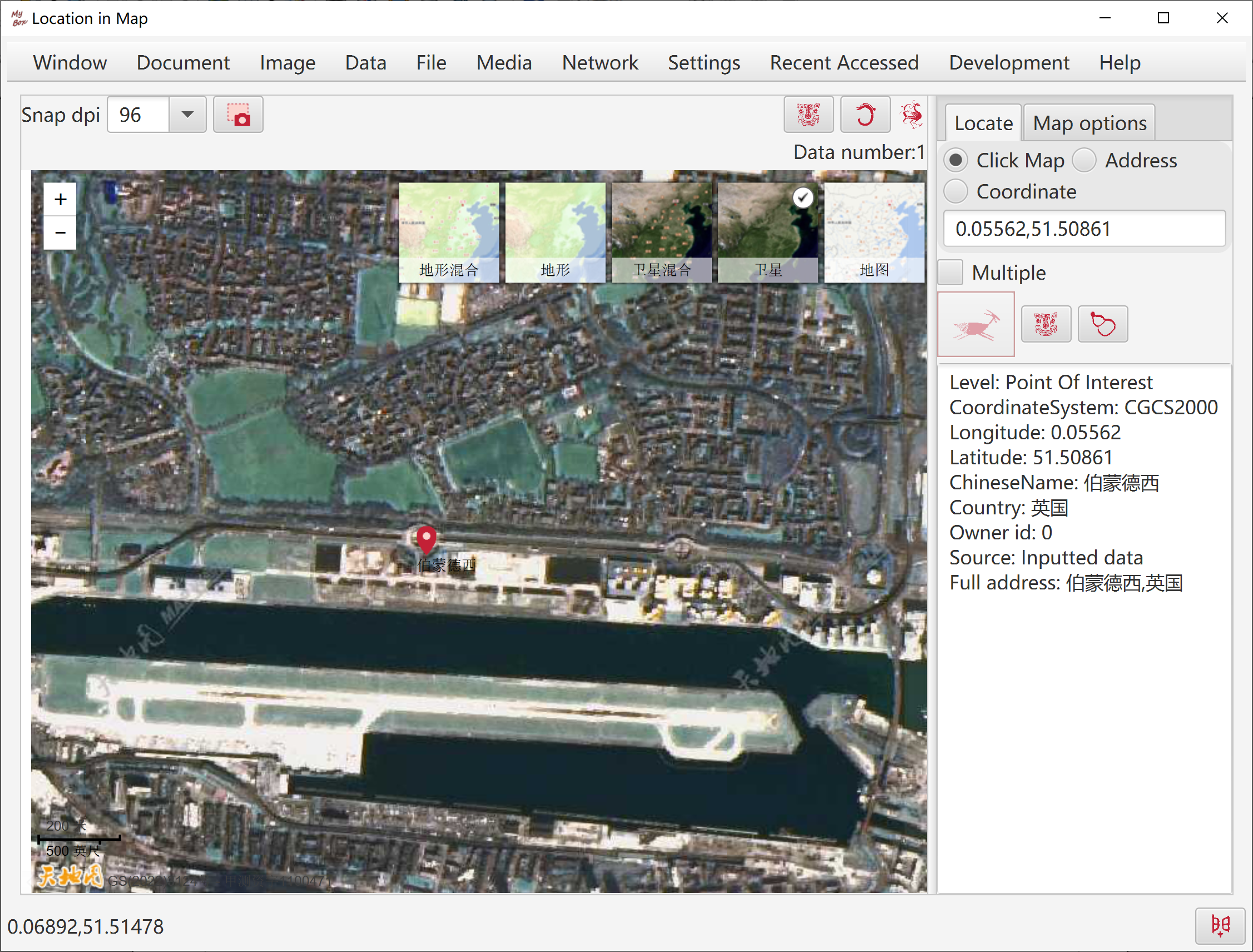
Basical attributes: data set, label, longitude, latitude, start time, end time.
Auxiliary attributes: altitute, precision, coordinate system, speed, direction, data value, data size, image, comments.
Each location data belongs to a data set.
Data set defines common attributes of some location data, examples:
Date format
Whether omit "AD" for date AD
Text color
Image
These attributes help to distinguish data points in map.
List of data sets. Multiple nodes can be selected.
Time tree(Start time). Multiple nodes can be selected.
At beginning, the first data is made as map center.
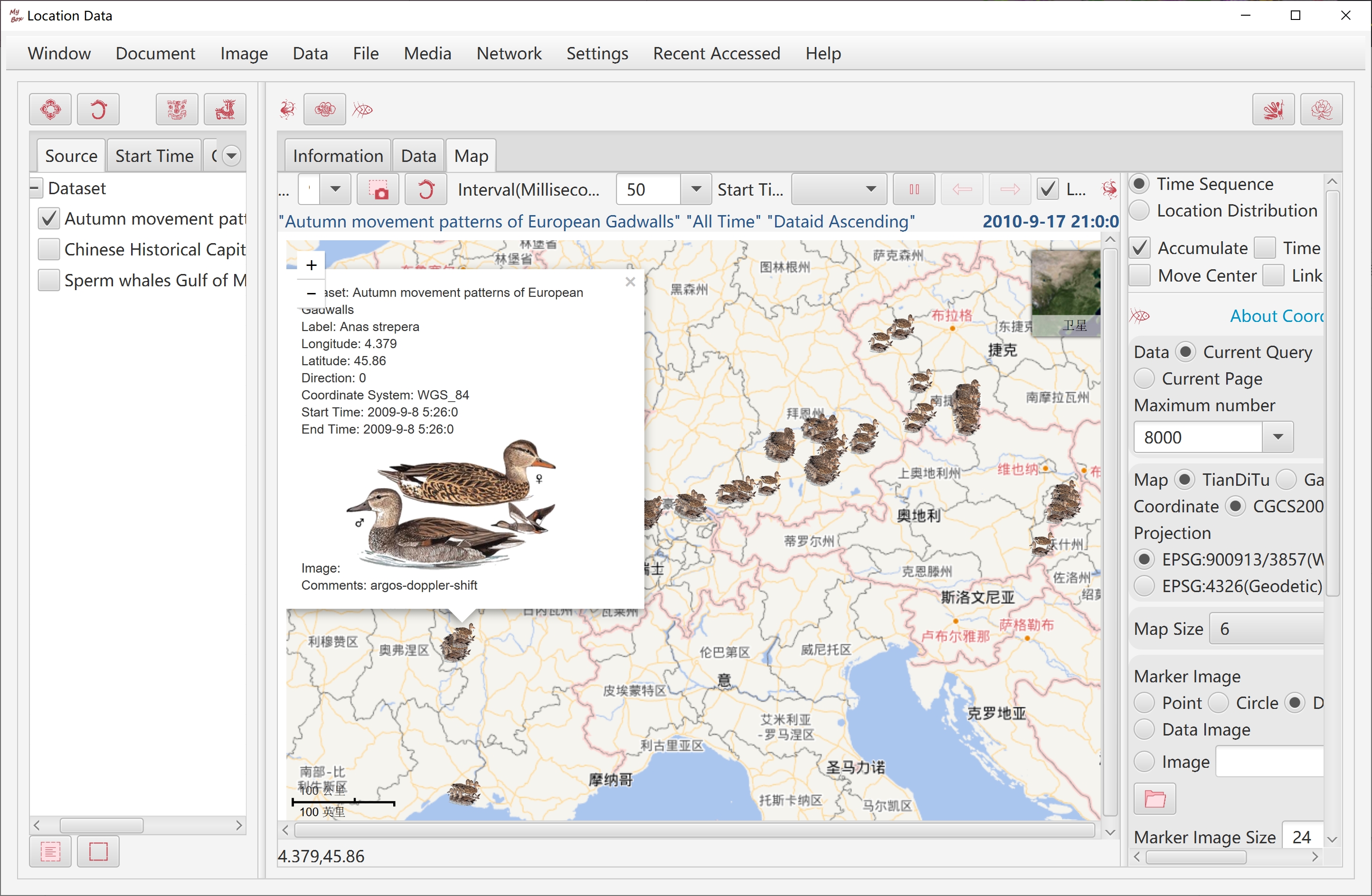
Location Distribution: All data are displayed in map.
Time Sequence:
Data are displayed in frames as "Start Time" in ascending order.
When "Accumulated" is selected, drawn points will not be erased and points are shown more and more.
When "Time Overlay" is selected, all data whose duration(between "start time" and "end time") has intersection with duration of current frame will be treated as valid points of current frame.
Example, current frame has "start time" of "1044 BC" and "end time" of "221 BC", then all data who or part of who appears in this duration will be displayed in current frame.
When "Move Center" is selected, each frame will adjust its map center.
When "Link" is selected, lines between adjacent 2 points will be shown.
Control frames:
Set interval.
Select a frame(by start time).
Pause/Continue playing.
Previous/Next frame.
Whether loop.
For "Location Distribution":
html:Data and snapshot of current frame
Snapshot of current frame. All supported image formats can be selected.
For "Time Sequence", more choices:
jpg:Snapshots of all frames
png:Snapshots of all frames
Animated gif:Snapshots of all frames(May out of memory)
If data include a dataset which is not in database, the new dataset will be added in database automatically.
Necessary fields: Dataset,Longitude,Latitude
Optional fields: Label,Address,Altitude,Precision,Speed,Direction,Coordinate System, Data Value,Data Size,Start Time,End Time,Image,Comments
Download address:
https://www.datarepository.movebank.org/
Comma-delimited CSV file.
Necessary fields: timestamp,location-long,location-lat,study-name
Coordinate system is WGS_84.
Chinese Historical Capitals
Autumn movement patterns of European Gadwalls
Sperm whales Gulf of Mexico
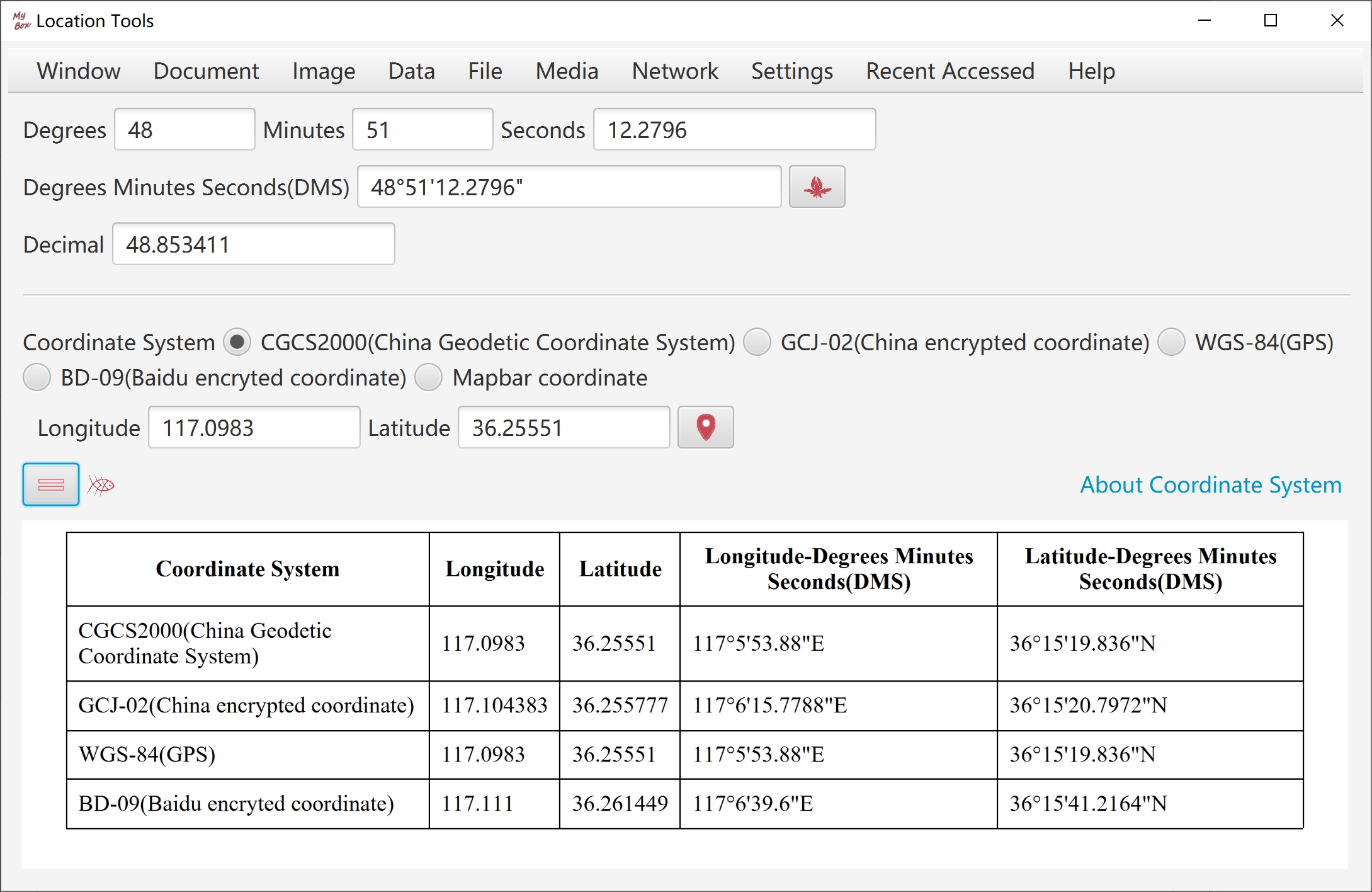
Convert coordinate value between decimal and DMS. Valid examples of DMS:
48°51'12.28"
-77° 3' 43.9308"
48°51'12.28"N
2°20'55.68"E
S 34° 36' 13.4028"
W 58° 22' 53.7348"
118度48分54.152秒
-32度04分10.461秒
东经118度48分54.152秒
北纬32度04分10.461秒
西经118度48分54.152秒
南纬32度04分10.461秒
Convert coordinate values as other coordinate systems.
Basical attributes: dataSet, time, location, source.
Basical values: confirmed, healed, dead.
Subtraction statistic: increased confirmed, increased healed, increased dead.
Calculated by adjacent rows.
Division statistics:
healed/confirmed permillage, dead/confirmed permillage
confirmed/population permillage, healed/population permillage, dead/population permillage,
confirmed/area permillage, healed/area permillage, dead/area permillage.
When value of "area"/"population" of location is invalid(zero or negitive), corresponding statistics data are meaningless.
Predefined data "countries" have valid "area"/"population" and they have meaningful statistics values.
Accumulation statistics:
Values of some countries. Calculated by values of country's provinces.
Values of continents. Calculated by values of continent's countries.
Values of Earth. Calculated by values of continents.
Not null values: dataSet, time, location
Values of "source": "Inputted data", "Predefined data", "Filled data", "Statistics data".
"location" is foreign key of "Geography Code", which must have row defined in that table.
In "confirm", "healed", "dead", at least one should be larger than zero.
One of following can determine a data row:
Match id, which is assigned by MyBox automatically. This is accurate matching.
Match "dataSet" + "date" + "location". This is accurate matching.
This version assumes that only one valid data in each day for same dataSet plus same location.
When in single data, location is set by selecting node from locations tree.
In interface of "Epidemic Reports of Chinese Provinces" or "Epidemic Reports of Countries", multiple rows can be inputted for same dataSet and time.
Modify values of "source" for selected data rows.
COVID-19 historical data from Johns Hopkins University.(Till 2020-09-24)
Download address:
https://github.com/Mararsh/MyBox_data/tree/master/md/COVID19/en
Necessary fields: Data Set,Time,Confirmed,Healed,Dead,
And location data which are enough to define a geography code: Longitude,Latitude,Level,Continent,Country,Province,City,County,Town,Village,Building,Point of Interest
Optional fields: Increased Confirmed,Increased Healed,Increased Dead
Coordinate system is CGCS2000.
Download address:
https://github.com/CSSEGISandData/COVID-19/tree/master/csse_covid_19_data/csse_covid_19_time_series
Necessary fields: Province/State,Country/Region,Lat,Long.
And date list like "1/22/20,1/23/20..."
Coordinate system is WGS_84.
Australia, Canada and China are reported at the province/state level, and others are at country level.
Items whose values are all zero will be skipped.
Download address:
https://github.com/CSSEGISandData/COVID-19/tree/master/csse_covid_19_data/csse_covid_19_daily_reports
Data fields are change as time flowing...
Following is format of "01-22-2020.csv":
Province/State,Country/Region,Last Update,Confirmed,Deaths,Recovered
Following is format of "05-15-2020.csv":
FIPS,Admin2, Province_State,Country_Region, Last_Update,Lat,Long_,
Confirmed, Deaths, Recovered,Active, Combined_Key
Coordinate system is WGS_84.
Items whose values are all zero will be skipped.
Option: Statistics against dataset.
Time of all data are changed as “23:59:00”.
If data include a geography code which is not in database, the new geography code will be added in database automatically.
Option to accumulate date
Option to calculate subtraction statistic for different location levels.
Data Sources Tree: Data sets and their different sources are organized a tree. Multiple nodes can be selected.
Locations Tree: All geograhy codes in MyBox are organized as a tree by their subordination relationship. Multiple nodes can be selected.
Times Tree: All times involved in Epidemic Reports of MyBox are organized as a tree. Multiple nodes can be selected.
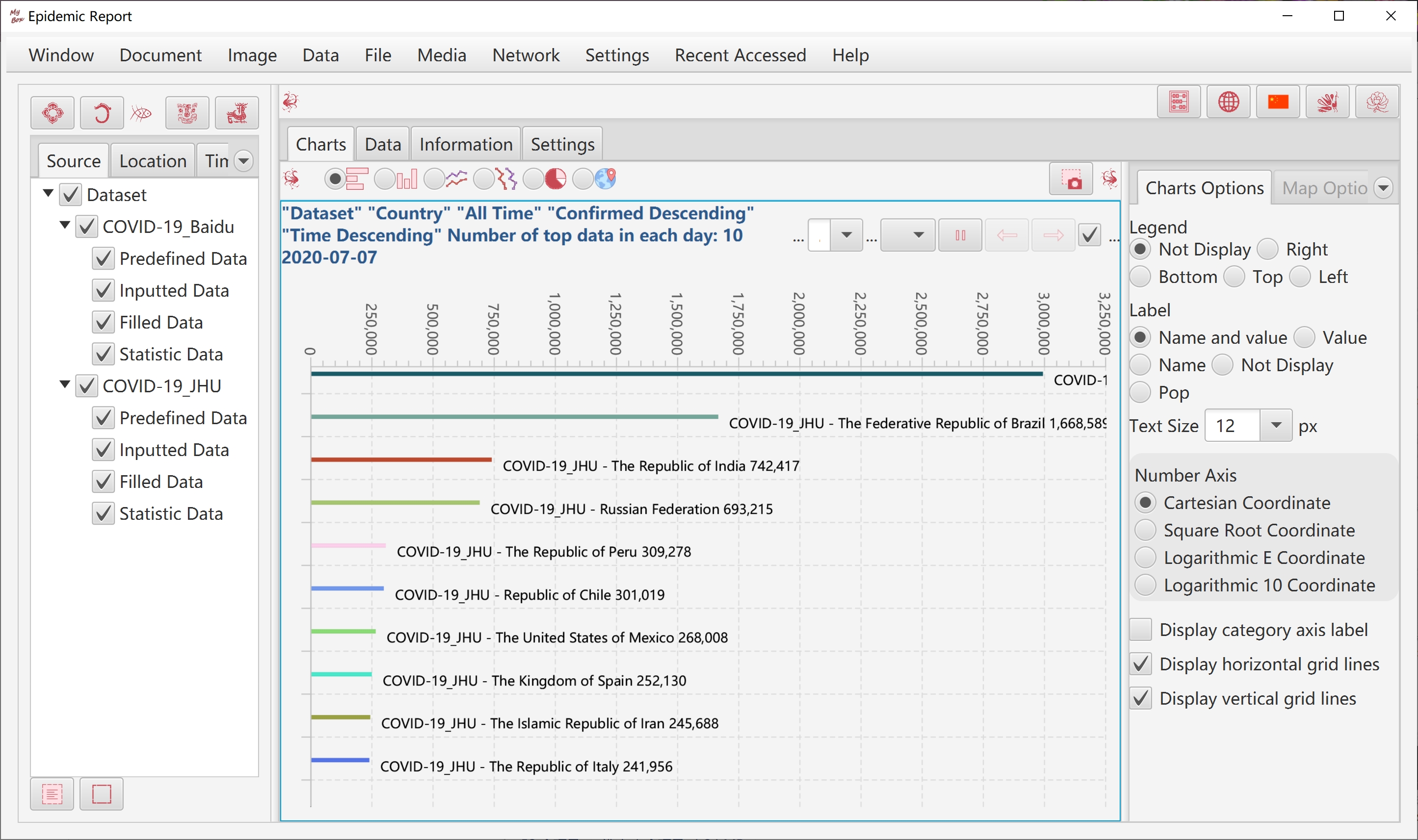
Number of Top Data in Each Day:
Unlimit. Charts will not be displayed. Data are queried as condition.
Valid value:
Data are queried as condition, and then be truncated as top data of each day, by which charts and data are displayed.
"Time Descending" is always as the first ordering element automactically.
At least one more column should be picked as ordering element.
Beside "Time Descending", the first ordering element is called "major quering attribute".
Number of Top Data in Each Day" and "Elements of ordering" work for Query and Export, and not for Clear.
Edit condition: title, where, order by, fetch, "Number of Top Data in Each Day"(0 or -1 means Unlimit), which are combined together as the final condition.
Only when query condition satisfies requirements, charts are displayed. Charts' data are always "Daily top data" and have "Major query attribute".
Beside "Major query attribute" , more attribues can be selected, to display multiple dimension data in same chart, or show multiple charts at same time.
Chart type: horizontal bars, vertical bars, horizontal lines, vertical lines, pie, map.
When there are multiple times in data,charts are animated. Data charts of each time are displayed frame by frame in time ascending.
For animated charts, support Pause/Continue, Jump to frame of a time, Last frame, Next frame, setting interval.
Common settings, which take effect immediately:
Legend location: not display, top, bottom, left, right.
Value's label: name and value, value, name, not display, pop
Whether display: category axis, horizontal grid lines, vertical grid lines
Number axis: Cartesian Cordinate, Square Root Cordinate, Logarithmic E Cordinate, Logarithmic 10 Cordinate.
Font size
Parameters of map: level, layers, language
Snap chart.
Snapshot of current frame. All supported image formats can be selected.
jpg:Snapshots of all frames
png:Snapshots of all frames
Animated gif:Snapshots of all frames(May out of memory)
Snap dpi, maximum width of snapped animated images, time to loading chart's data.
These parameters are related to memory usage and computer's calculation capacity.
Customize colors of data rows as column "source". Provide "Default" and "Random" buttons.
Customize colors of data values in charts. Provide "Default" and "Random" buttons.
Customize colors of location values in charts. Provide "Random" buttons.
Supported 1-d barcodes:
Types: Code39, Code128, Codabar, Interleaved2Of5, ITF_14, POSTNET, EAN13, EAN8, EAN_128, UPCA, UPCE, Royal_Mail_Customer_Barcode, USPS_Intelligent_Mail
Options about 1-d barcodes: Orientation, width/height, dpi, text location, font size, quiet-zone width, etc.
Supported 2-d barcodes:
Types: QR_Code, PDF_417, DataMatrix
Options about 2-d barcodes: Width/height, margin, error correction level, compact mode, etc.
A picture can be shown in center of QR_Code. Its size can be adjusted automatically according to error correction level.
Examples of parameters and suggested values.
Validate generated barcode at once.
Supported 1-d barcodes: Code39, Code128, Interleaved2Of5, ITF_14, EAN13, EAN8, EAN_128, UPCA, UPCE
Supported 2-d barcodes: QR_Code, PDF_417, DataMatrix
Display contents of barcodes and its meta data including barcode type and error correction level if any.
Create digest for files or inputted texts.
Support MD2, MD5, SHA-1, SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512/224, SHA-512/256, SHA3-224, SHA3-256, SHA3-384, SHA3-512.
Ouput: Base64, Hexadecimal, Formatted hexadecimal.
Encode file or texts as Base64.
Decode Base64 file or Base64 texts.
Set charset for texts.
Output as file or texts.
<End of Document>
Page